Processing Methods Assemble
Summary of most frequently used data processing methods (Non-DNN method). Most of them are related to unsupervised learning and representation learning.
cluster methods
in
sklearn.cluster
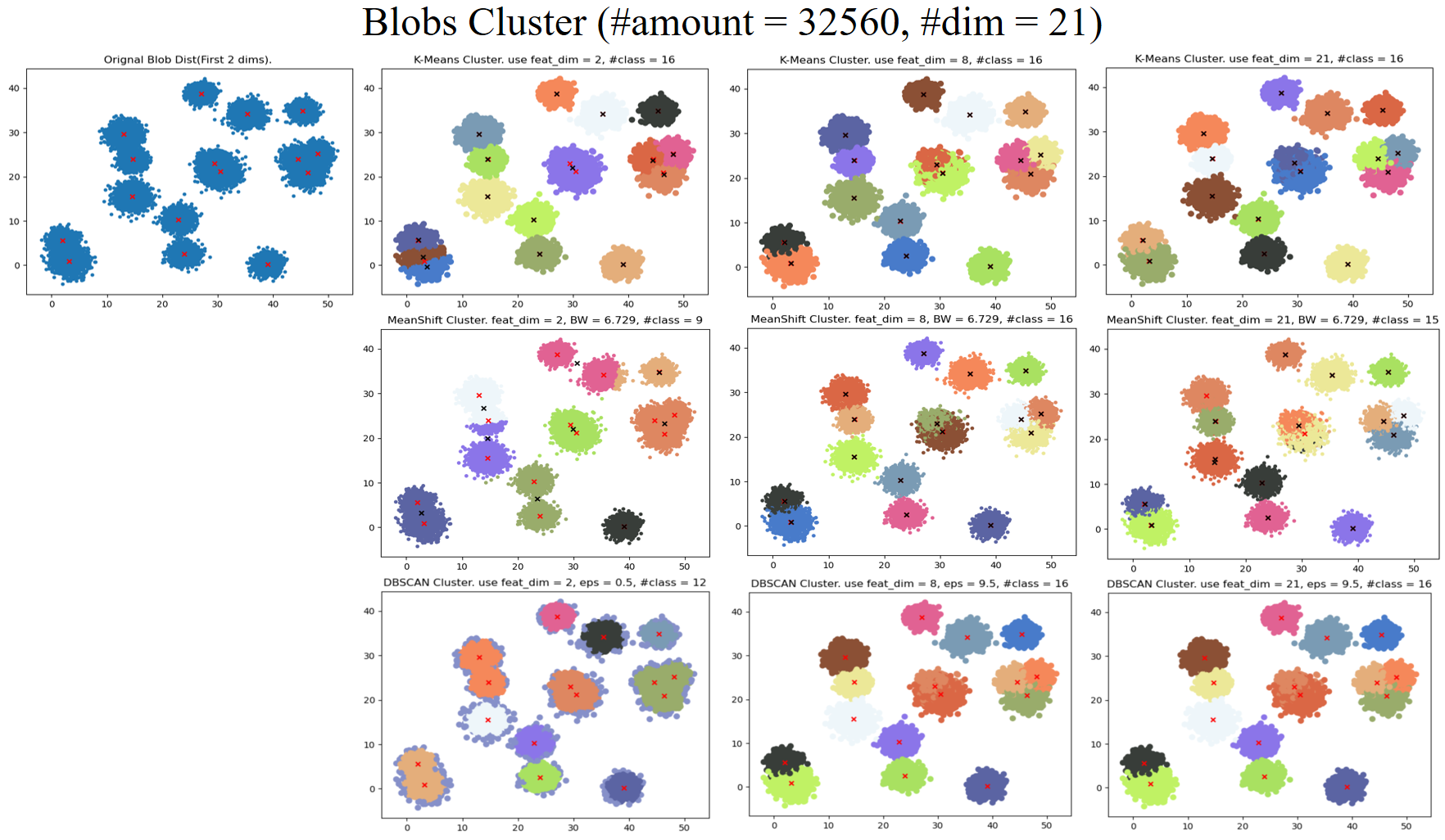
Using datasets. make_blobs The high-order data generated by blobs, using the clustering results of the above three clustering methods
| Method Name | Hyper-Para | Description |
|---|---|---|
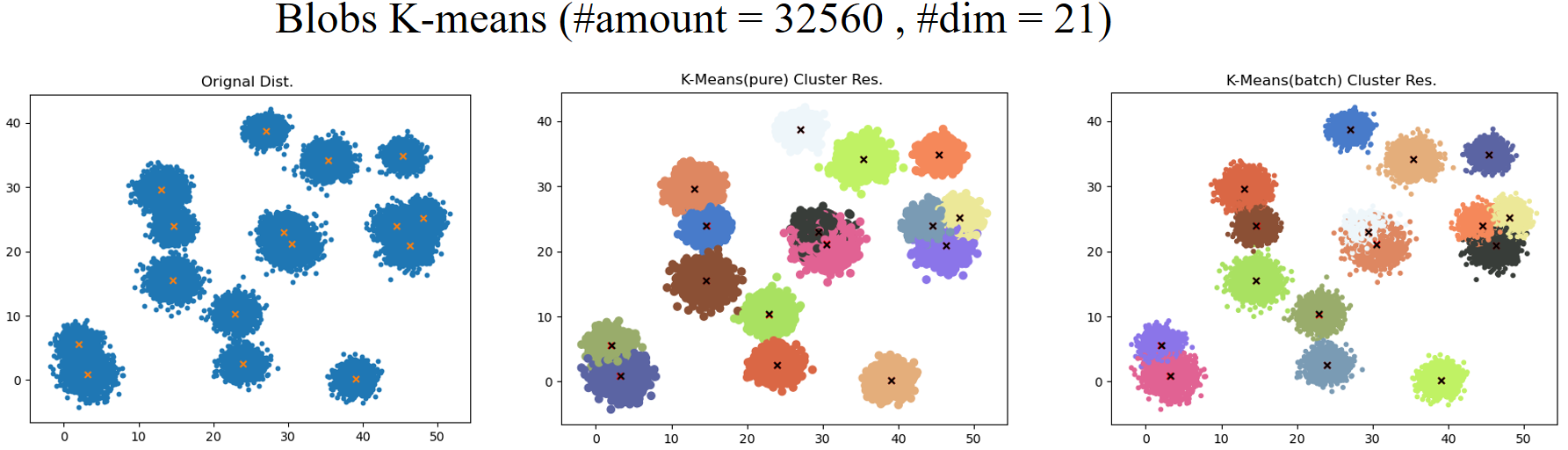
| K-Means | #classes | Specify the number of categories in advance as Hyper-Para. Batch-wise version: minibatch |
| Mean-Shift | band width | Smaller BW get more #classes |
| DBSCAN | eps, | For nonlinear clustering, each class cannot give the central coordinates |
dimensionality reduction methods
in
sklearn.decomposition(PCA),sklearn.discriminant_analysis(LDA),sklearn.manifold(t-SNE, LLE)
| Method Name | Hyper-Para | Description |
|---|---|---|
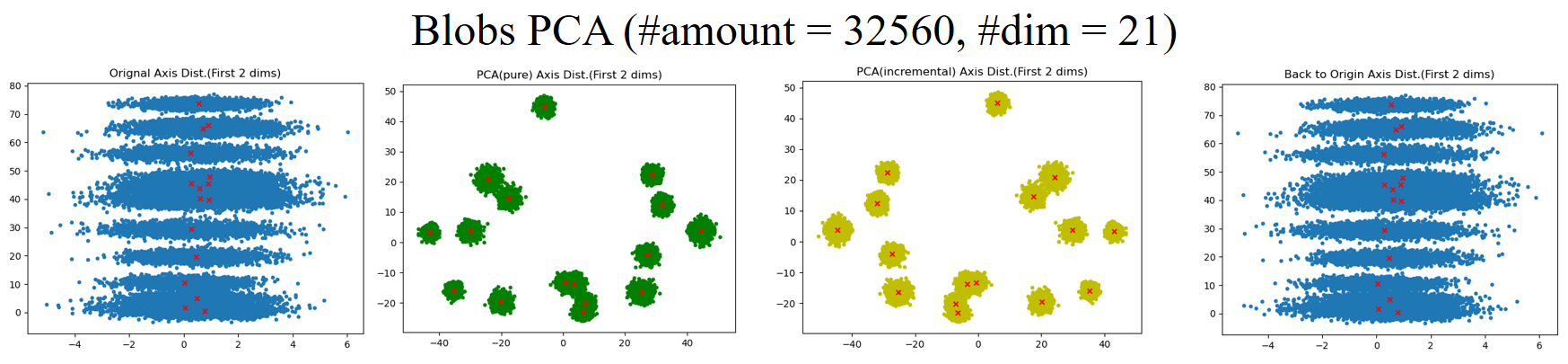
| PCA | #components | The covariance matrix is optimized so that the diagonal elements are in descending order and other positions are 0. Batch-wise version: incremental |
| LDA | Class Label. | Maximize the distance between classes and minimize the distance within classes. |
| LLE | --- | --- |
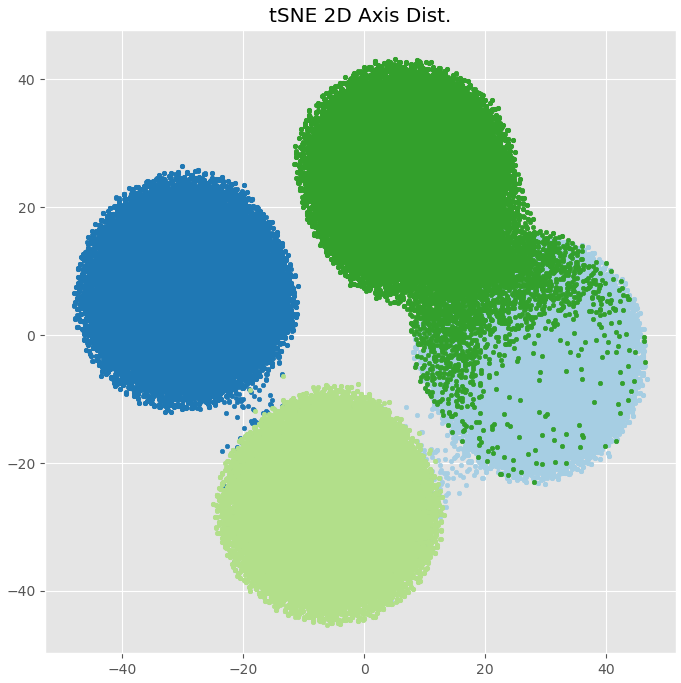
| t-SNE | #components | On the premise of keeping the high-dimensional distance unchanged, the data points are remapped to 2 or 3 dimensions for visualization. It is not a clustering algorithm, but a means to analyze the effectiveness of clustering. Original space (n-D): Gaussian dist. ; Embedded space (2-D): t dist. |