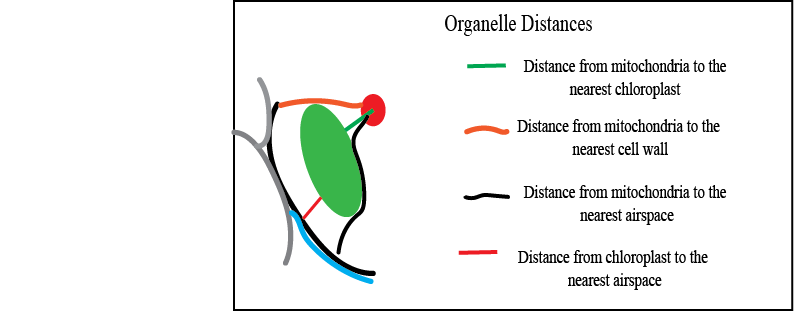
The "Call Organelle Script" will call each distance script and run fro each smample (that is all 9 cells)- it gets The distance from chl to mit The distance from cw mit The distance from air to mit The distance from chl to air
As described in Harwood et al., (2020) https://nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/nph.16219 we imaged 3 different chickpea genotypes with serial block face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM). We furthered our previous work by segmenting the mitochondria and measuring mesophylly conductance (gm) at 21% and 2% Oxygen.
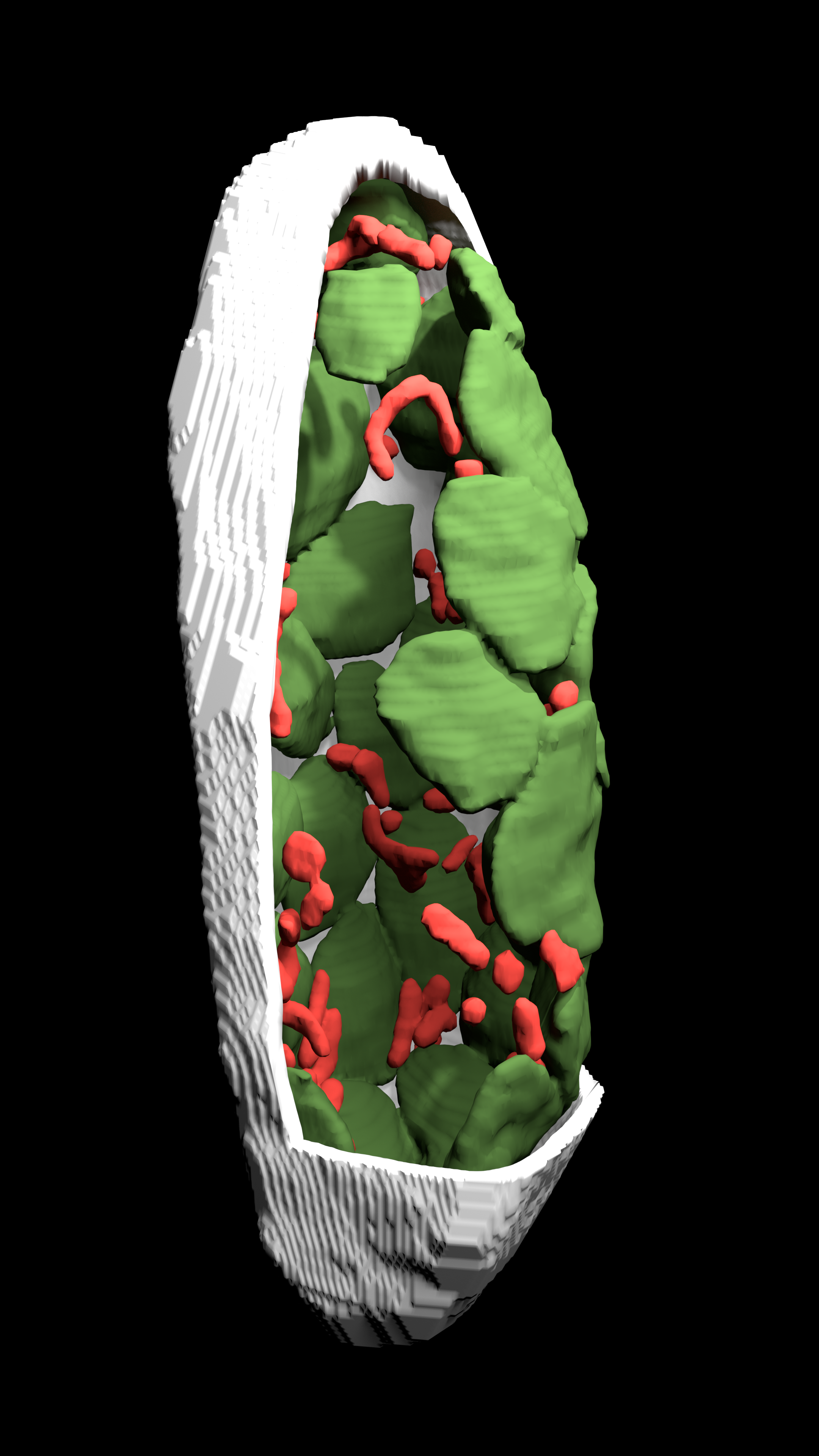
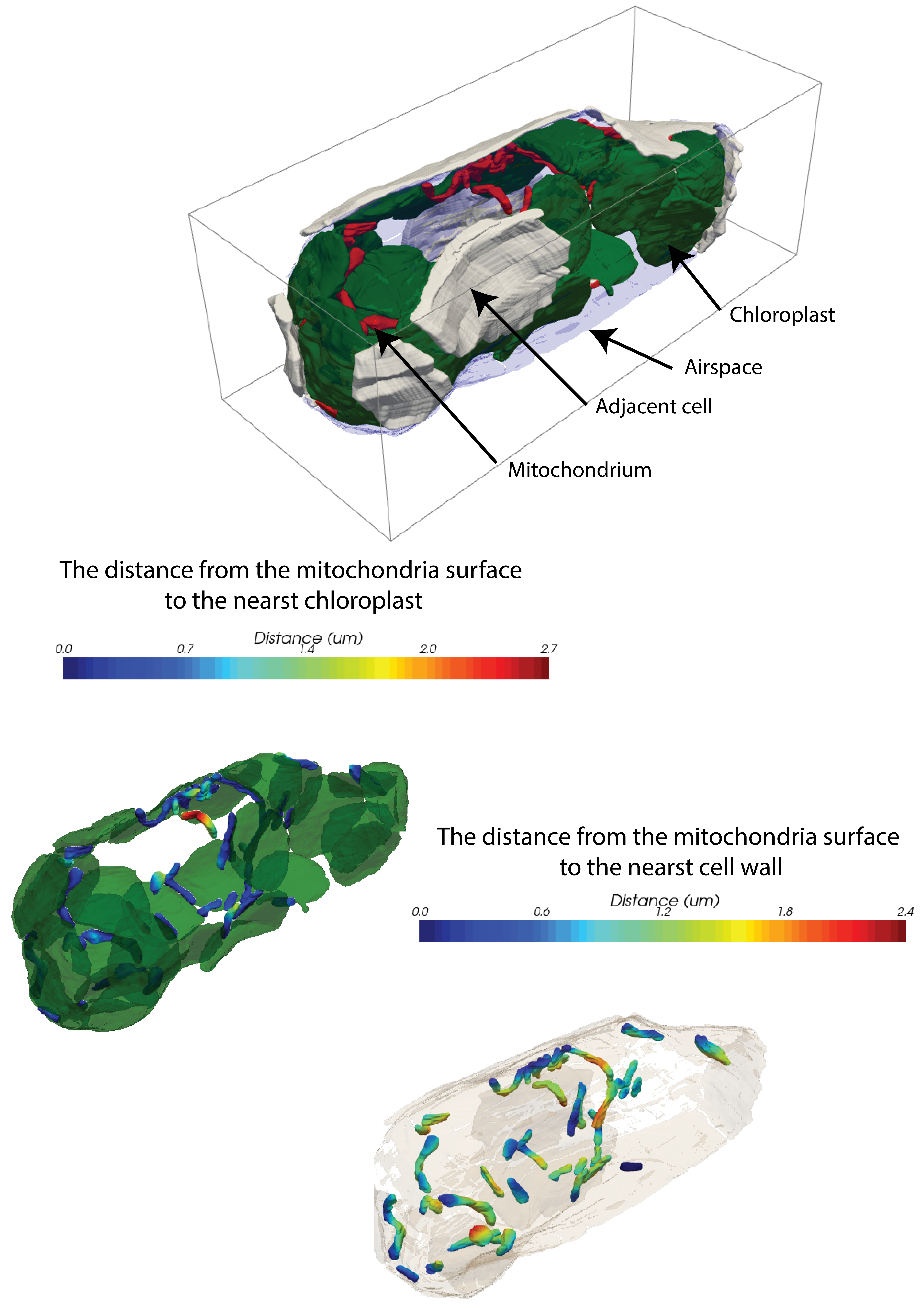
Here is what a chickpea mesophyll cell looks like (chloroplasts are green, mitochondria are red and the cell wall is white)
Mesophyll conductance (gm) refers to the passage of CO2 as a gas and a liquid from the sub-stomatal airspace to the site of carboxylation inside the chloroplast. gm is influenced by aquaporins, carbonic anhydrase and leaf anatomy. An important part of understanding gm is quantifying the role respiration and photorespiration has. Estimates of gm are influenced by the amount of respiratory and photorespiratory CO2 released from the mitochondria diffusing towards the chloroplasts the ratio of recapture vs leakage to the atmosphere is not uniform across species and likely related to the position of the mitochondria, the surface are area of mesophyll exposed to the airspace and the surface area of chloroplast exposed to the airspace.
We take the 3D images/models and calculate a suite of distance metrics
The images are broken down into 5 different "parts" and loaded into Python as follows
Start by loading packages
import numpy as np
import os
from scipy.ndimage.morphology import distance_transform_edt, binary_erosion
import skfmm
import imageio
import skimage.io as io
from skimage import img_as_ubyte, img_as_bool, img_as_float32
from skimage.util import invert
from skimage.measure import label, regionprops, marching_cubes_lewiner, mesh_surface_area
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
from scipy.ndimage import zoom
import gcWe then define two functions - one to "erode" surfaces to create outlines and one to threshold specific gray scale values
def Erosion3DimJ(input_img):
tmp = np.zeros(input_img.shape)
for i in range(input_img.shape[0]):
tmp[i, :, :] = binary_erosion(input_img[i, :, :])
return tmp
def Threshold(input_img, Th_value):
tmp = np.zeros(input_img.shape, dtype=np.bool)
if isinstance(Th_value, int):
tmp[input_img == Th_value] = 1
else:
if isinstance(Th_value, float):
tmp[input_img > 0. & input_img < 1.] = 1
else:
for th_val in range(len(Th_value)):
tmp[input_img == Th_value[th_val]] = 1
return tmpWe then set file locations and names of tiffs (This is all automated later from a master scipt)
image_dir = 'Z:/ALLTIFS3DMIT/';sample="D2C1_"
import runpy;import os;os.chdir('C:/Users/Richard/Desktop/Organelles/OrganelleScripts/')
chl_name='D2C1CHL.tif';mit_name='D2C1MIT.tif';cell_w_org_name="D2C1VAC.tif"
cell_name="D2C1CELL.tif";air_name="D2C1AIR.tif"Now we set voxel dimensions
voxel_dims = [0.05,0.04,0.04] Load in chloroplast images
chl=io.imread(image_dir + chl_name)
chl=zoom(chl, (1, 0.5, 0.5)) #This is the same as Image > adjust >size in FIJI
chl[chl==0] = 0
chl[chl==1] = 255
chl=img_as_bool(chl)
plt.imshow(chl[400])Load in air images
air=io.imread(image_dir + air_name)
air=zoom(air, (1, 0.5, 0.5)) #This is the same as Image > adjust >size in FIJI
air[air==0] = 0
air[air==1] = 255
air=img_as_bool(air)
io.imshow(air[400])mito = io.imread(image_dir + mit_name)
mito=zoom(mito, (1, 0.5, 0.5))
mito[mito==0] = 0
mito[mito==1] = 255
plt.imshow(mito[400])
mito=img_as_bool(mito)These are the images we need for this calculation To make the simulation run we need a chl +mit image (these are the "obstructions" in the cell)
chl_mito = chl + mitoThe technique used here gets a distance value for every voxel, but we are only intersted in teh mitochondria edge, so lets extract that:
mito_outline_smaller = Erosion3DimJ(invert(mito))
mito_edge = invert(Threshold(invert(mito)-mito_outline_smaller, 0))
mito_edge[0,:,:] = False
mito_edge[-1,:,:] = False
mito_edge[:,0,:] = False
mito_edge[:,-1,:] = False
mito_edge[:,:,0] = False
mito_edge[:,:,-1] = False
del mito_outline_smaller
plt.imshow(mito_edge[400])We now create an array which will have the start point (the air) and the obstructions (chl +mit)
air_masked_array = np.ma.masked_array(invert(air), chl_mito)We then get the distance for every voxel in the 3D image stack
D_geo_from_air = skfmm.distance(air_masked_array, dx=voxel_dims)Then we extract the values at the mitochndria edge
L_geo_edge_air_mit = np.asarray(D_geo_from_air[(mito_edge == True)])Then we export these values as a .CSV
np.savetxt(sample+"L_geo_edge_air_mit.csv", L_geo_edge_air_mit, delimiter=",")