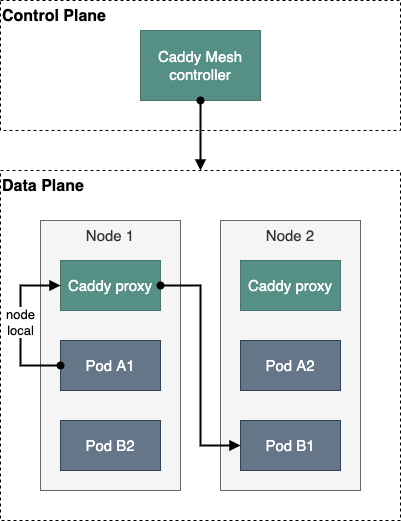
Caddy service mesh based on the host/node architecture.
- Timeouts
- Retries
- Circuit Breaking
- Rate Limiting
- Traffic Splitting
Build the image for Caddy Mesh controller:
$ make build-image tag=v0.1.0If using any plugins, you need to build the Caddy image locally:
$ make build-caddy-image tag=2.6.0-beta.3-custom$ make helm-installAll features provided by Caddy Mesh can be enabled by using annotations on Kubernetes services.
Timeouts can be enabled by using the following annotations:
mesh.caddyserver.com/timeout-dial-timeout: "<duration>"
mesh.caddyserver.com/timeout-read-timeout: "<duration>"
mesh.caddyserver.com/timeout-write-timeout: "<duration>"
Parameters:
timeout-dial-timeout: How long to wait before timing out trying to connect to an upstream. Default:3s. (See dial_timeout.)timeout-read-timeout: The maximum time to wait for next read from backend. Default: no timeout. (Requires Caddy v2.6.0-beta.3.)timeout-write-timeout: The maximum time to wait for next write to backend. Default: no timeout. (Requires Caddy v2.6.0-beta.3.)
Retries can be enabled by using the following annotations:
mesh.caddyserver.com/retry-count: "<count>"
mesh.caddyserver.com/retry-duration: "<duration>"
mesh.caddyserver.com/retry-on: "<expression>"
Parameters:
retry-count: How many times to retry selecting available backends for each request if the next available host is down. Default: disabled. (Requires Caddy v2.6.0-beta.3.)- If
retry-durationis also configured, then retries may stop early if the duration is reached.
- If
retry-duration: How long to try selecting available backends for each request if the next available host is down. Default: disabled. (See try_duration.)retry-on: An expression matcher that restricts with which requests retries are allowed. Default:"". (See retry_match.)- If either
retry-countorretry-durationis specified,retry-onwill default to"true".
- If either
Rate limiting can be enabled by using the following annotations:
mesh.caddyserver.com/rate-limit-key: "<key>"
mesh.caddyserver.com/rate-limit-rate: "<rate>"
mesh.caddyserver.com/rate-limit-zone-size: "<zone_size>"
Note that this feature requires the caddy-ext/ratelimit plugin.
Traffic splitting can be enabled by using the following annotations:
mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-expression: "<expression>"
mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-new-service: "<name>"
mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-old-service: "<name>"
Parameters:
traffic-split-expression: An expression matcher that restricts with which requests will be redirected to the new service (or, if unmatched, to the old service). Default:"".traffic-split-new-service: The name of the new Kubernetes Service. Default:"".traffic-split-old-service: The name of the old Kubernetes Service. Default:"".
(This workflow is inspired by SMI TrafficSplit.)
In this example workflow, the user has previously created the following resources:
- Deployment named
server-v1, with labels:app: serverandversion: v1. - Service named
server, with a selector ofapp: server. - Service named
server-v1, with selectors:app: serverandversion: v1. - Clients use the FQDN of
serverto communicate.- To leverage Caddy Mesh, clients must use
server.test.caddy.mesh(instead ofserver.test.svc.cluster.local).
- To leverage Caddy Mesh, clients must use
In order to update an application, the user will perform the following actions:
-
Enable Traffic splitting on
server(without redirecting traffic toserver-v2).--- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: server namespace: test labels: app: server + annotations: + mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-expression: "false" + mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-new-service: server-v2 + mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-old-service: server-v1 spec: ...
-
Create a new deployment named
server-v2, with labels:app: serverandversion: v2. -
Create a new service named
server-v2, with selectors:app: serverandversion: v2. -
Once the deployment is healthy, spot check by sending manual requests to the
server-v2.
When ready, the user begins to redirect traffic to server-v2:
-
For example, the user first route Chrome consumers to
server-v2:--- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: server namespace: test labels: app: server annotations: - mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-expression: "false" + mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-expression: "header({'User-Agent': '*Chrome*'})" mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-new-service: server-v2 mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-old-service: server-v1 spec: ...
-
Verify health metrics and become comfortable with the new version.
-
The user decides to redirect all traffic to the new version:
--- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: server namespace: test labels: app: server annotations: - mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-expression: "header({'User-Agent': '*Chrome*'})" + mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-expression: "true" mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-new-service: server-v2 mesh.caddyserver.com/traffic-split-old-service: server-v1 spec: ...
When completed, cleanup the old resources:
- Delete the old
server-v1deployment. - Delete the old
server-v1service. - Remove the Traffic splitting annotations as it is no longer needed.