Table of Contents
The theremin (/ˈθɛrəmɪn/; originally known as the ætherphone/ether phone, thereminophone or termenvox/thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the thereminist (performer). It is named after its inventor, Leon Theremin, who patented the device in 1928.
The instrument's controlling section usually consists of two metal antennas that sense the relative position of the thereminist's hands and control oscillators for frequency with one hand, and amplitude (volume) with the other. The electric signals from the theremin are amplified and sent to a loudspeaker.
The sound of the instrument is often associated with eerie situations. Thus, the theremin has been used in movie soundtracks such as Miklós Rózsa's Spellbound and The Lost Weekend, Bernard Herrmann's The Day the Earth Stood Still, and Justin Hurwitz's First Man, as well as in theme songs for television shows such as the ITV drama Midsomer Murders and the Disney+ series Loki, the latter composed by Natalie Holt. The theremin is also used in concert music (especially avant-garde and 20th- and 21st-century new music), and in popular music genres such as rock.
Major frameworks/libraries used in this project:
1. What you will learn?
By building an ultrasonic theremin, you will learn:
- How to detect distances with an ultrasonic distance sensor.
- How to communicate variables between Sonic Pi and Python.
2. What you will need?
-
2.1. Hardware:
- 330Ω Resistor
- 470Ω Resistor
- Solderless Breadboard
- Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
- 3 x Male to Male Jumper Leads
- 4 x Male to Female Jumper Leads
-
2.2. Software:
This project relies on the latest version of Sonic Pi and python-osc. To install the software you need, run the following commands in a terminal window:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y sudo pip3 install python-osc
3. Setting up the circuitry
An ultrasonic distance sensor is a device that sends out pulses of ultrasonic sound, and measures the time they take to bounce off nearby objects and be reflected back. They can measure distances fairly accurately, up to about a meter.
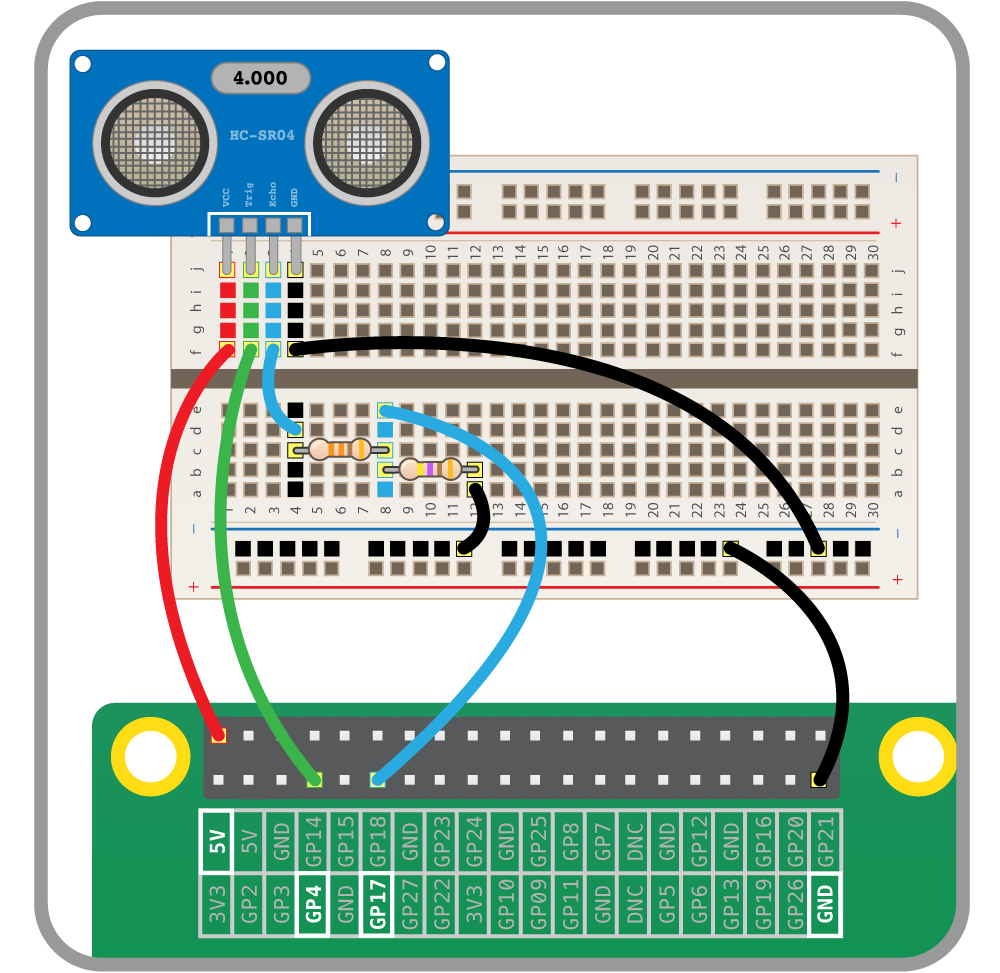
An ultrasonic distance sensor has four pins. They are called Ground (Gnd), Trigger (Trig), Echo (Echo) and Power (Vcc).
To use an ultrasonic distance sensor you need to connect the Gnd pin to the ground pin on the Raspberry Pi, the Trig pin to a GPIO pin on the Raspberry Pi and the Vcc pin to the 5V pin on the Raspberry Pi.
The Echo pin is a little more complicated. It needs to be connected through a 330 ohm resistor to a GPIO pin on the Raspberry Pi, and that pin needs to be grounded through a 470 ohm resistor.
The diagram below shows one suggested arrangement for setting this up.
🔎
Rabih ND - @RabihND
Project Link: https://github.com/RabihND/UltrasonicTheremin
- [x]