HybridNets: End-to-End Perception Network
by Dat Vu, Bao Ngo, Hung Phan 📧 FPT University
(📧) corresponding author.
arXiv technical report (arXiv 2203.09035)
Table of Contents
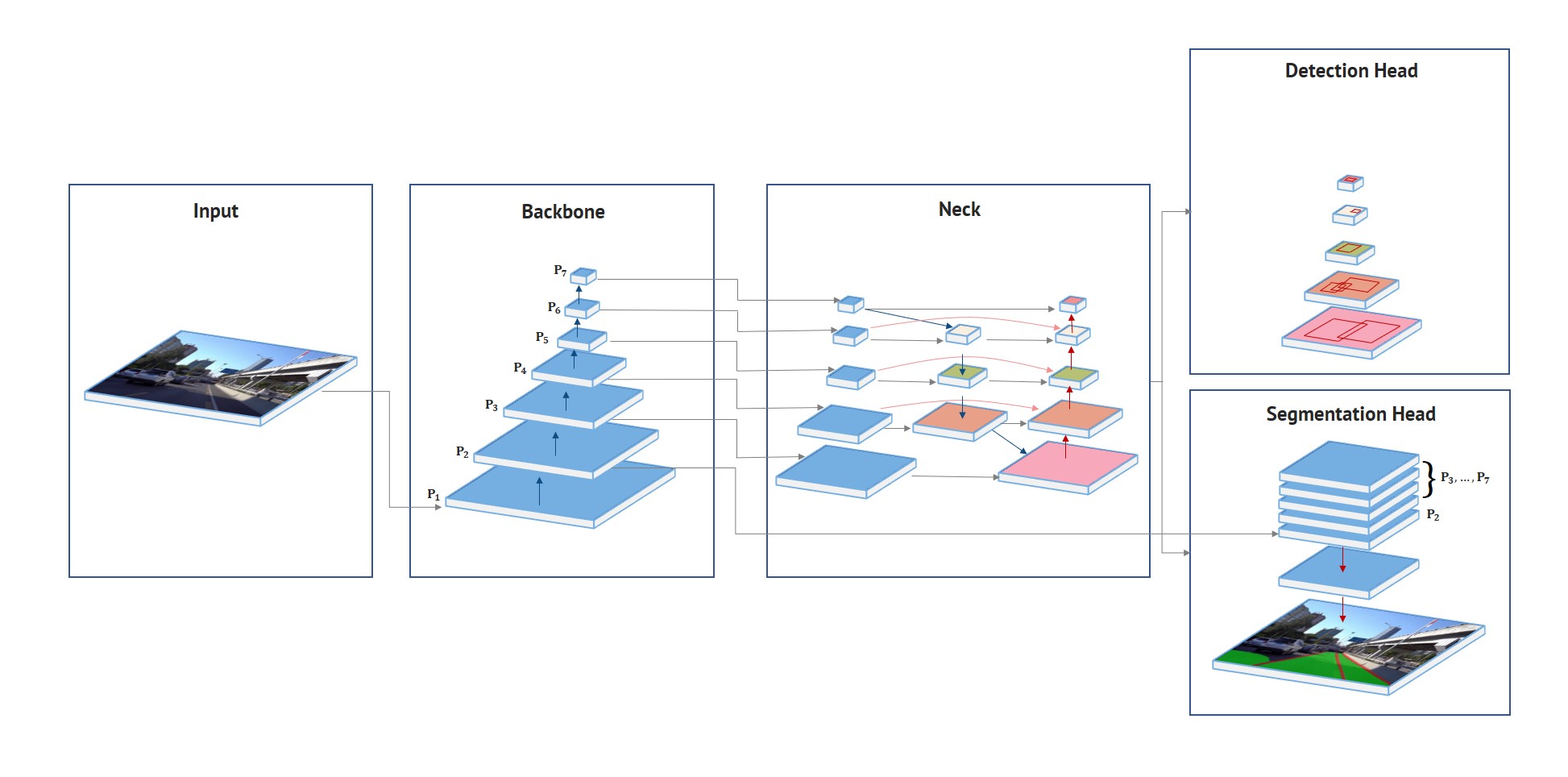
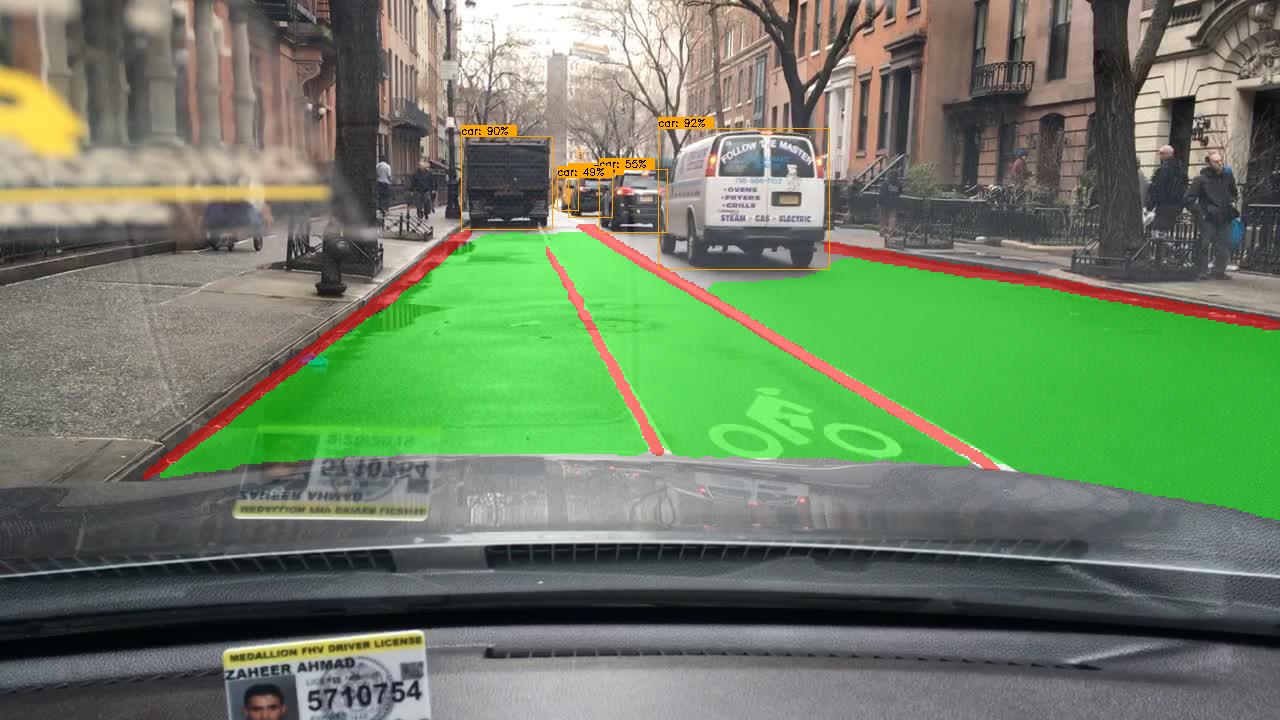
HybridNets is an end2end perception network for multi-tasks. Our work focused on traffic object detection, drivable area segmentation and lane detection. HybridNets can run real-time on embedded systems, and obtains SOTA Object Detection, Lane Detection on BDD100K Dataset.

HybridNets
│ backbone.py # Model configuration
│ hubconf.py # Pytorch Hub entrypoint
│ hybridnets_test.py # Image inference
│ hybridnets_test_videos.py # Video inference
│ train.py # Train script
│ train_ddp.py # DistributedDataParallel training (Multi GPUs)
│ val.py # Validate script
│ val_ddp.py # DistributedDataParralel validating (Multi GPUs)
│
├───encoders # https://github.com/qubvel/segmentation_models.pytorch/tree/master/segmentation_models_pytorch/encoders
│ ...
│
├───hybridnets
│ autoanchor.py # Generate new anchors by k-means
│ dataset.py # BDD100K dataset
│ loss.py # Focal, tversky (dice)
│ model.py # Model blocks
│
├───projects
│ bdd100k.yml # Project configuration
│
└───utils
│ plot.py # Draw bounding box
│ smp_metrics.py # https://github.com/qubvel/segmentation_models.pytorch/blob/master/segmentation_models_pytorch/metrics/functional.py
│ utils.py # Various helper functions (preprocess, postprocess, eval...)The project was developed with Python>=3.7 and Pytorch>=1.10.
git clone https://github.com/datvuthanh/HybridNets
cd HybridNets
pip install -r requirements.txt# Download end-to-end weights
curl --create-dirs -L -o weights/hybridnets.pth https://github.com/datvuthanh/HybridNets/releases/download/v1.0/hybridnets.pth
# Image inference
python hybridnets_test.py -w weights/hybridnets.pth --source demo/image --output demo_result --imshow False --imwrite True
# Video inference
python hybridnets_test_videos.py -w weights/hybridnets.pth --source demo/video --output demo_result
# Result is saved in a new folder called demo_resultRecommended dataset structure:
HybridNets
└───datasets
├───imgs
│ ├───train
│ └───val
├───det_annot
│ ├───train
│ └───val
├───da_seg_annot
│ ├───train
│ └───val
└───ll_seg_annot
├───train
└───valUpdate your dataset paths in projects/your_project_name.yml.
For BDD100K: imgs, det_annot, da_seg_annot, ll_seg_annot
# mean and std of dataset in RGB order
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
# bdd100k anchors
anchors_scales: '[2**0, 2**0.70, 2**1.32]'
anchors_ratios: '[(0.62, 1.58), (1.0, 1.0), (1.58, 0.62)]'
# BDD100K officially supports 10 classes
# obj_list: ['person', 'rider', 'car', 'truck', 'bus', 'train', 'motorcycle', 'bicycle', 'traffic light', 'traffic sign']
obj_list: ['car']
obj_combine: ['car', 'bus', 'truck', 'train'] # if single class, combine these classes into 1 single class in obj_list
# leave as empty list ([]) to not combine classes
seg_list: ['road',
'lane']
dataset:
color_rgb: false
dataroot: path/to/imgs
labelroot: path/to/det_annot
laneroot: path/to/ll_seg_annot
maskroot: path/to/da_seg_annot
...python train.py -p bdd100k # your_project_name
-c 3 # coefficient of effnet backbone, result from paper is 3
OR -bb repvgg_b0 # change your backbone with timm
-n 4 # num_workers
-b 8 # batch_size per gpu
-w path/to/weight # use 'last' to resume training from previous session
--freeze_det # freeze detection head, others: --freeze_backbone, --freeze_seg
--lr 1e-5 # learning rate
--optim adamw # adamw | sgd
--num_epochs 200Please check python train.py --help for cheat codes.
IMPORTANT: If you want to train on multiple gpus, use train_ddp.py. Tested on NVIDIA DGX with 8xA100 40GB.
Why didn't we combine DDP into the already existing train.py script?
- Lots of if-else.
- Don't want to break functioning stuffs.
- Lazy.
python val.py -p bdd100k -c 3 -w checkpoints/weight.pthIf your dataset is intrinsically different from COCO or BDD100K, or the metrics of detection after training are not as high as expected, you could try enabling autoanchor in project.yml:
...
model:
image_size:
- 640
- 384
need_autoanchor: true # set to true to run autoanchor
pin_memory: false
...This automatically finds the best combination of anchor scales and anchor ratios for your dataset. Then you can manually edit them project.yml and disable autoanchor.
If you're feeling lucky, maybe mess around with base_anchor_scale in backbone.py:
class HybridNetsBackbone(nn.Module):
...
self.pyramid_levels = [5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6]
self.anchor_scale = [1.25,1.25,1.25,1.25,1.25,1.25,1.25,1.25,1.25,]
self.aspect_ratios = kwargs.get('ratios', [(1.0, 1.0), (1.4, 0.7), (0.7, 1.4)])
...and model.py:
class Anchors(nn.Module):
...
for scale, ratio in itertools.product(self.scales, self.ratios):
base_anchor_size = self.anchor_scale * stride * scale
anchor_size_x_2 = base_anchor_size * ratio[0] / 2.0
anchor_size_y_2 = base_anchor_size * ratio[1] / 2.0
...to get a grasp on how anchor boxes work.
And because a picture is worth a thousand words, you can visualize your anchor boxes in Anchor Computation Tool.
We experimented with training stages and found that this settings achieved the best results:
--freeze_seg True~ 100 epochs--freeze_backbone True --freeze_det True~ 50 epochs- Train end-to-end ~ 50 epochs
The reason being detection head is harder to converge early on, so we basically skipped segmentation head to focus on detection first.
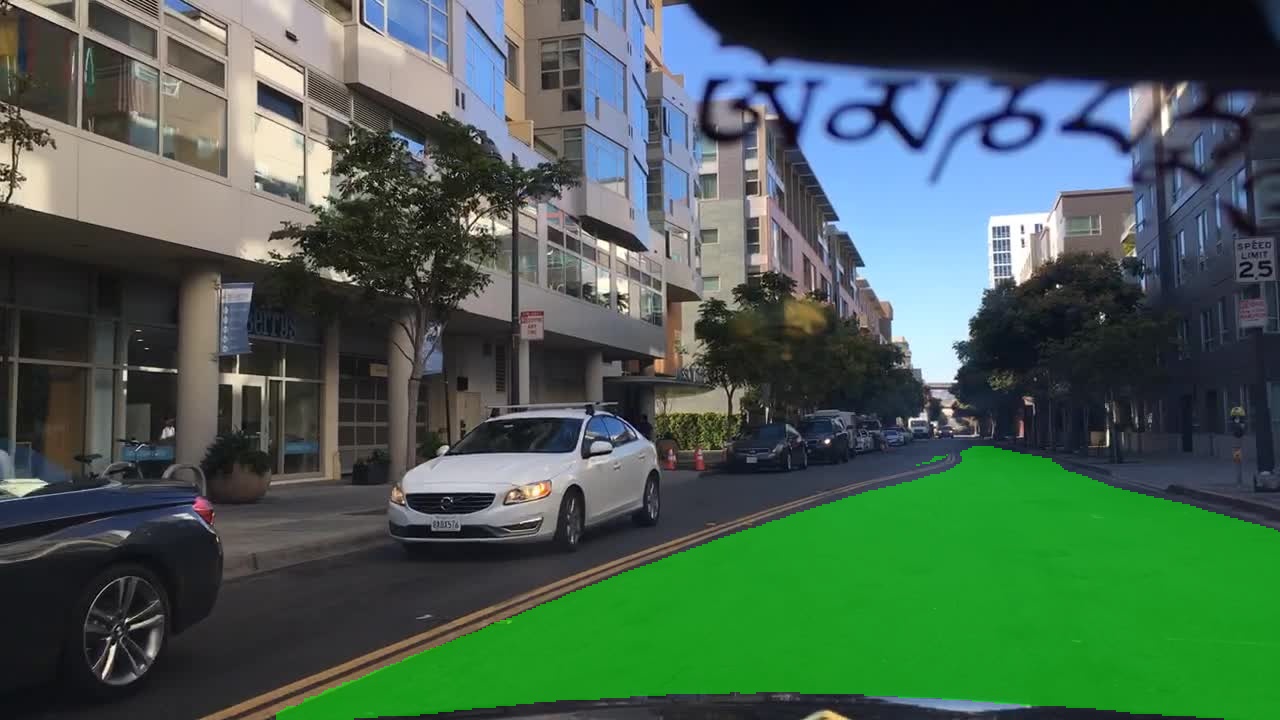
| Result | Visualization | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
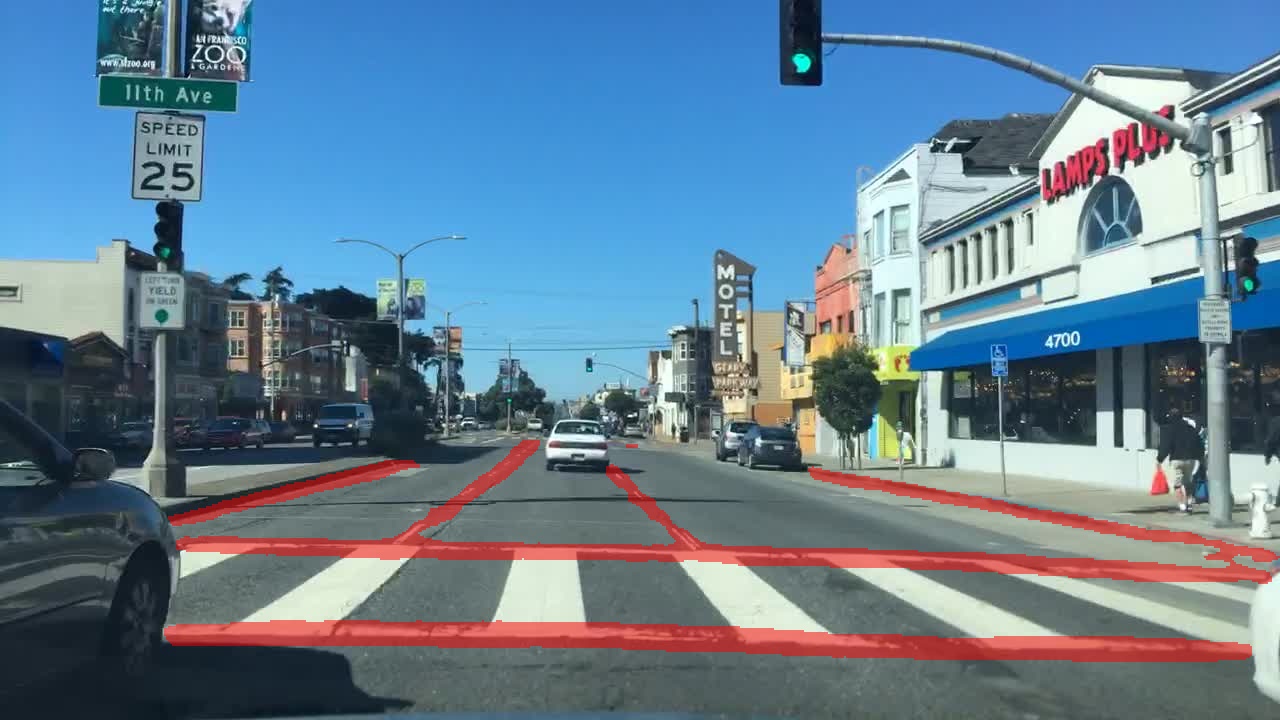
| Result | Visualization | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
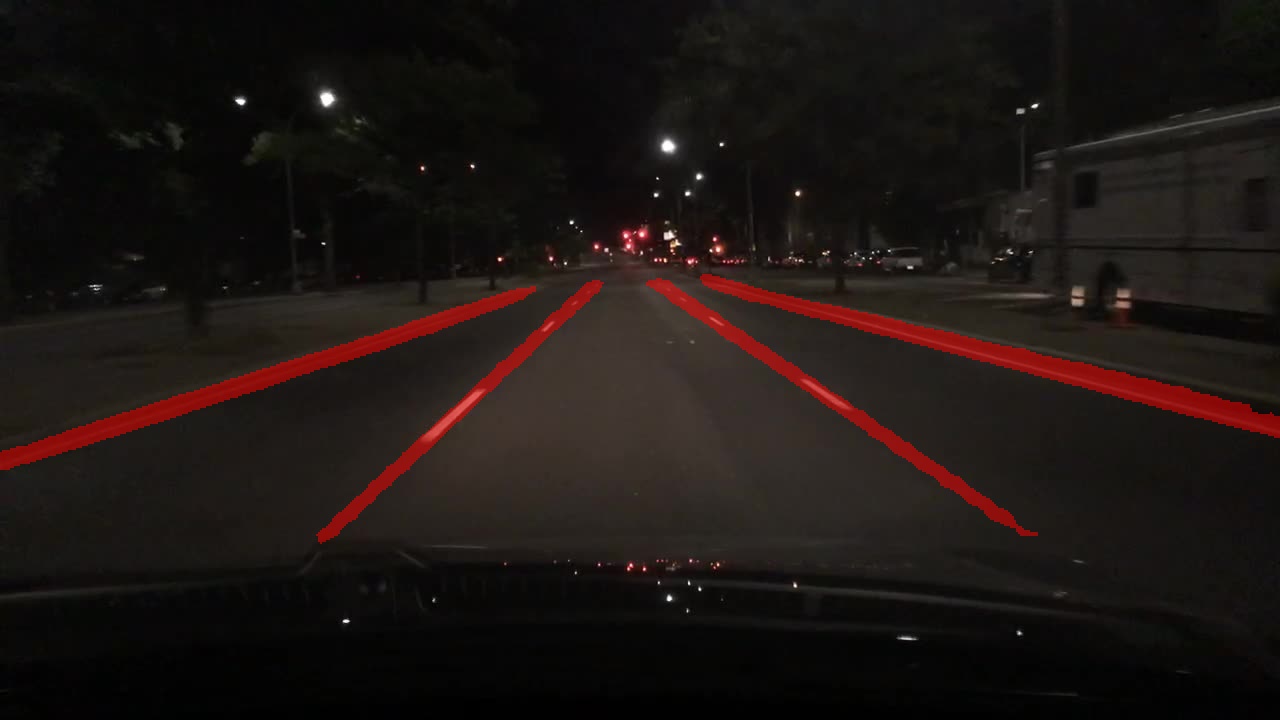
| Result | Visualization | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Original footage courtesy of Hanoi Life
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for more information.
Our work would not be complete without the wonderful work of the following authors:
If you find our paper and code useful for your research, please consider giving a star ⭐ and citation 📝 :
@misc{vu2022hybridnets,
title={HybridNets: End-to-End Perception Network},
author={Dat Vu and Bao Ngo and Hung Phan},
year={2022},
eprint={2203.09035},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}