lmt is a cli program written in go that can be used to run applications with resource limits enforced using cgroupsv2
This program works only on linux and requires cgroupsv2 support. Most newer linux distros already come with cgroupsv2 installed and enabled by default.
The following distributions are known to use cgroup v2 by default:
- Fedora (since 31)
- Arch Linux (since April 2021)
- openSUSE Tumbleweed (since c. 2021)
- Debian GNU/Linux (since 11)
- Ubuntu (since 21.10)
- RHEL and RHEL-like distributions (since 9)
On other systemd-based distros, cgroup v2 can be enabled by adding systemd.unified_cgroup_hierarchy=1 to the kernel cmdline.
You can check if its enabled and mounted using the following command:
mount | grep -q 'cgroup2' && echo "cgroupsv2 hierarchy is mounted" || echo "cgroupsv2 hierarchy is NOT mounted"
Make sure go is installed and $HOME/go/bin is in your path, then run
go install "github.com/Rohansjamadagni/lmt@latest"
Usage:
lmt run [flags] <program>
Flags:
-c, --cpu-limit int8 Percentage of cpu to limit the process to [0-100] (default 100)
-h, --help help for run
-m, --mem-limit float Set memory limit in MB (default 0 [no limit])
-n, --num-cores int8 Number of cores to allow the process to use (default [nproc])
Usage:
lmt ps [flags]
Flags:
-h, --help help for ps
-w, --watch watch command output
Change the cgroup resource limits of a container
Usage:
lmt set ctr id [flags]
Flags:
-c, --cpu-limit int8 Percentage of cpu to limit the process to (default 100)
-h, --help help for ctr
-m, --mem-limit float Set memory limit in MB
-n, --num-cores int8 Number of cores to allow the process to use (default 16)
-p, --podman Use with podman containers (default false)
-r, --rootless Manually set rootless might be needed inside a container (default true)
Tries to change the limits of an existing container with the desired limits. It may fail if you set the limits too low since it may conflict with what podman/docker sets as a minimum. The id is the container's partial/full hash, which is seen in the id field when you run "docker ps or podman ps".
Note:
- For docker containers command must be run as root.
- The container must be running for the command to work.
- To unset limits just run set without any flags -
lmt set ctr id- for docker andlmt set ctr -p idfor podman
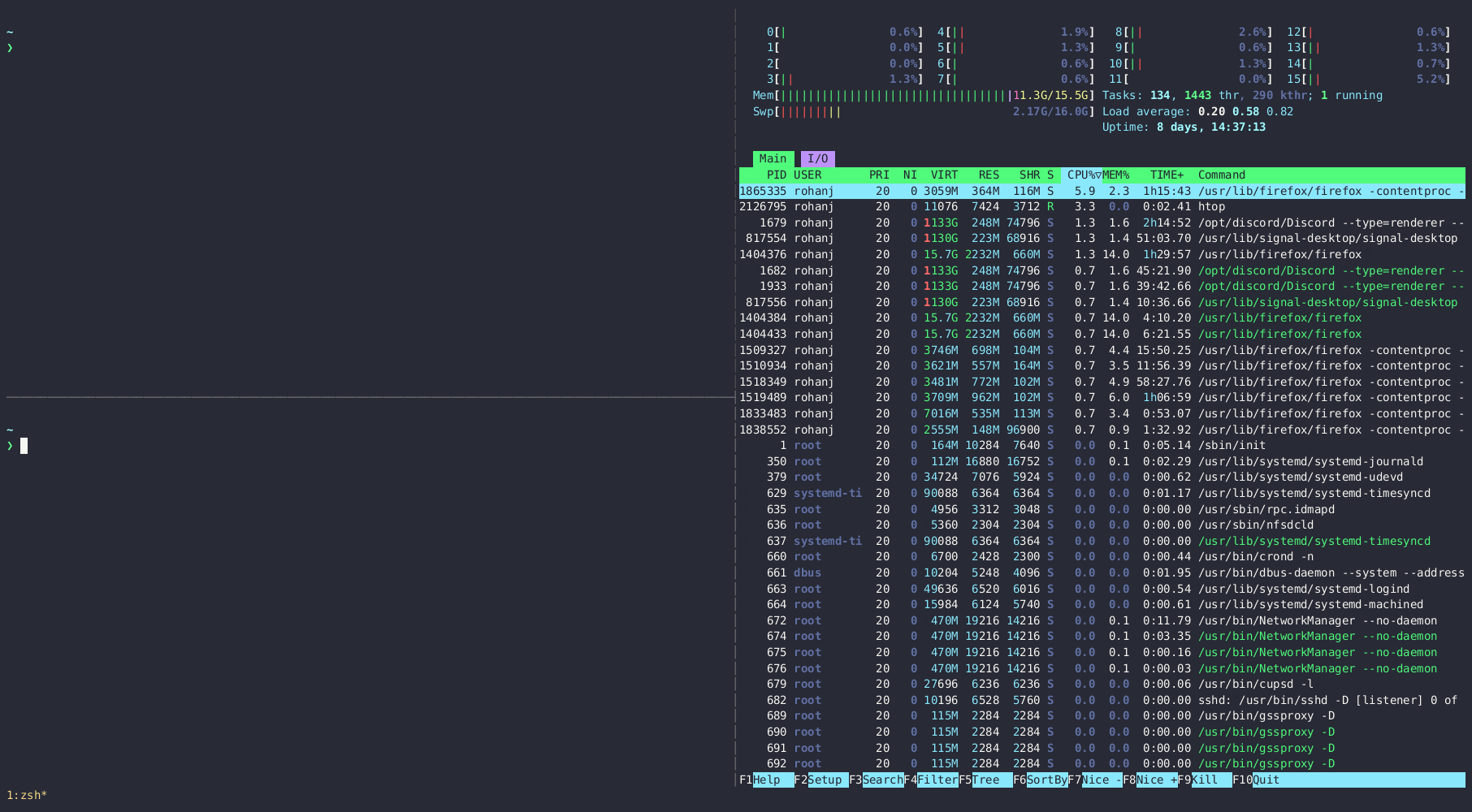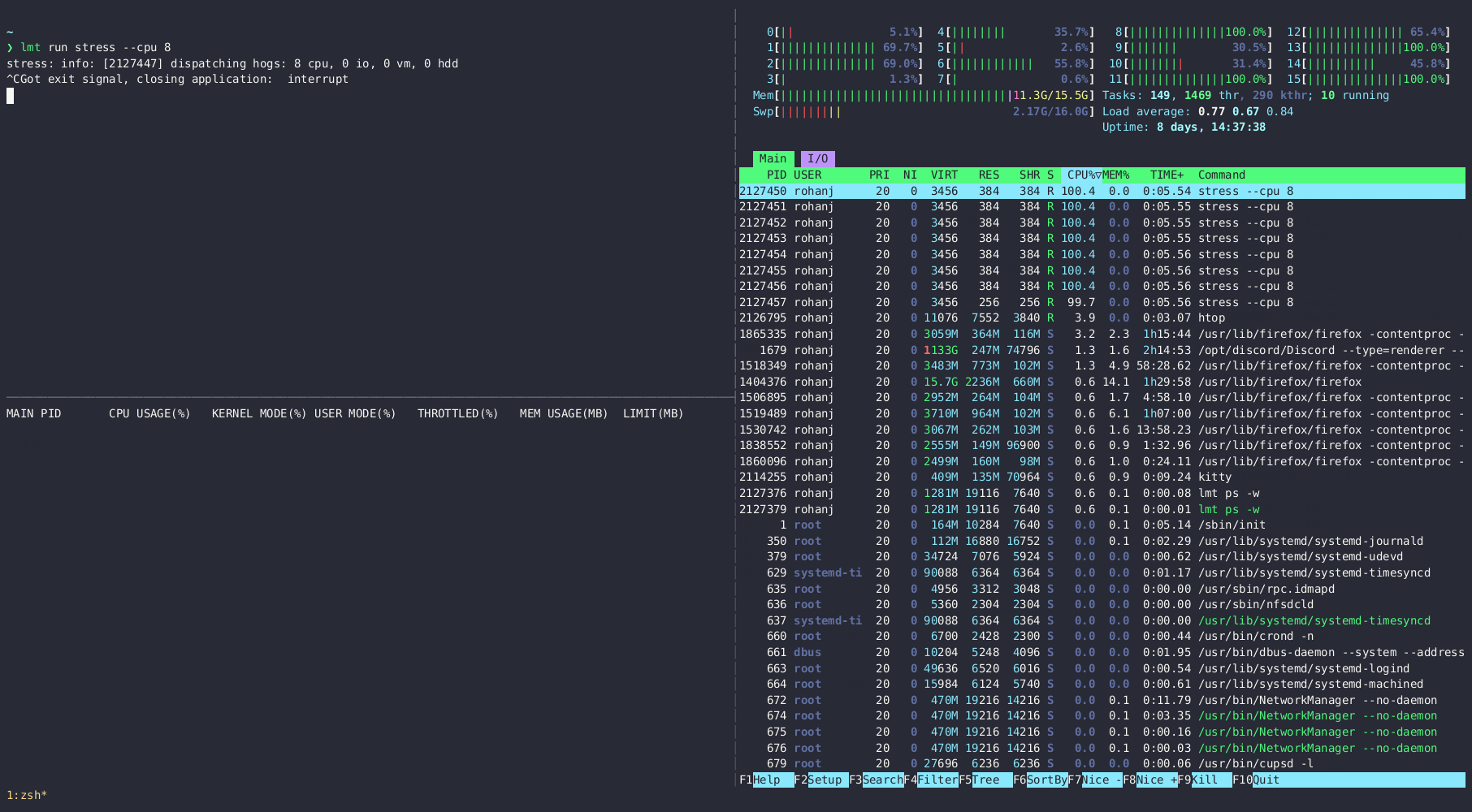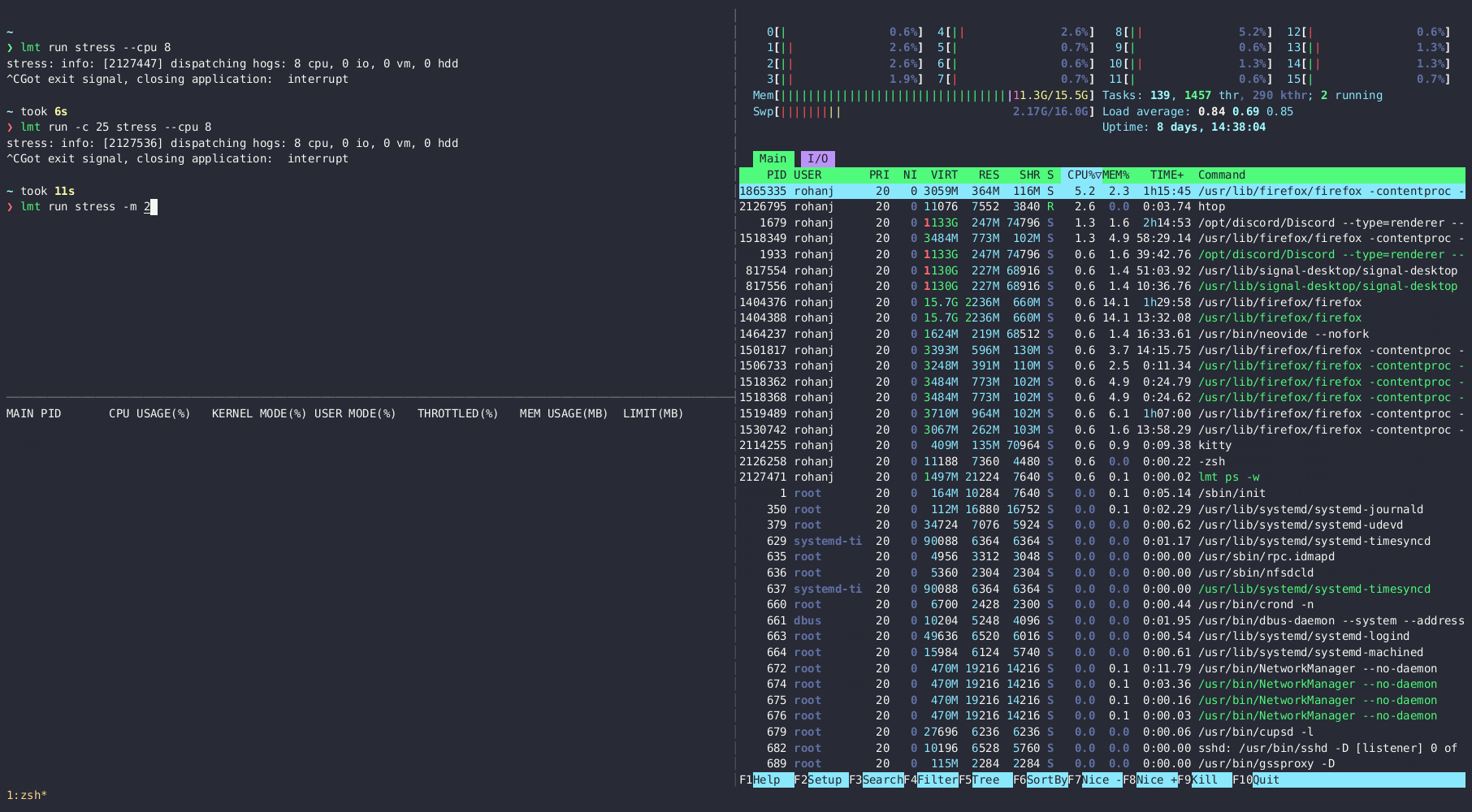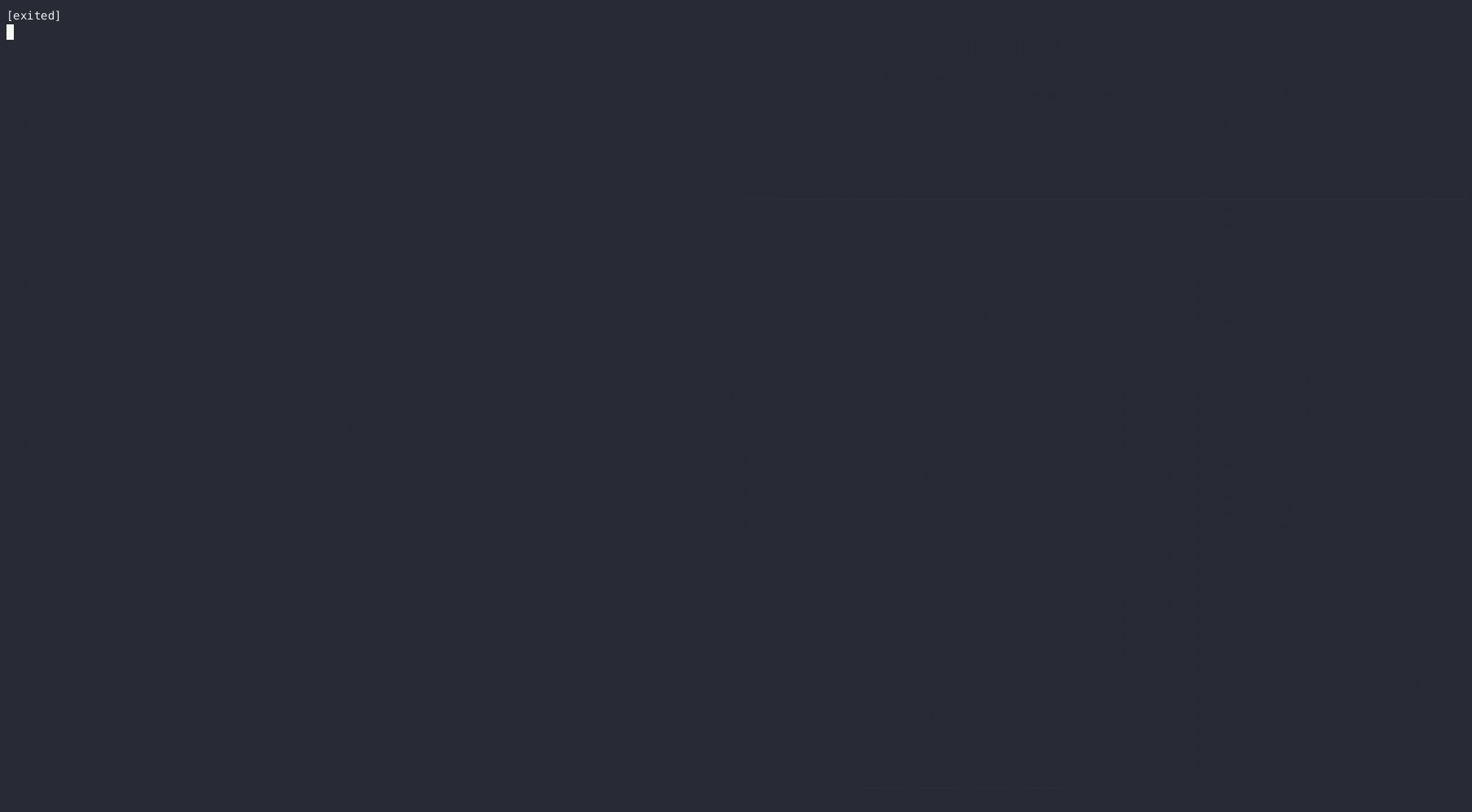
lmt run -m 500 firefox
Note: Interactive TUI apps are a bit tricky to handle, so as a workaround launch a tmux session (or even a new terminal session) with the desired limits and run applications from there.
It also can't be used inside containers in root or rootless mode because I'm using some systemd libraries to create and manage cgroups. However, I'm working on writing my own cgroup manager that would work inside containers and non-systemd distros.
lmt set ctr -m 100 7f
Gives a live view of the resources used by programs run with lmt.
lmt ps
lmt ps -w