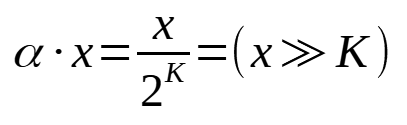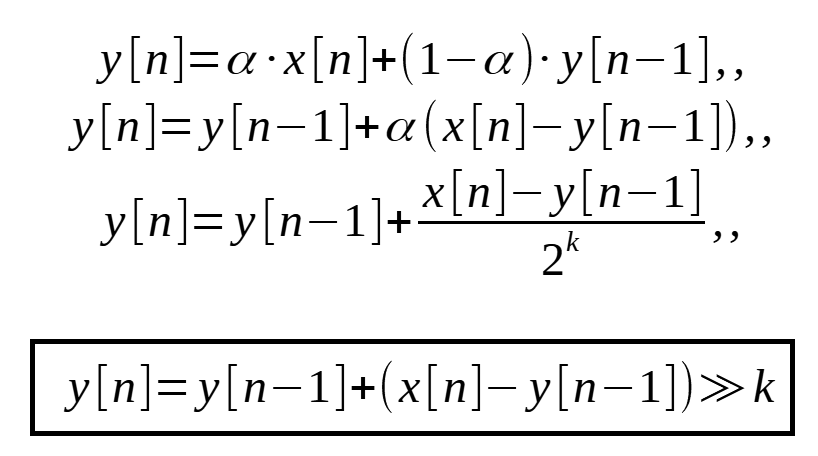Arduino library for Exponential Moving Average filter (EMA), implemented very easily and efficiently.
The EMA (exponential moving average) or EWMA (exponentially weighed moving average) is the name for what is probably the easiest realization of the (first-order) low-pass on discrete time-domain data.
Y[n] = alpha * X[n] + (1 - alpha) * Y[n-1]A moving average is commonly used with time series data to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends or cycles. When AVR,s (as Arduino) get the value from ADC port, it can get small fluctuations in the measure.
The factor alpha in the difference equation of the Exponential Moving Average filter is a number between zero and one. There are two main ways to implement this multiplication by alpha: Either we use floating point numbers and calculate the multiplication directly, or we use integers, and express the multiplication as a division by 1/alpha > 1.
Both floating point multiplication and integer division are relatively expensive operations, especially on embedded devices or microcontrollers.
We can, however, choose the value for alpha in such a way that 1/alpha = 2^K.
This is useful, because a division by a power of two can be replaced by a very fast right bitshift:
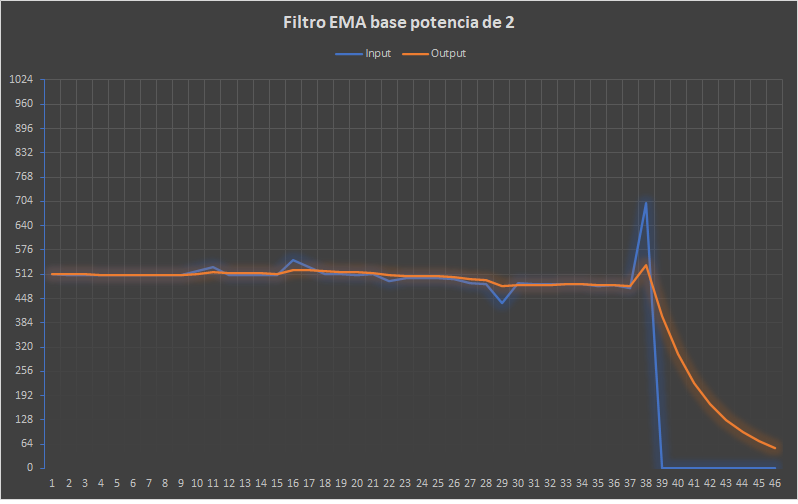
We can now rewrite the difference equation of the EMA with this optimization in mind:In this graphics shows an EMA filter (K=2) using values from an analog port on Arduino Uno.
For a tutorial on how to install new libraries for use with the Arduino development environment please refer to the following website: http://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/Libraries
--- or ---
- Download the ZIP file from the page releases to your machine.
- In the Arduino IDE, choose Sketch/Include Library/Add Zip Library.
- Navigate to the ZIP file, and click Open.
How to use the library in PlatformIO see documentation of Library Manager.
The only one simple step is to define dependencies in “platformio.ini” (Project Configuration File). For example,
# platformio.ini – project configuration file
[env:my_build_env]
platform = atmelavr
framework = arduino
lib_deps =
# RECOMMENDED
# Accept new functionality in a backwards compatible manner and patches
rafaelreyescarmona/EMA @ ^0.1.1
# Accept only backwards compatible bug fixes
# (any version with the same major and minor versions, and an equal or greater patch version)
rafaelreyescarmona/EMA @ ~0.1.1
# The exact version
rafaelreyescarmona/EMA @ 0.1.1
For Manual installation in PlatformIO Core:
- Run a terminal and type for search the library:
pio lib search EMA
- Type for install:
pio lib install 13380
--- or ---
- Search "EMA" in search box of Libraries of panel.
- Click Add to project button. Library will be included in the project and "platformio.ini" updated.
In Arduino IDE, Choose Sketch/Include Library/Scroll and select "EMA".
There are a two examples files with the library. In the Arduino IDE, choose File/Examples/EMA, and you can see "EMA".
--- or ---
Example of use:
/**
* Example sketch for the EMA library.
*/
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <EMA.h>
#define PIN_READ A0
void setup() {
pinmode(PIN_READ, INPUT);
}
void loop(){
uint16_t read;
uint16_t read_filtered;
static EMA<2> EMA_filter(250); // Initial value for EMA filter.
read = analogRead(PIN_READ);
read_filtered = EMA_filter(read);
Serial.print("Read from ADC : ");
Serial.print(read);
Serial.print(" , Filtered value: ");
Serial.print(read_filtered);
Serial.print("\n");
delay(250);
}On AVR,s (as ATMega328) analogRead returns an integer between 0 and 1023, which can be represented using 10 bits, so Resolution = 10. Input is uint16_t so the maximum shift factor K is 16 - Resolution = 6.
If analogRead returns an 12 bits integer (an integer between 0 and 4095), the maximum shift factor K will be 16 - 12 = 4.
- Initialize filter to zero or optional given value.
- Initial version.
This file is part of EMA Library.
EMA Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
EMA Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with EMA Library. If not, see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/.
Copyright © 2022 Francisco Rafael Reyes Carmona. Contact me: rafael.reyes.carmona@gmail.com
Electric meter icon at the beginning is from Flaticon.es designed by Freepik and licensed by free license.