@INPROCEEDINGS{8272792,
author={Rocchetta, Roberto and Patelli, Edoardo},
booktitle={2017 2nd International Conference on System Reliability and Safety (ICSRS)},
title={Stochastic analysis and reliability-cost optimization of distributed generators and air source heat pumps},
year={2017},
volume={},
number={},
pages={31-35},
doi={10.1109/ICSRS.2017.8272792}}[]R. Rocchetta and E. Patelli, "Stochastic analysis and reliability-cost optimization of distributed generators and air source heat pumps," 2017 2nd International Conference on System Reliability and Safety (ICSRS), 2017, pp. 31-35, doi: 10.1109/ICSRS.2017.8272792.
[] X. Liu, J. Wu, N. Jenkins and A. Bagdanavicius, "Combined analysis of electricity and heat networks", Applied Energy, vol. 162, pp. 1238-1250, 2016.
MC_HP.m : power production model for multi-compressor Air-to-Water HPs ;
OnOff_HP.m : power production model for the On-Off Air-to_Water Heat Pumps model Maneurop SH 140-4 ;
HPP.m: sample from homogeneous Poisson Process HPP;
MarkovFailure.m : randomize failures of the network components;
MC_HEATPOWER(X, D) : Monte Carlo simulation of the combined grid X= allocation matrix D=data structure for the combined grid;
D.mat data structure containing;
Del data for the electrical grid;
Dth data for the thermal grid ;
Weather : data to simulate the weather conditions;
DG_module.m : This class simulate the power production behaviour of different types (PV, EV, ST, WT, HP) of distributed generators;
Weather_Simulator.m : simulates weather conditions on the power grid given geo-location and day of the year (wind speed, irradiance, lightning strike density;
PowEl2PowTh.m : function converting electrical power to thermal power;
OPF.m : Optimal power flow function considering virtual generators;
Clear_Sky_IT : Compute clear sky irradiance
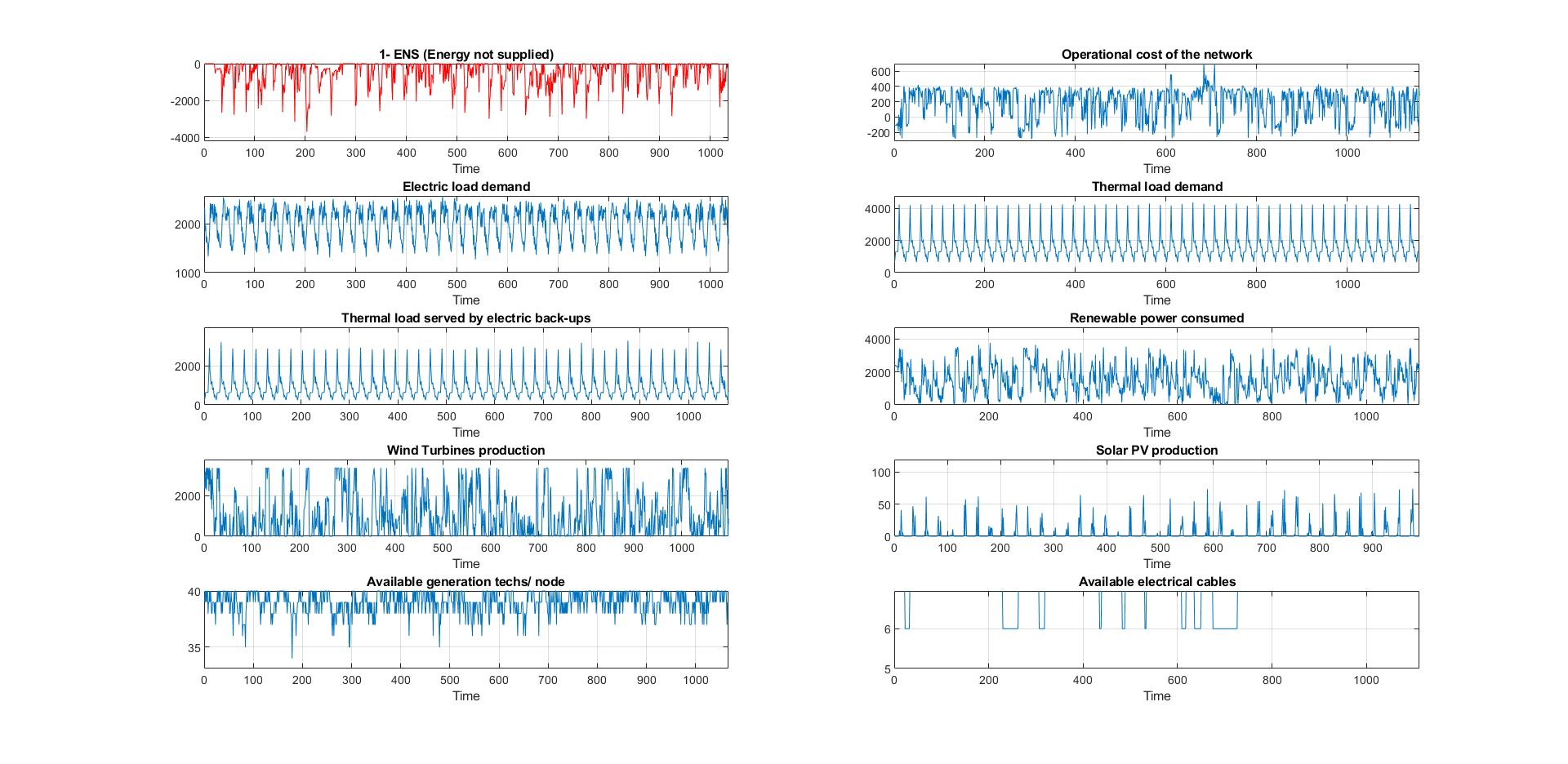
Example1_MonteCarlo.m : an example of reliability/resilience assessment (energy not suppllied distribution) by the combined heat and electric power grid. Carried out via Monte Carlo simulation for an allocation matrix;
Data_intro_ElectricThermal_NetworkBarryIsalnd.m : step-by-step description of the combined grid data and economic dispatch simulation;
Temp=load('D.mat'); % load data
D = Temp.D; # all data in the structure D
Del= Temp.D.Del; % electrical grid data
Dth= Temp.D.Dth; % thermal grid data
Wtr= Temp.D.Weather; % weather data
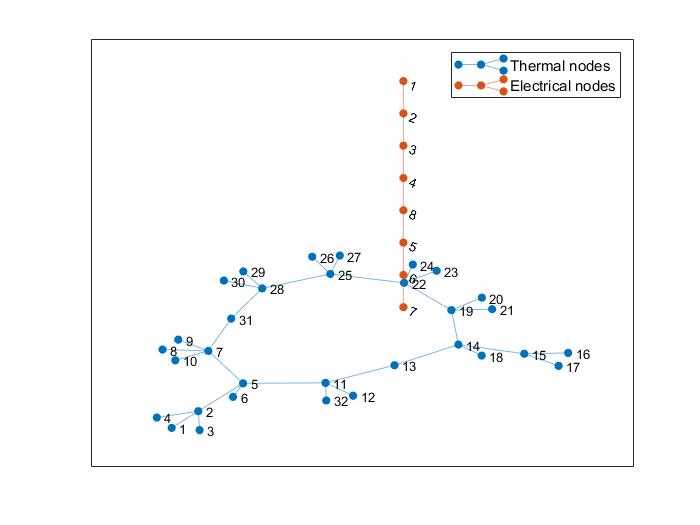
%% show topology of the two networks (not linked and separatelly)
figure(10)
G_th=graph(D.Dth.From_Node,D.Dth.To_Node);
G_th.plot;
hold on; grid on
G_el=graph(D.Del.FDks,D.Del.FDke);
G_el.plot
legend('Thermal nodes', 'Electrical nodes')
% electrical allocation matrix
% MS PV WT EV ST
x_el=[0,11, 0,0,13 % node 1
1, 0,11,0, 1 % node 2
0,11,23,0,10 % node 3
0, 0,11,0,21 % node 4
0,11, 0,0,11 % node 5
0, 0, 0,0, 2 % node 6
1,11,11,0, 0 % node 7
1,11,11,0,11]; % node 8
x_th = [5 % node 1
0 % node 2
0 % node 3
0 % node 4
0 % node 5
14 % node 6
0 % node 7
0]; % node 8
Xnom= [x_el x_th];
% Run MC simulation for data structure D and thermal-eletrical allocation Xnom
[RES] = MC_HEATPOWER(Xnom,D);