This project builds an information retrieval (IR) chatbot that can scrape Wikipedia using BeautifulSoup in the topic of user's interest and collect information against user's queries following a heuristic backed by TF-IDF score and cosine-similarity score. This Wiki-IR-ChatBot is user-friendly in permitting users to choose any topic and presenting either crisp and short response or detailed response. It leverages NLTK library to do text processing and scikit-learn library to do modeling. Find more details with the supporting blog article published at LinkedIn!
Wiki_IR_ChatBot.py - A Python version of ChatBot
wiki-ir-chatbot_1.ipynb - A Interactive Notebook version of ChatBot (Earlier versions also available)
requirements.txt - Explores Python libraries requirements to run the project
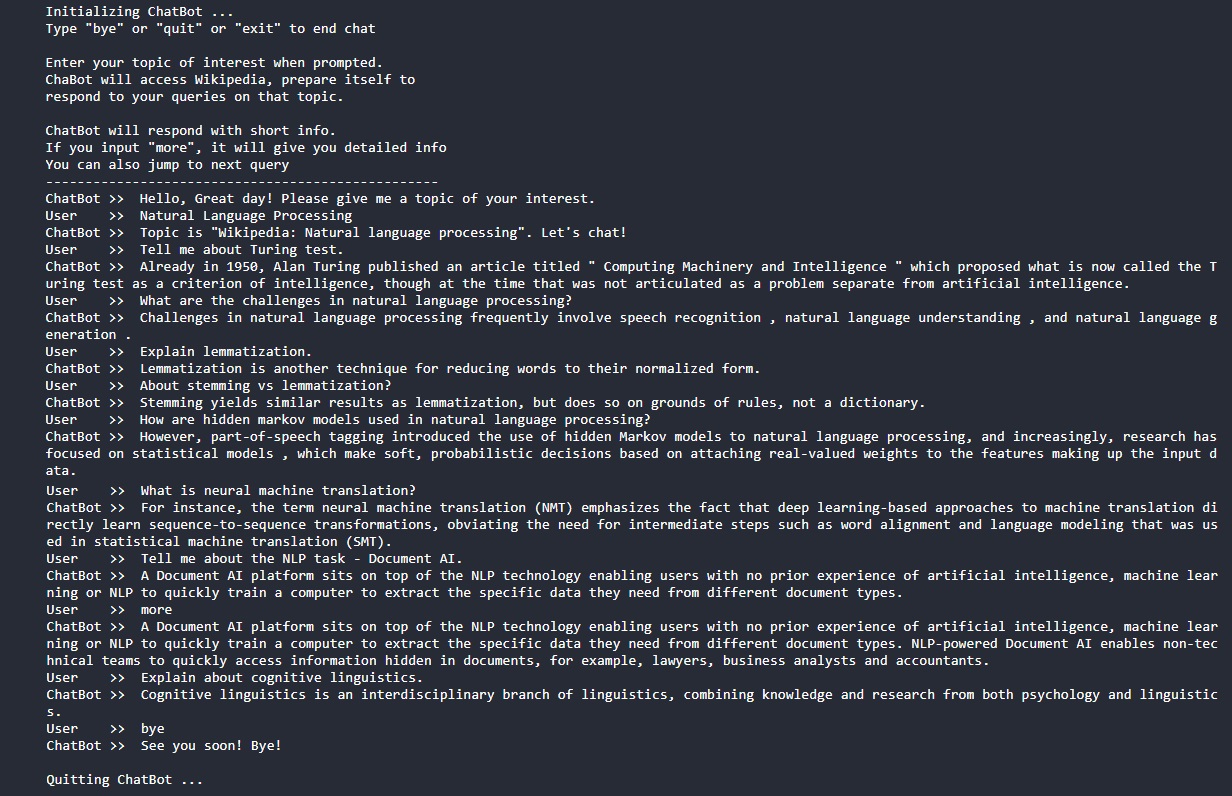
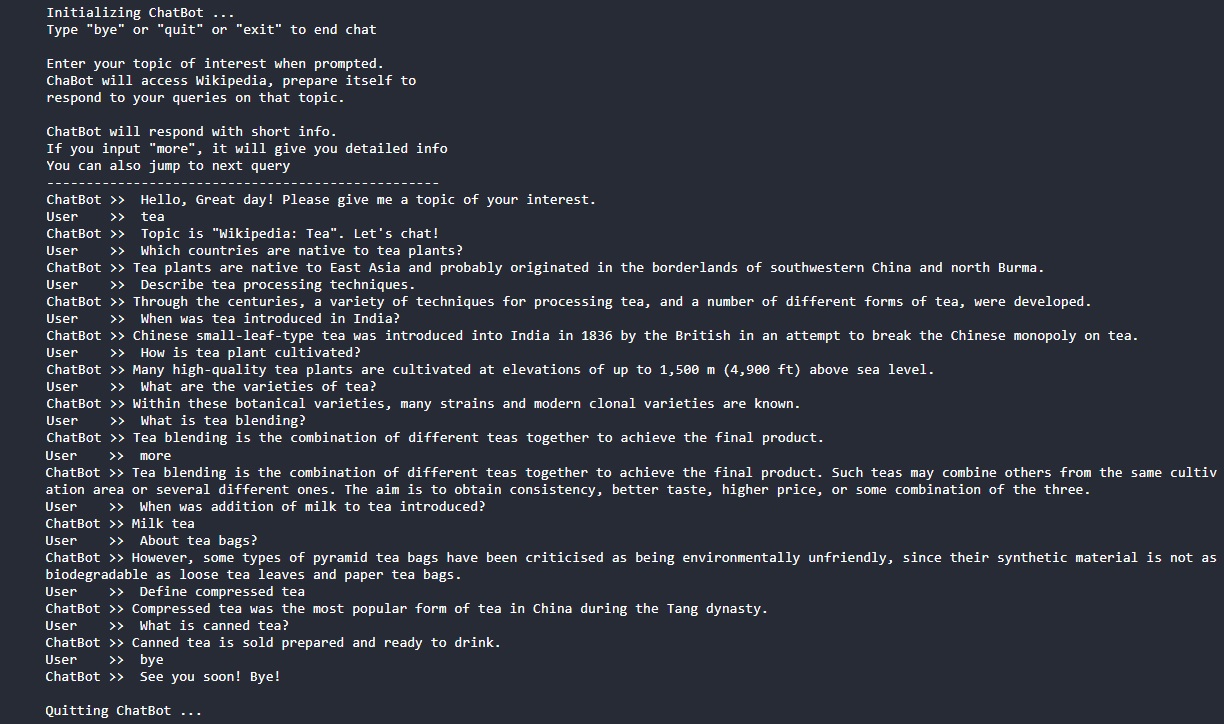
wiki_ir_chatbot_chats_x.jpg - Screenshots of some chats by this project (replace x with 1, 2, 3)
A ChatBot is a kind of virtual assistant that can build conversations with human users! A Chatting Robot. Building a chatbot is one of the popular tasks in Natural Language Processing.
Information Retrieval (or, IR in short) is the task of identifying and collecting the most relevant information from a source based on a pre-defined heuristic. Text data is a good example of unordered data while it is abudant everywhere. It is hard to find the information manually from a huge collection of text data. Since need of information is time-bound in general, a good IR system is always in need.
Chatbots fall under three common categories:
These bots respond to users' inputs based on certain pre-specified rules. For instance, these rules can be defined as if-elif-else statements. While writing rules for these chatbots, it is important to expect all possible user inputs, else the bot may fail to answer properly. Hence, rule-based chatbots do not possess any cognitive skills.
These bots respond to users' inputs by retrieving the most relevant information from the given text document. The most relevant information can be determined by Natural Language Processing with a scoring system such as cosine-similarity-score. Though these bots use NLP to do conversations, they lack cognitive skills to match a real human chatting companion. This Wiki-IR-ChatBot falls under this category!
These bots respond to users' inputs after understanding the inputs, as humans do. These bots are trained with a Machine Learning Model on a large training dataset of human conversations. These bots are cognitive to match a human in conversing. Popular Virtual Assistants such as Amazon's Alexa, Apple's Siri fall under this category. Further, most of these bots can make conversations based on the preceding chat texts. Conversational AI ChatBot, built by Author, employs Microsoft's DialoGPT to make intelligent conversations!