This repository implements some algorithms related to point clouds and is developed based on OpenCV.
It's worth celebrating that the features implemented in this repository have been merged into the OpenCV 5.x branch 3D module!
Related PR in:
- Add 3D point cloud sampling functions to branch next. opencv/opencv#20784
- Accelerated 3D point cloud Farthest Point Sampling calculation using SIMD. opencv/opencv#21095
- Add support for 3D point cloud segmentation, using the USAC framework. opencv/opencv#21276
Related documents:
Both the farthest point sampling algorithm and the USAC framework have added SIMD support, so if you want to take full advantage of SIMD optimization, you can refer to the OpenCV configuration options reference.
CPU optimization level
On x86_64 machines the library will be compiled for SSE3 instruction set level by default. This level can be changed by configuration option:
cmake -DCPU_BASELINE=AVX2 ../opencv
git clone https://github.com/Ryyyc/opencv_3d.git
mkdir opencv_3d/build && cd opencv_3d/build
cmake ..
make
./opencv_3d ../data/Cassette_GT_.ply-sampled-0.2.plyPlease make sure to have an OpenCV environment, or see OpenCV installation tutorial.
If cmake cannot automatically detect the OpenCV installation path, please set OpenCV_DIR before find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED) in CMakeLists.txt file.
set(OpenCV_DIR ".../opencv/build/x64/vc15/lib")This can use Point Cloud Library or Open3D to visualize the results.
The following is an example of visualizing using Open3D-Python.
// install open3d-python in Ubuntu
pip3 install open3d
// Visualize point clouds
python ./samples/misc/python/Pointcloud-Visualization-With-Open3D.py -cloud ./data/Cassette_GT_.ply-sampled-0.2.ply
// Visualize point clouds with labels
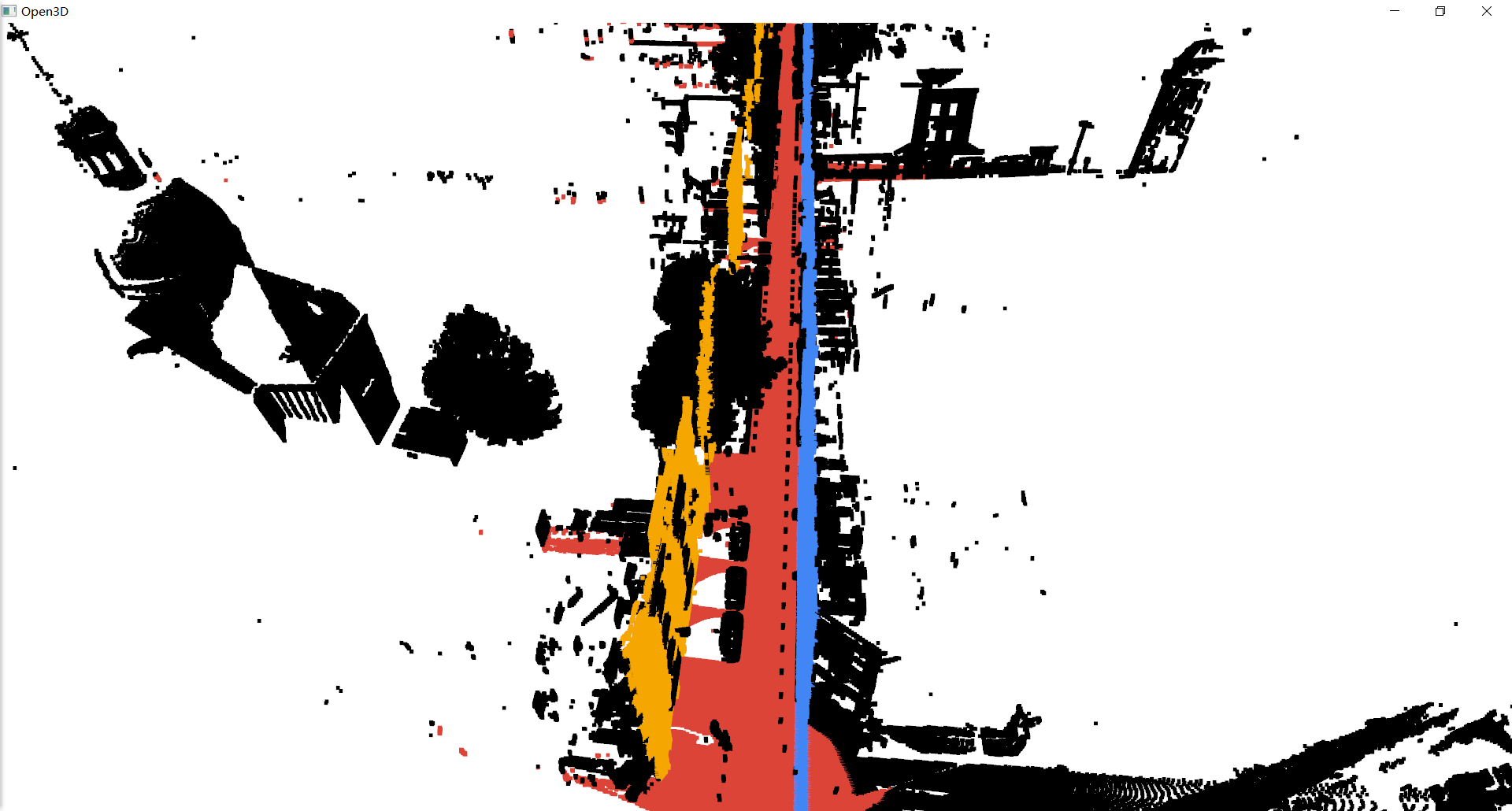
python ./samples/misc/python/Pointcloud-Visualization-With-Open3D.py -cloud ./data/Cassette_GT_.ply-sampled-0.2.ply -label ./data/Cassette_GT_.ply-sampled-0.2.ply-labels.txtUse data structure cv::Mat(size: n x 3) to store point cloud 3D coordinate information
Creates a 3D voxel grid (a set of tiny 3D boxes in space) over the input point cloud data, in each voxel (i.e., 3D box), all the points present will be approximated (i.e., downsampled) with the point closest to their centroid.
Randomly select some points from point cloud as sampling results.
The farthest point sampling is a kind of uniform sampling, and the sampling points are generally distributed near the boundary of the point cloud. The basic steps:
-
The input point cloud is denoted as set
C, the sampling point is denoted as setS, andSis initialized as an empty set. -
Randomly select a seed point and put it in
S. -
Sampling one point at a time, put in
S. The method of sampling is to find a point that is farthest from the setSin the setC - S(point inCbut not inS). The distance from a point to the point cloud set is the smallest distance from this point to all points in the set.
Fit the plane by the Total Least Squares.
pdf in Total-Least-Squares-in-3D.pdf
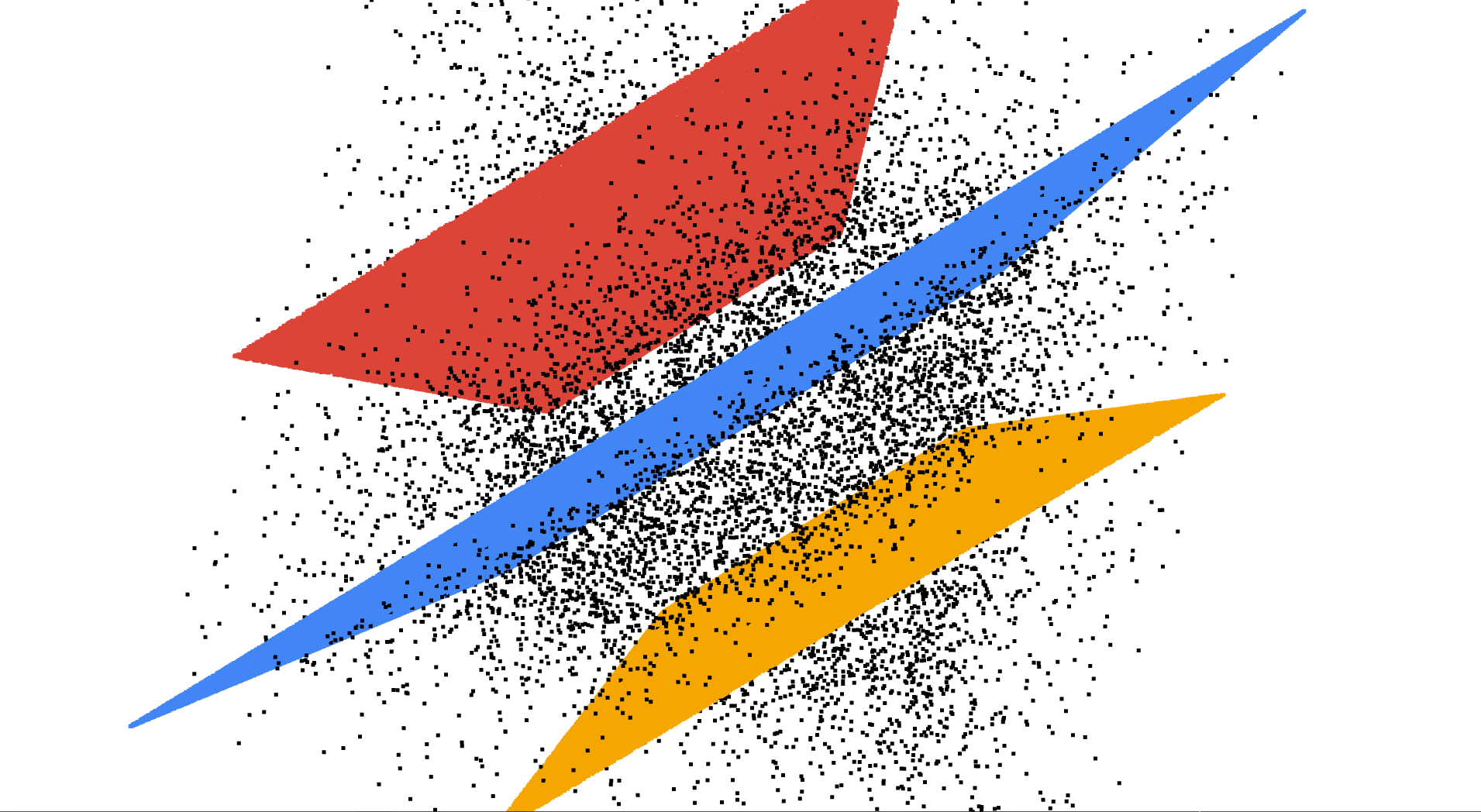
The basic idea of RANSAC is to select many planes by randomly pick 3 points from point cloud, then calculate the number of inlier points within a tolerance threshold for each plane. Finally, the plane matched the most inlier points is the best plane in the point cloud.
The RANSAC algorithm requires that most of the points in the point cloud belong to inlier points of the plane.
In the iterative process, the current optimal solution appears, and Lo-RANSAC is performed.
One method is to sample the calculation plane from the inlier points of the returned result, set a fixed number of iterations (10-20 times) and select the best local result as the improved result.
If the angle between the normal vector of the fitted plane and the normal vector of the constraint is greater than a threshold, the plane is discarded. The normal vector of the plane finally fitted (detected) by the algorithm will meet the given constraints
Use the optimized RANSAC algorithm to detect a plane from the point cloud, and label the inlier points on this plane, and the unlabeled points are added to the next round of detection. In this way, multi-plane detection is realized.
For very large point cloud (tens of millions of points), down-sampling can be used first to reduce the point cloud size while maintaining the point cloud characteristics, which will greatly accelerate the plane detection process.
func RANSAC_PLANE_FIT(point_cloud, thr, iteration, desired_num_planes)
init array best_planes
pc_samped = voxel_grid_samping(point_cloud)
for i in 1...desired_num_planes:
init best_plane to NULL
max_inlier_cnt = 0
for j in 1...iteration:
plane = random_three_point_fit_plane(pc_samped)
inlier_cnt = calculate_the_number_of_inlier_points_in_plane(plane)
if inlier_cnt > max_inlier_cnt:
best_plane = local_optimal_RANSAC(pc_samped, plane)
max_inlier_cnt = inlier_cnt
iteration = update_iteration(max_inlier_cnt)
add best_plane to array best_planes
label inlier points of best_plane and remove them from pc_samped
init array result
for best_plane in best_planes:
plane_fit = local_optimal_RANSAC(point_cloud, plane)
add plane_fit to array result
label inlier points of plane_fit and remove them from point_cloud
return array result
Point cloud data Cassette_GT_.ply-sampled-0.2.ply comes from IQmulus & TerraMobilita Contest, the down-sampled version of Cassette_idclass.
Point cloud data check.ply is generated by standard plane equations and noise points are added. Author Zoom1111.
Cassette_GT_.ply-sampled-0.2.ply
check.ply