This is the official code for our paper accepted at IPCAI 2023 and IJCARS.
If you find our project useful, please cite
@article{shu2023twin,
title={Twin-S: a digital twin for skull base surgery},
author={Shu, Hongchao and Liang, Ruixing and Li, Zhaoshuo and Goodridge, Anna and Zhang, Xiangyu and Ding, Hao and Nagururu, Nimesh and Sahu, Manish and Creighton, Francis X and Taylor, Russell H and others},
journal={International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery},
pages={1--8},
year={2023},
publisher={Springer}
}
We present a digital twin paradigm for skull base surgery named Twin-S. It models and tracks the critical
components of skull-base surgery, including the surgical tool, patient anatomy,
and surgical camera. Significantly, Twin-S updates patient anatomy to account
for the real-world tool to tissue interactions in real-time.
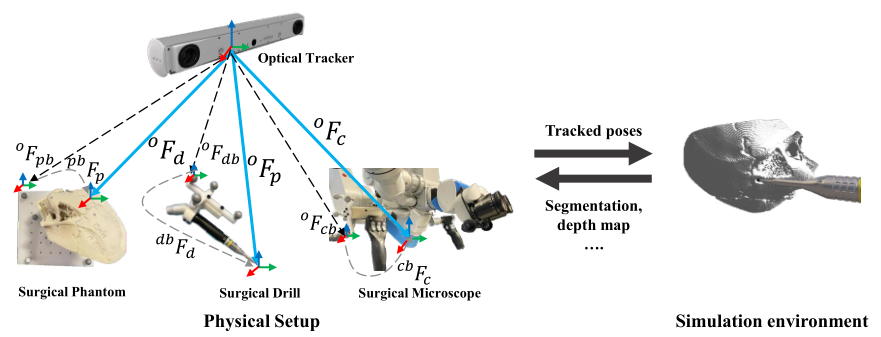
To run our project as a whole requires you to implement many adaptations based on your current hardware API. For instance, Camera Acquisition Pipelines and Optical Tracker may be faced a large fix if we are using different platform when you are pursuing the equivalent accuracy as we have evaluated.
- Our system has been tested on Ubuntu 20.04 and Ubuntu 18.04.
- We use ROS Noetic for data synchronization and visulization.
- Before you start, make sure AMBF and the volmetric drilling plugin is properly built.
- We use Atracsys FusionTrack-500 to track 6 DoF poses for each critical components.
- We use ZED mini to capture stereo images. Build the ZED-ros-wrapper.
- Record the ROS bag of pivot tool's poses.
./recordAll.sh -p <$path>- Load the poses from bag, perform pivot calibration and save the result.
./pivot_calibration.sh -p <$path> -s <$save_name> -t <$topic>- With a calibrated pointer tool, you can manually sample hundards of points on the phantom surface. Make sure to set you own OUTPUT_PATH.
cd optical_tracking/atracsys_subscriber
python atracsys_subscriber.py- Then the ICP registration can be used to register your 3d model to tracker's coordinate. Adjust the paths accordingly before using.
cd optical_tracking
python phantom_registration_T_p_pb.py- Record the ROS bag of the left images and poses of optical markers fixed on the camera.
./recordAll.sh -h <$path>- We use ChArUco board which can be generated from here for camera pose estimation. Extract the camera poses directly from ros bag.
cd preparation
python camera_pose_extraction.py --bag <$bag_path> --outdir <$output_path> --l_topic <$ros_topic> --csv <$poses_output_csv>- To run the hand-eye calibration, properly build the calibration tool. Then run the following.
rosrun hand_eye_calibration compute_complete_handeye_calibration.sh <$optical_markers_poses_csv> <$camera_poses_csv>Put the tracking geometry files in: 'catkin_ws/src/cisst-saw/sawAtracsysFusionTrack/share'. Follow the command lines then below.
cd <$your_path>/catkin_ws/src/cisst-saw/sawAtracsysFusionTrack/share
rosrun atracsys_ros atracsys_json -j <$configFile.json>Start zed-ros-wrapper, make sure you can subscribe the published image topics with ROS.
roslaunch zed_wrapper zedm.launchProperly follow the instructions of AMBF and the volmetric drilling plugin and prepare your own launch and other config files.
You can simply run the bash file. It contains few scripts:
- synchronizer.py automatically syncs ros topics of tracking poses and stereo images.
- drill_move_imgPub.py processes and commands the drill and phantom to move in AMBF.
- offline_segm_eval.py generates overlay of RGB images and simulation images, then pulish to a new topic for visualization.
- recordAll.sh records poses and images, and save it to a ros bag.
./data_collection.sh -c <$config_file> -s <$save_path>