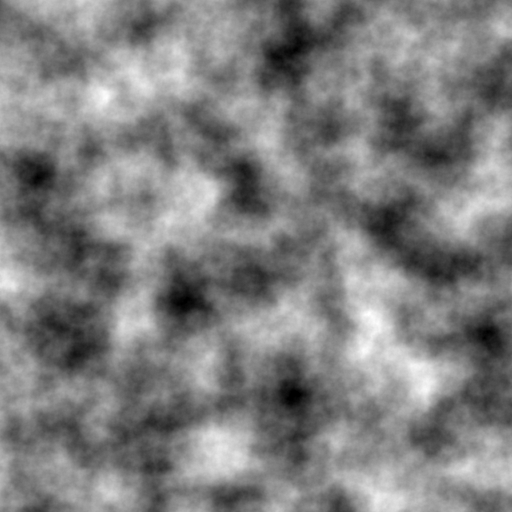
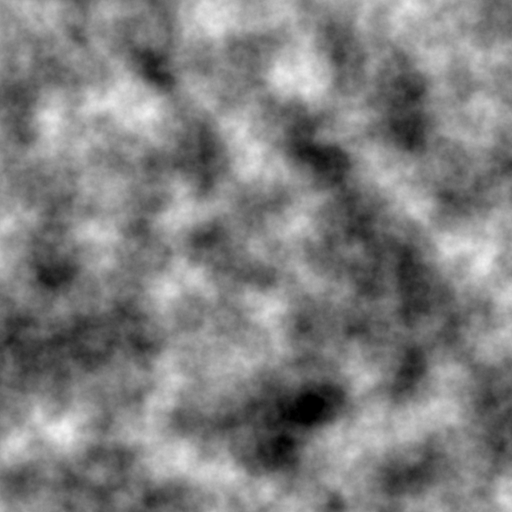
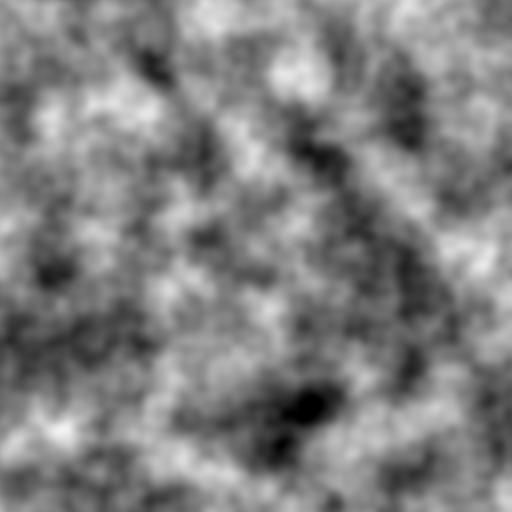
siv::PerlinNoise is a header-only Perlin noise library for modern C++ (C++17/20).
The implementation is based on Ken Perlin's Improved Noise.
- 1D / 2D / 3D noise
- octave noise
- initial seed
- (✨ new in v3.0) produce the same output on any platform (except for floating point errors)
siv::PerlinNoise is distributed under the MIT license.
# include <iostream>
# include "PerlinNoise.hpp"
int main()
{
const siv::PerlinNoise::seed_type seed = 123456u;
const siv::PerlinNoise perlin{ seed };
for (int y = 0; y < 5; ++y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < 5; ++x)
{
const double noise = perlin.octave2D_01((x * 0.01), (y * 0.01), 4);
std::cout << noise << '\t';
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
}- Typedefs
using PerlinNoise = BasicPerlinNoise<double>;using state_type = std::array<std::uint8_t, 256>;using value_type = Float;using default_random_engine = std::mt19937;using seed_type = typename default_random_engine::result_type;
- Constructors
constexpr BasicPerlinNoise();BasicPerlinNoise(seed_type seed);BasicPerlinNoise(URBG&& urbg);
- Reseed
void reseed(seed_type seed);void reseed(URBG&& urbg);
- Serialization
constexpr const state_type& serialize() const noexcept;constexpr void deserialize(const state_type& state) noexcept;
- Noise (The result is in the range [-1, 1])
value_type noise1D(value_type x) const noexcept;value_type noise2D(value_type x, value_type y) const noexcept;value_type noise3D(value_type x, value_type y, value_type z) const noexcept;
- Noise (The result is remapped to the range [0, 1])
value_type noise1D_01(value_type x) const noexcept;value_type noise2D_01(value_type x, value_type y) const noexcept;value_type noise3D_01(value_type x, value_type y, value_type z) const noexcept;
- Octave noise (The result can be out of the range [-1, 1])
value_type octave1D(value_type x, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type octave2D(value_type x, value_type y, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type octave3D(value_type x, value_type y, value_type z, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;
- Octave noise (The result is clamped to the range [-1, 1])
value_type octave1D_11(value_type x, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type octave2D_11(value_type x, value_type y, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type octave3D_11(value_type x, value_type y, value_type z, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;
- Octave noise (The result is clamped and remapped to the range [0, 1])
value_type octave1D_01(value_type x, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type octave2D_01(value_type x, value_type y, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type octave3D_01(value_type x, value_type y, value_type z, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;
- Octave noise (The result is normalized to the range [-1, 1])
value_type normalizedOctave1D(value_type x, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type normalizedOctave2D(value_type x, value_type y, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type normalizedOctave3D(value_type x, value_type y, value_type z, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;
- Octave noise (The result is normalized and remapped to the range [0, 1])
value_type normalizedOctave1D_01(value_type x, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type normalizedOctave2D_01(value_type x, value_type y, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;value_type normalizedOctave3D_01(value_type x, value_type y, value_type z, std::int32_t octaves, value_type persistence = value_type(0.5)) const noexcept;
Run example.cpp with the following parameters.
frequency = 8.0
octaves = 8
seed = 12345
frequency = 8.0
octaves = 8
seed = 23456
frequency = 8.0
octaves = 3
seed = 23456