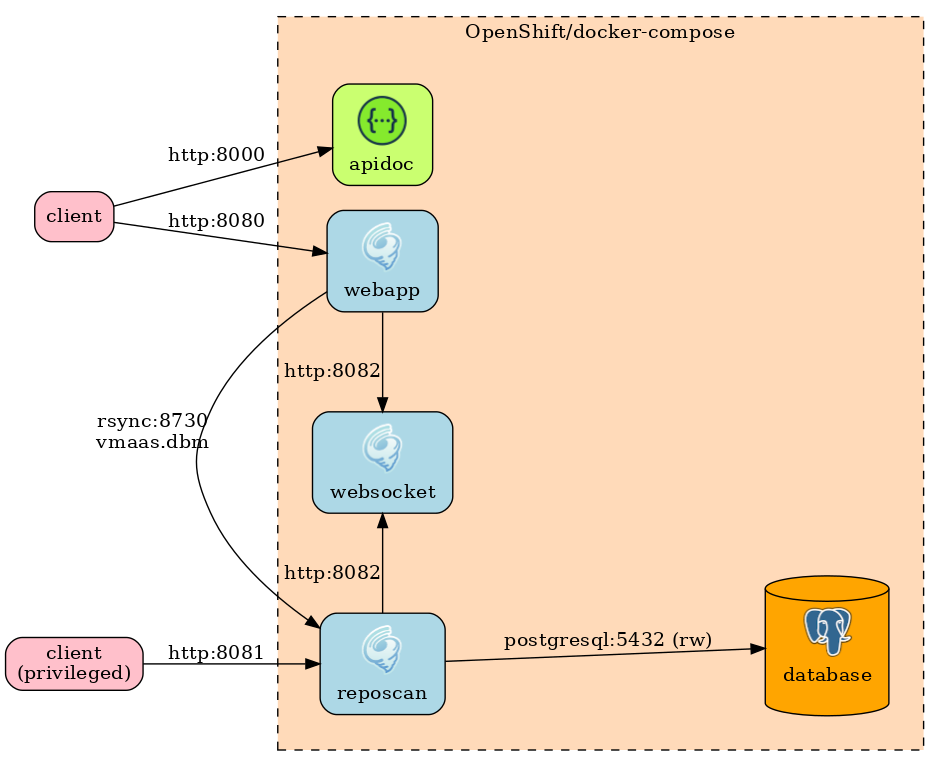
Vulnerability Metadata as a Service
VMaaS is intended to be a microservice that has access to data connecting RPMs, repositories, errata, and CVEs, and can answer the question "What security changes do I have to apply to the following set of RPMs?"
The goal is to have a common set of data, that can be updated from multiple sources, and
accessed from an arbitrary number of web-service instances. To that end, database
contains the docker-definitions for getting the data store up and running, webapp is the
service that uses the data to answer a variety of vulnerability-related questions, and
reposcan is an example of a plugin whose job is to fill the datastore with vulnerability
information.
VMaaS is NOT intended to be an inventory-management system. It doesn't 'remember' system profiles or containers, or manage inventory workflow in any way. An inventory-management system could use VMaaS as one source of 'health' information for the entities being managed.
docker-compose up # Build images and start containers
docker-compose down # Stop and remove containers (built images will persist)
docker-compose down -v # Stop and remove containers and database data volume (built images will persist)docker-compose buildAll at once
docker-compose start
docker-compose stopSingle service
docker-compose start vmaas_database
docker-compose stop vmaas_databaseYou can run all tests from scratch just after cloning repo using command:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.test.yml up --build --abort-on-container-exitYou can build and start your container in "developer mode". You can tune metrics using Prometheus and Grafana dev containers, see doc/metrics.md.
oc project vmaas-stage
# Dump database
oc exec -c vmaas-reposcan-service $(oc get pod -l pod=vmaas-reposcan-service --no-headers -o custom-columns=:metadata.name) -- bash -c 'PGPASSWORD=vmaas_writer_pwd pg_dump -h $(python3 -c "import app_common_python as a;print(a.LoadedConfig.database.hostname)") -U vmaas_writer vmaas | gzip > /data/pgdump.sql.gz'
# Download database dump
oc port-forward $(oc get pod -l pod=vmaas-reposcan-service --no-headers -o custom-columns=:metadata.name) 10000:10000
curl http://localhost:10000/pgdump.sql.gz > /tmp/pgdump.sql.gz
# Populate local database
docker-compose up -d
docker-compose exec vmaas_database psql -U vmaas_admin postgres -c "drop database vmaas"
docker-compose exec vmaas_database psql -U vmaas_admin postgres -c "create database vmaas"
cat /tmp/pgdump.sql.gz | gzip -d | docker-compose exec -T vmaas_database psql -U vmaas_admin vmaas
# Generate new webapp sqlite dump
./scripts/turnpike-mock curl -X PUT http://localhost:8081/api/v1/export/dumpWebapp-go can be profiled using /net/http/pprof. Profiler is exposed on app's private port.
- set
ENABLE_PROFILE=truein theconf/common.env docker-compose up --buildgo tool pprof http://localhost:9000/debug/pprof/{heap|profile|block|mutex}
- set
ENABLE_PROFILE=truein the ClowdApp - download the profile file using internal api
/api/vmaas/v1/pprof/{heap|profile|block|mutex|trace} go tool pprof <saved.file>