This project aims to process radar data files, convert them into GeoTIFF format, and subsequently convert these GeoTIFF files into ASCII format for the Texas state boundary. The project involves three main steps: downloading radar data, selecting appropriate data, and converting the data to the desired formats.
- Operating System: Windows
- Software:
- R and RStudio
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
- WCT Tool (
wct-4.2.0-win32)
The directory structure for this project is as follows:
/working-directory
/RadarData_to_Tiff_to_ASC.R
/wctBatchConfig_updated.xml
/Texas_State_Boundary/
Texas_State_Boundary.shp
Texas_State_Boundary.dbf
Texas_State_Boundary.prj
Texas_State_Boundary.shx
/wct-4.2.0-win32/
wct.exe
other necessary files
/RAW DATA/
/2021/
radar_data_files
/2022/
radar_data_files
/2023/
radar_data_files
/OUTPUT/
-
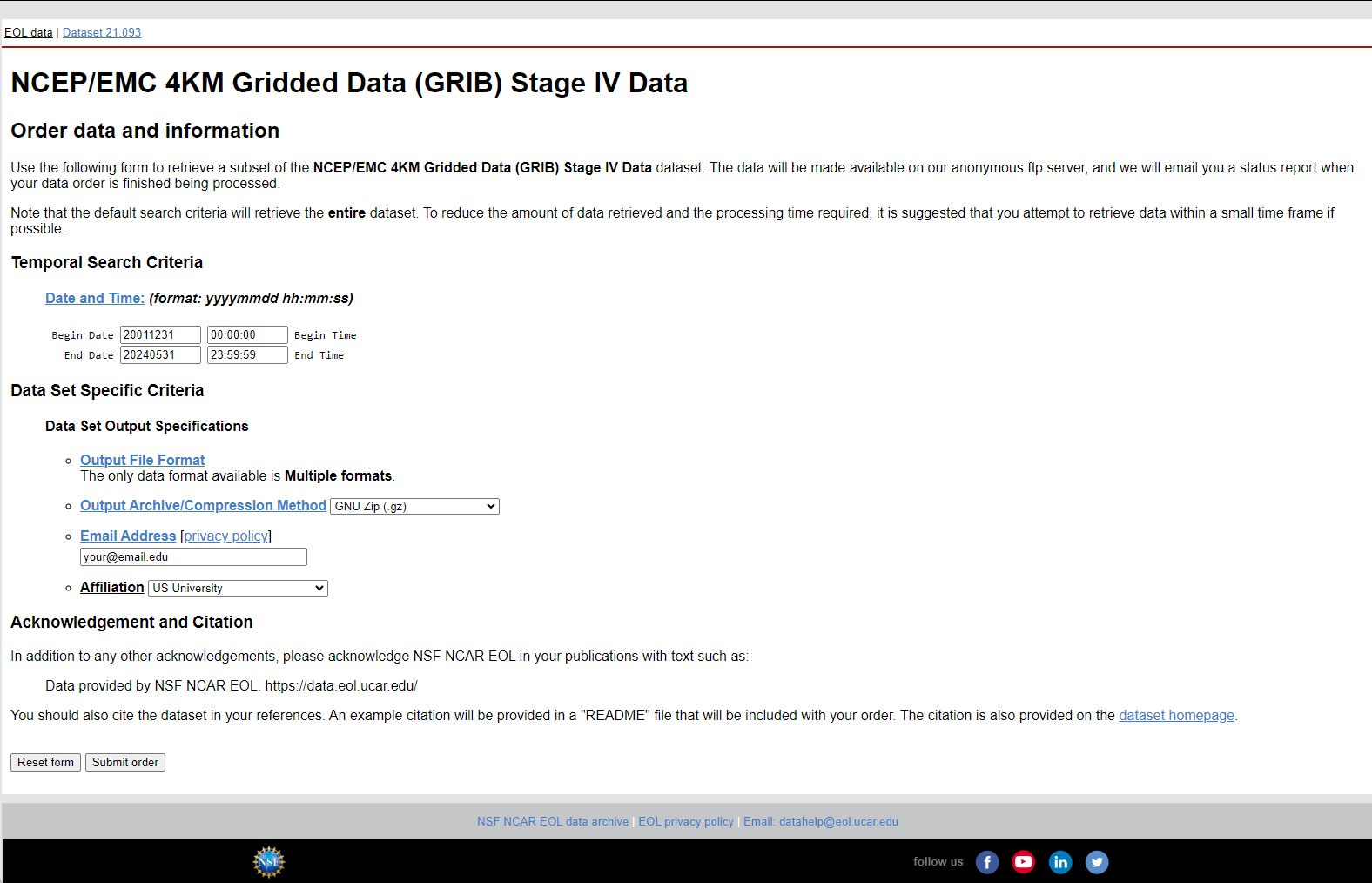
Access the Website: Go to the NSF NCAR EOL Data Archive.
-
Select Date Range:
- Begin Date: Set the start date for the data you need.
- End Date: Set the end date for the data you need. Note that you can only request up to 3 months of data per order and up to 4 years of data per day.
-
Specify Output Options:
- Output Archive/Compression Method: Select
GNU Zip (.gz). - Email Address: Enter your email address.
- Affiliation: Select your affiliation from the dropdown menu.
- Output Archive/Compression Method: Select
-
Submit the Order: Click the "Submit order" button to request the data.
After submitting your data request, you will receive an email with download instructions. Use the provided FTP details to download the data using the wget command:
wget -rc -nH --cut-dirs=3 --no-netrc --ftp-user=anonymous ftp://data.eol.ucar.edu/pub/download/data/your_directory/After downloading the data, use the provided Python script copyTargetFiles.py to select files with the required frequency and accumulate them into a single folder. The put the year-wise folders into the 'RAW DATA' folder.
import os
import shutil
import re
def copyTargetFiles(source_folders, destination_folder):
"""
Copies files matching a specific naming convention from multiple source folders to a destination folder.
This function searches through the specified source folders for files that match the naming
convention 'st4_conus.2023MMDDHH.01h.grb2.gz' where '2023MMDDHH' is any valid date and hour of 2023.
Matched files are then copied to the destination folder.
Parameters:
- source_folders (list of str): List of source folder paths to search for files.
- destination_folder (str): Path to the destination folder where matched files will be copied.
Example Usage:
--------------
source_folders = ['A', 'B', 'C']
destination_folder = 'F'
copyTargetFiles(source_folders, destination_folder)
"""
# Create the destination folder if it doesn't exist
if not os.path.exists(destination_folder):
os.makedirs(destination_folder)
# Define the regex pattern for the naming convention
pattern = re.compile(r'^st4_conus\.2023\d{6}\.01h\.grb2\.gz$')
# Iterate over each source folder
for folder in source_folders:
print(f"Checking folder: {folder}")
for filename in os.listdir(folder):
print(f"Found file: {filename}")
if pattern.match(filename):
print(f"Matched file: {filename}")
# Construct the full file paths
source_file = os.path.join(folder, filename)
destination_file = os.path.join(destination_folder, filename)
print(f"Copying from {source_file} to {destination_file}")
# Copy the file to the destination folder
shutil.copy2(source_file, destination_file)
print("Files copied successfully.")
# Example usage
copyTargetFiles(['mahbu1141503', 'Mahbu1149534', 'Mahbu1224557', 'Mahbu1267555'], '2023')The provided script converts radar data files into GeoTIFF format and subsequently into ASCII format for the Texas state boundary.
Install the necessary packages in R:
install.packages(c("raster", "rgdal", "XML", "data.table", "parallel", "doSNOW", "dplyr", "tools", "future", "furrr", "purrr"))Ensure you have Java installed on your system. Download it from the Official Java website.
Ensure to download the WCT tool from the NOAA Weather and Climate Toolkit page (Please unzip the wct-4.2.0-win32.zip file). Download it from the Official NOAA NCEI download page.
The wct-4.2.0-win32 folder should contain all necessary files, including wct.exe. Verify the installation by running wct.exe:
- Navigate to the
wct-4.2.0-win32directory in your command prompt. - Execute the
wct.exefile to check if it runs without errors.
Open RStudio, set the working directory to the folder containing the script, and run the RadarData_to_Tiff_to_ASC.R script.
setwd("path/to/working/directory")
source("RadarData_to_Tiff_to_ASC.R")This project involves downloading radar data, selecting appropriate files, and converting them to GeoTIFF and ASCII formats. Ensure all necessary tools and packages are installed, and follow the steps outlined to complete the data processing.