The following repository corresponds to Spantree's Elasticsearch workshop. It uses Vagrant, Virtualbox and Puppet to bootstrap a virtual machine that allows you to play along with our exploration of Elasticsearch. It also contains all the slides in our deck, courtesy of reveal.js.
Cedric Hurst: Principal & Lead Software Engineer
Kevin Greene: Senior Software Engineer
Gary Turovsky: Senior Software Engineer
We ask that you walk through these steps before you stop by since you'll need to download stuff and we don't want to crush the hotel bandwidth. The project itself will likely evolve up until the time of the presentation, but the virtual machine stuff shouldn't change too much.
Install the following tools to bootstrap your environment
- Install Git
- Install VirtualBox (version 4.3.8 or above)
- Install Vagrant (version 1.6.4 or above)
From the command line, install the hostmanager and vbguest vagrant plugins. We use these Vagrant plugins to manage /etc/hosts entries and make sure you have the right version of Virtualbox Guest Additions installed.
vagrant plugin install vagrant-hostmanager
vagrant plugin install vagrant-vbguestNext, you'll want to clone this repository via Git.
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/Spantree/elasticsearch-talk.git
cd elasticsearch-talkFinally, you'll want to start the Vagrant virtual machine instance.
vagrant upThis will download a base Virtualbox Ubuntu image, set it up as a virtual machine to run locally, and install all the tools extra tools you'll need to play along.
Please note that you may be prompted for your host system password. We aren't installing viruses or keyloggers, we promise. This is just so that the hostmanager plugin can write out mappings to your /etc/hosts file. If you're feeling particularly paranoid, you can add the following entries to /etc/hosts manually.
192.168.80.100 es1.local esdemo.local kibana.local
192.168.80.101 es2.local
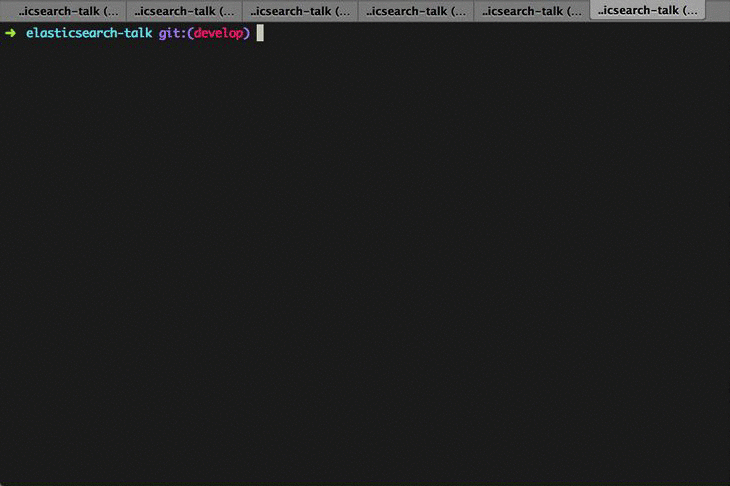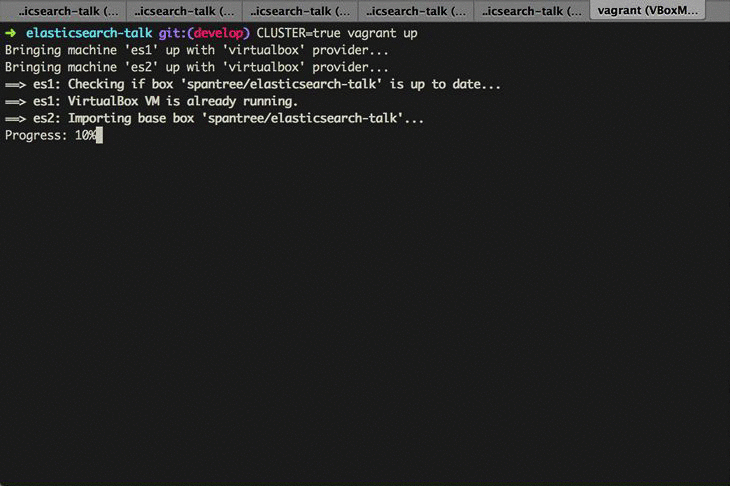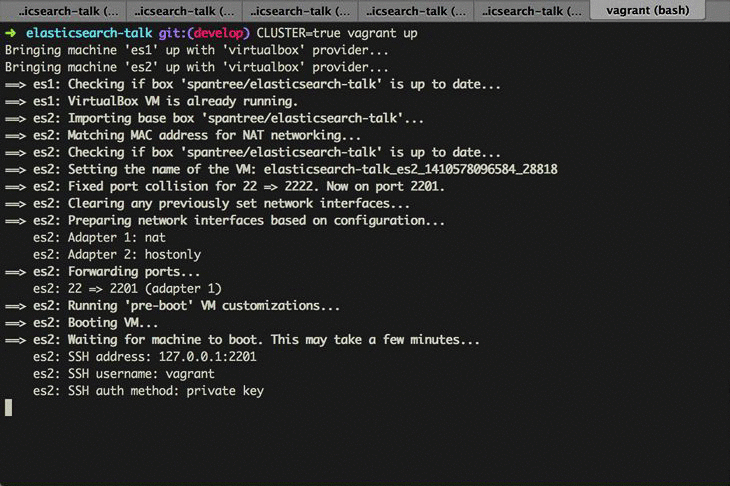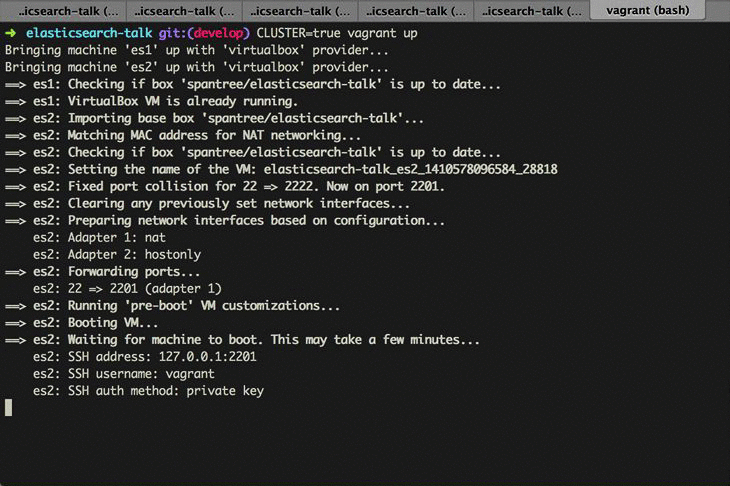
The whole process from end to end should look like this...
If you're feeling adventurous, you also have the option of setting up a second Elasticsearch VM to set up a cluster. Running both VMs requires at about 4GB of available RAM on the host machine.
To spin up a second node, just re-run the Vagrant up command with the CLUSTER=true environment variable.
CLUSTER=true vagrant upThat's it. That's all there is to it.
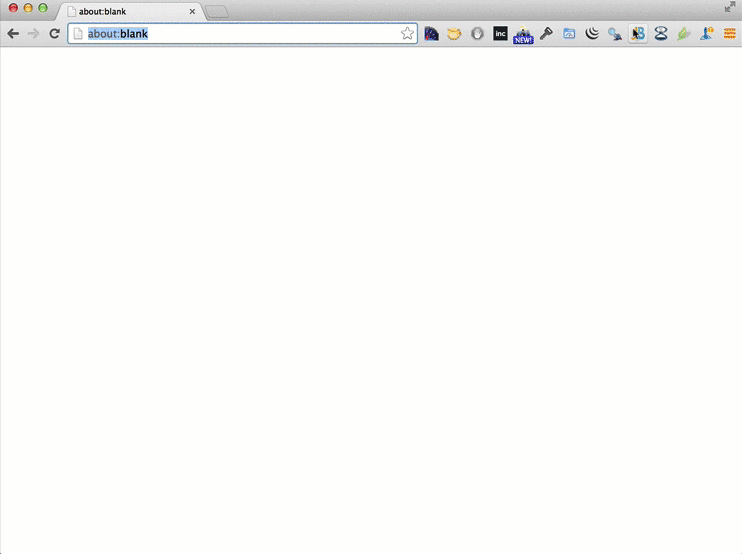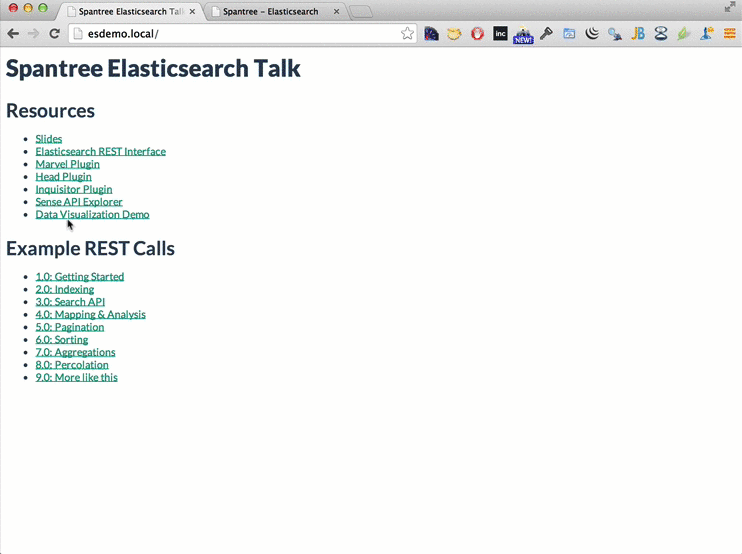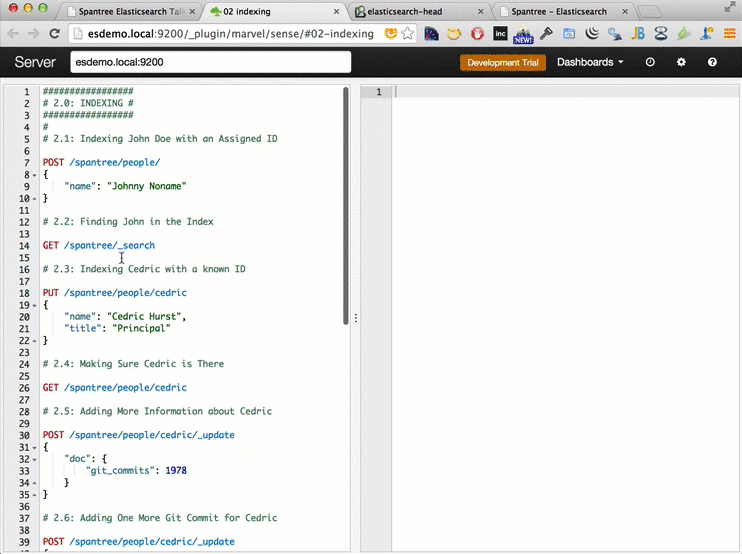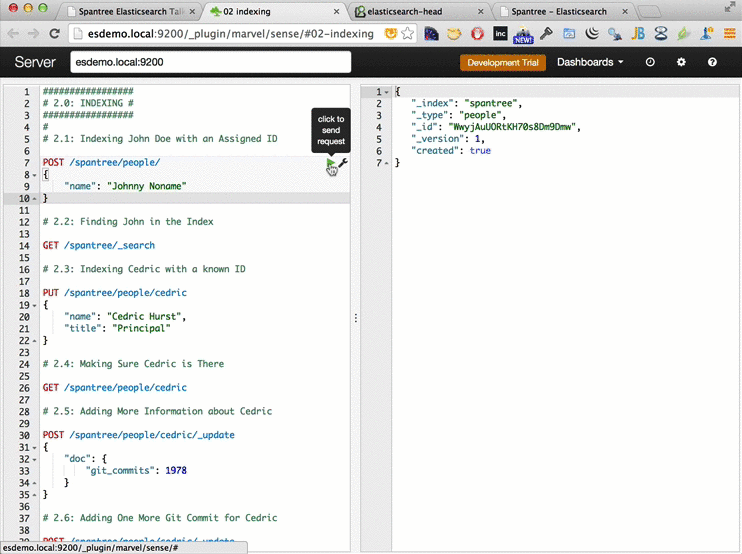
You should now be able to access elasticsearch on your machine from a web browser at http://esdemo.local:
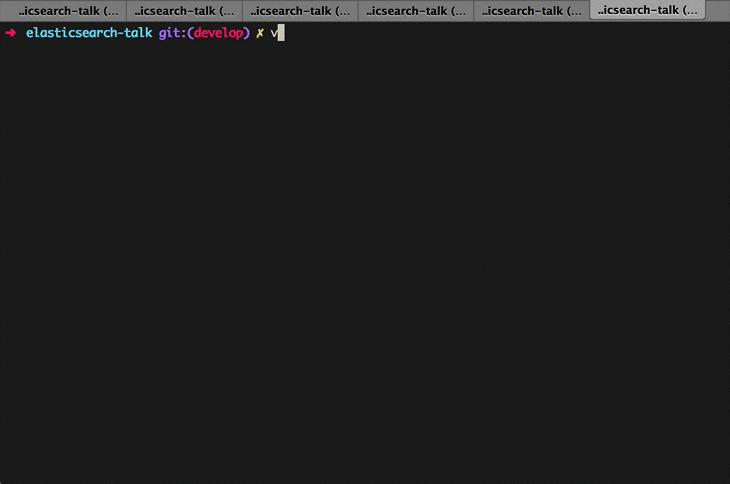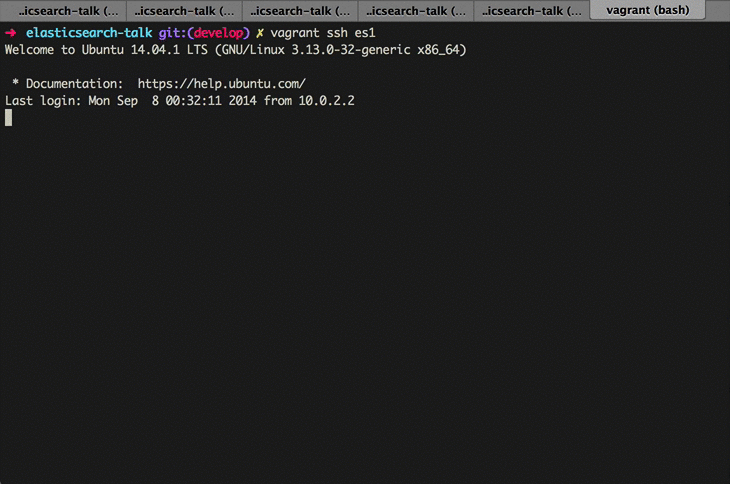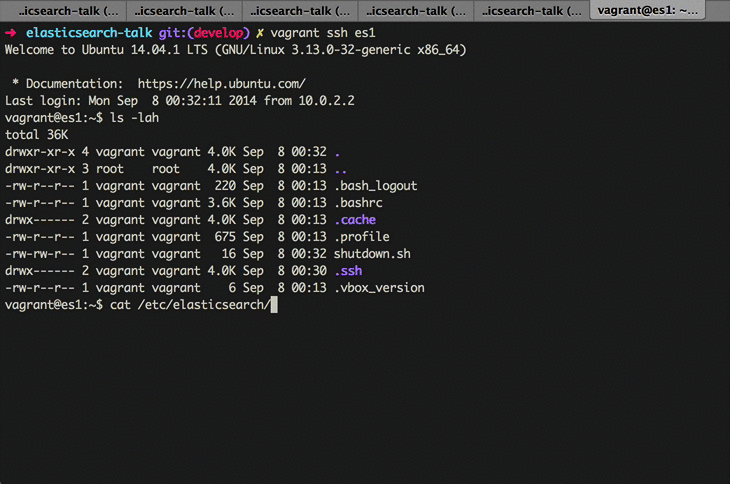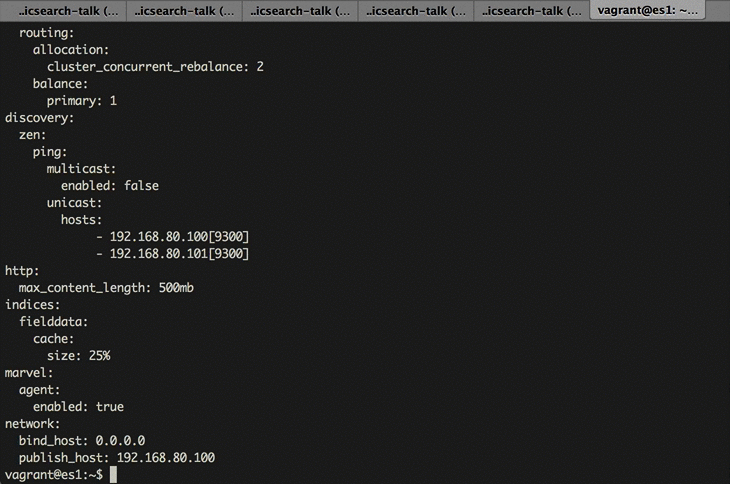
You should also be able to ssh into your virtual machine using the vagrant ssh es1 command.
If you enabled clustering, you can also ssh into the second VM using vagrant ssh es2.
As mentioned, we may be altering the vagrant configuration up until the time of the presentation, so make sure you have the latest changes by doing the following from your host terminal:
git pull
vagrant reload --provision
When you're all done elasticsearching, you can gracefully shut down your vagrant instance by running:
vagrant halt
This will close the VM.
If you want to conserve disk space, you can get rid of the disk images via the destroy command:
vagrant destroy
This repo will here for you should you need it again.
Email info@spantree.net if you run into issues. We'd be happy to help.