Usage of the library: Source the library
. .\libmetex.ps1Create a new instance
$Metex=new-object MetexM3850D("COM5")Open the COM Port
$Metex.Open()Read Measures
$Metex.ReadMeasureSynchron()
$MeasureResult=$Metex.ReadMeasureSynchron()Output should be something like this
MeasuringUnit : Diode
Value : 0
RawMeasureString : DI OL mV
Result : Overload
Unit : V
RawValue : OL
RawUnit : mV
MeasuringUnit : Capacity
Value : 4E-12
RawMeasureString : CA 0.004 nF
Result : OK
Unit : F
RawValue : 0.004
RawUnit : nF
MeasuringUnit : CurrentDC
Value : -1E-07
RawMeasureString : DC -000.1 uA
Result : OK
Unit : A
RawValue : -000.1
RawUnit : uA
Close the COM Port
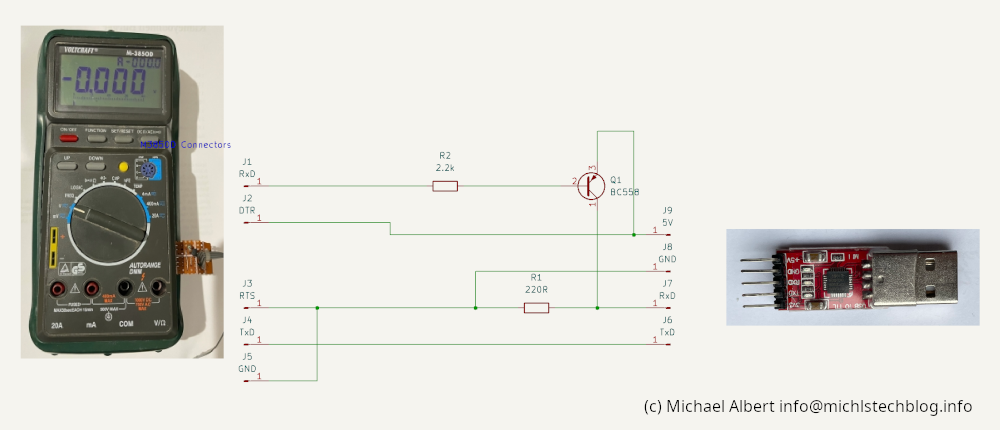
$Metex.Close()The Kicad project is a simple converte to connect a M3850D by a TTL UART to USB Converter to PC.
The Description of the Serial port pins of the Multimeter:
RxD and TxD Ports are MAX232 compatible. Means -12V = High and +12V is Low Level.
Therefore the ports must be inverted (done by Transistor Q1) to deal with a TTL USB adapter. This is only necessary for RxD because to start a measurement read, only a falling rise at TxD port is requiered, indepentend which character is send to the multimeter.
The multimeter serial port is isolated by optocouplers from the multimeter. A supply voltage is needed.
DTR and RTS Ports are just used for the power supply of the optocouplers not for a serial handshake.
In my test a 5V supply is sufficent. RTS=GND DTR=5V
This is the schmetic: