Authors: Jonathan Kim and Stefan Bekiranov
Adapted from work authored by Maria Schuld and Aroosa Ijaz
Correspondence: sb3de@virginia.edu
The code in this repository can be used to demonstrate the generalization performance of 'quantum metric learning' classifiers. Quantum metric learning is first introduced in Lloyd, Schuld, Ijaz, Izaac, Killoran (2020) and is used to train a quantum embedding, which can be used for classifying data. Quantum embeddings are learned by maximizing Hilbert-Schmidt distances of datapoints from two classes. After training, datapoints of different classes become maximally separated in Hilbert space. This results in a simple linear decision boundary in Hilbert space which represents a complex decision boundary in the original feature space.
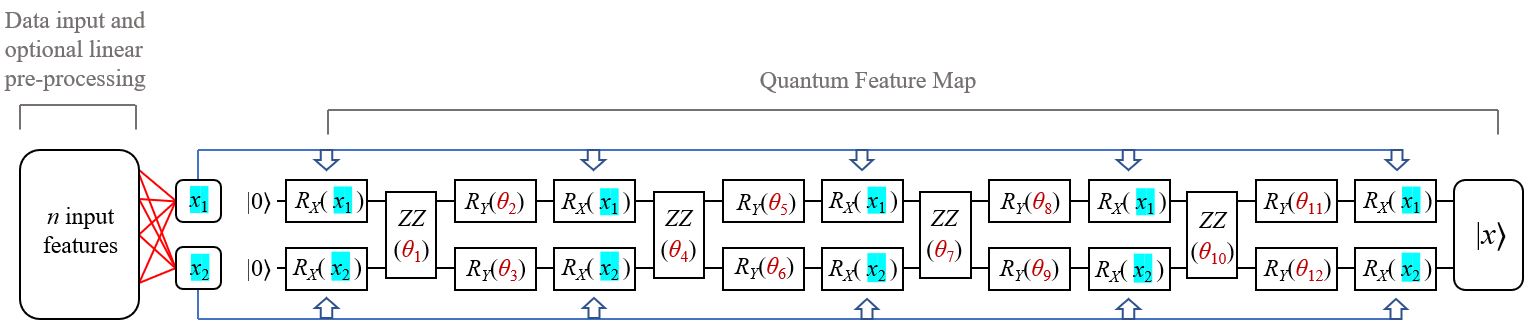
Below is the general form of a quantum metric learning circuit:
The circuit takes classical inputs parameters, x1 and x2, alongside 'quantum' parameters denoted by
With the code in this repository, the effects of varying the number of input parameters through different datasets and dimensional reduction methods can be explored. Precision, recall and F1 scores are used alongside training cost & test cost to assess how well each trained model generalizes for test data. More details on this topic can be found in the research paper, Generalization Performance of Quantum Metric Learning Classifiers.
=======================================================
The resulting models are used to classify breast cancer data and ant/bee image data.
-
The breast cancer data comes from the UCI ML Breast Cancer (Diagnostic) Dataset and each sample can be classified as either 'benign' or 'malignant'.
-
The ant/bee image data comes from the ImageNet Hymenoptera dataset and each image can be classified as either 'ant' or 'bee'.
Data preparation files and resulting txt files can be found in the embedding_metric_learning folder.
The tutorial_embedding_generalization_antbee_original.py file can be run after running the antsbees_original.py data preparation file to produce results similar to those seen in Lloyd et al.'s 2020 work, "Quantum Embeddings for Machine Learning". Hilbert space mutual data overlap gram matrices and intermediary scatter plots are produced when tutorial_embedding_generalization_antbee_original.py is run. Resulting test set precision, recall and F1 scores are also returned.
The tutorial_embedding_generalization_antbee_pca.py file can be run after running the antsbees_general.py data preparation file (starting from 512 classical input features) or the antsbees_general_noresnet.py data preparation file (starting from 150528 classical input features) when applying PCA to the classical input to the circuit. Hilbert space mutual data overlap gram matrices and intermediary scatter plots are produced when tutorial_embedding_generalization_antbee_pca.py is run. Resulting test set precision, recall and F1 scores are also returned.
The tutorial_embedding_generalization.py file can be run after running the cancer_general.py data preparation file (which includes a PCA step) or the cancer_non-PCA.py data preparation file (which does not include a PCA step) to classify breast cancer data. Hilbert space mutual data overlap gram matrices and intermediary scatter plots are produced when tutorial_embedding_generalization.py is run. Resulting test set precision, recall and F1 scores are also returned.
By running the above files, it can be seen in the resulting outputs that:
- Quantum Metric Learning cannot generalize well for test data when using a dataset with too many initial features relative to the number of training samples (e.g., the ants/bees image dataset).
- Quantum Metric Learning results in good classification for datasets that have a much greater number of training samples than the intial number of parameters (e.g., the breast cancer diagnostic dataset).
- PCA can help improve generalizability and classification performance when applied to the initial input features of a dataset.
References: Seth Lloyd, Maria Schuld, Aroosa Ijaz, Josh Izaac, Nathan Killoran: "Quantum embeddings for machine learning" arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.03622.
Andrea Mari, Thomas R. Bromley, Josh Izaac, Maria Schuld, Nathan Killoran: "Transfer learning in hybrid classical-quantum neural networks" arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.08278.
Jonathan Kim and Stefan Bekiranov: "Generalization performance of quantum metric learning classifiers", https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111576.