Plot a combination matrix instead of the standard x-axis and create UpSet plots with ggplot2.
You can install the released version of ggupset from CRAN with:
# Download package from CRAN
install.packages("ggupset")
# Or get the latest version directly from GitHub
devtools::install_github("const-ae/ggupset")This is a basic example which shows you how to solve a common problem:
# Load helper packages
library(ggplot2)
library(tidyverse)
#> ── Attaching packages ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.2.1 ──
#> ✔ tibble 1.4.2 ✔ purrr 0.2.5
#> ✔ tidyr 0.8.2 ✔ dplyr 0.7.8
#> ✔ readr 1.2.1 ✔ stringr 1.4.0
#> ✔ tibble 1.4.2 ✔ forcats 0.3.0
#> ── Conflicts ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
#> ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
#> ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
# Load my package
library(ggupset)In the following I will work with a tidy version of the movies dataset from ggplot. It contains a list of all movies in IMDB, their release data and other general information on the movie. It also includes a list column that contains annotation to which genre a movie belongs (Action, Drama, Romance etc.)
tidy_movies
#> # A tibble: 50,000 x 10
#> title year length budget rating votes mpaa Genres stars
#> <chr> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <chr> <list> <dbl>
#> 1 Ei i… 1993 90 NA 8.4 15 "" <chr … 1
#> 2 Hamo… 1985 109 NA 5.5 14 "" <chr … 1
#> 3 Mind… 1963 99 NA 6.4 54 "" <chr … 1
#> 4 Trop… 1998 119 NA 4.5 20 "" <chr … 1
#> 5 Crys… 1995 85 NA 6.1 25 "" <chr … 1
#> 6 Tota… 1991 102 NA 6.3 210 "" <chr … 1
#> 7 Visi… 1995 100 NA 4.6 7 "" <chr … 1
#> 8 Pang… 1976 85 NA 7.4 8 "" <chr … 1
#> 9 Not … 1955 135 2000000 6.6 223 "" <chr … 1
#> 10 Auto… 1994 87 NA 7.4 5 "" <chr … 1
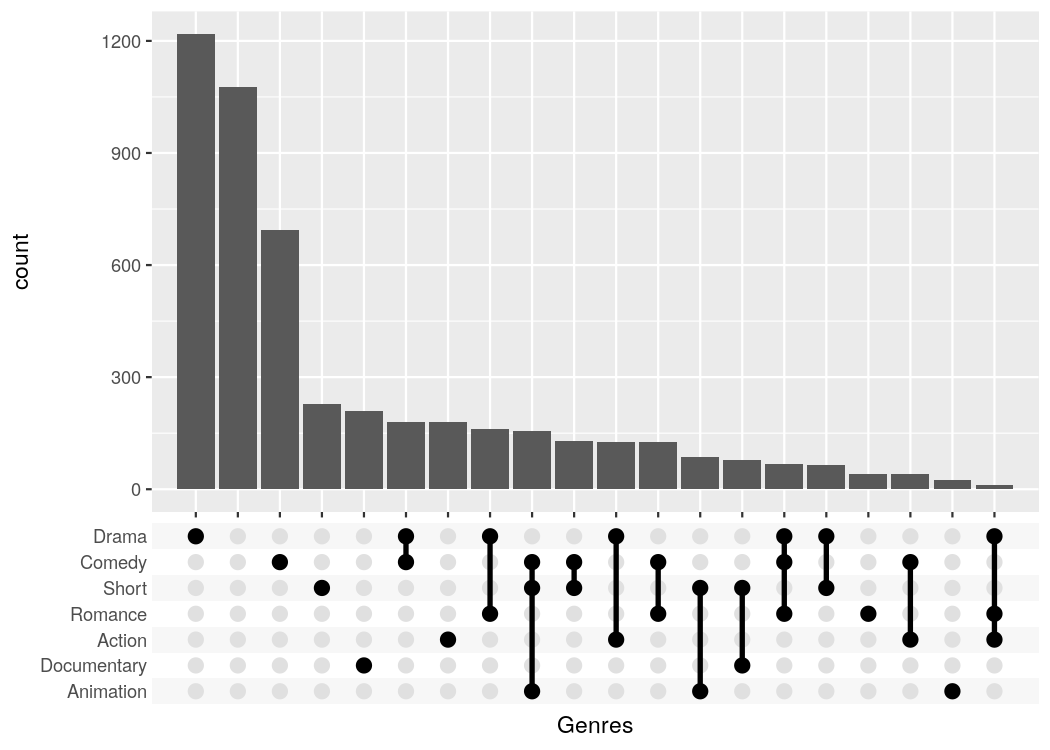
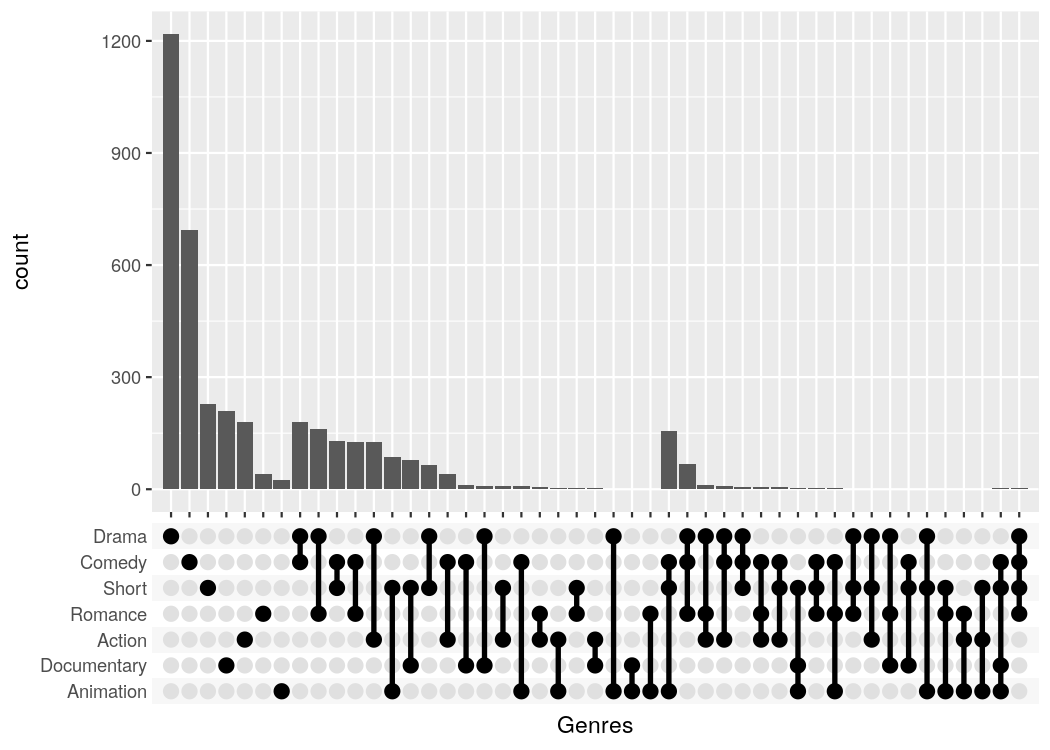
#> # ... with 49,990 more rows, and 1 more variable: percent_rating <dbl>ggupset makes it easy to get an immediate impression how many movies are in each genre and their combination. For example there are slightly more than 1200 Dramas in the set, more than 1000 which don't belong to any genre and ~170 that are Comedy and Drama.
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
geom_bar() +
scale_x_upset(n_intersections = 20)
#> Warning: Removed 100 rows containing non-finite values (stat_count).Often enough the raw data you are starting with is not in such a neat tidy shape. But that is a prerequisite to make such ggupset plots, so how can you get from wide dataset to a useful one? And how to actually create a list-column, anyway?
Imagine we measured for a set of genes if they are a member of certain pathway. A gene can be a member of multiple pathways and we want to see which pathways have a large overlap. Unfortunately, we didn't record the data in a tidy format but as a simple matrix.
A ficitional dataset of this type is provided as gene_pathway_membership variable
data("gene_pathway_membership")
gene_pathway_membership[, 1:7]
#> Aco1 Aco2 Aif1 Alox8 Amh Bmpr1b Cdc25a
#> Actin dependent Cell Motility FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> Chemokine Secretion TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> Citric Acid Cycle TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> Mammalian Oogenesis FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE
#> Meiotic Cell Cycle FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE
#> Neuronal Apoptosis FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSEWe will now turn first turn this matrix into a tidy tibble and then plot it
tidy_pathway_member <- gene_pathway_membership %>%
as_tibble(rownames = "Pathway") %>%
gather(Gene, Member, -Pathway) %>%
filter(Member) %>%
select(- Member)
tidy_pathway_member
#> # A tibble: 44 x 2
#> Pathway Gene
#> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 Chemokine Secretion Aco1
#> 2 Citric Acid Cycle Aco1
#> 3 Citric Acid Cycle Aco2
#> 4 Chemokine Secretion Aif1
#> 5 Chemokine Secretion Alox8
#> 6 Mammalian Oogenesis Amh
#> 7 Mammalian Oogenesis Bmpr1b
#> 8 Meiotic Cell Cycle Cdc25a
#> 9 Meiotic Cell Cycle Cdc25c
#> 10 Chemokine Secretion Chia1
#> # ... with 34 more rowstidy_pathway_member is already a very good starting point for plotting with ggplot. But we care about the genes that are members of multiple pathways so we will aggregate the data by Gene and create a list-column with the Pathway information.
tidy_pathway_member %>%
group_by(Gene) %>%
summarize(Pathways = list(Pathway))
#> # A tibble: 37 x 2
#> Gene Pathways
#> <chr> <list>
#> 1 Aco1 <chr [2]>
#> 2 Aco2 <chr [1]>
#> 3 Aif1 <chr [1]>
#> 4 Alox8 <chr [1]>
#> 5 Amh <chr [1]>
#> 6 Bmpr1b <chr [1]>
#> 7 Cdc25a <chr [1]>
#> 8 Cdc25c <chr [1]>
#> 9 Chia1 <chr [1]>
#> 10 Csf1r <chr [1]>
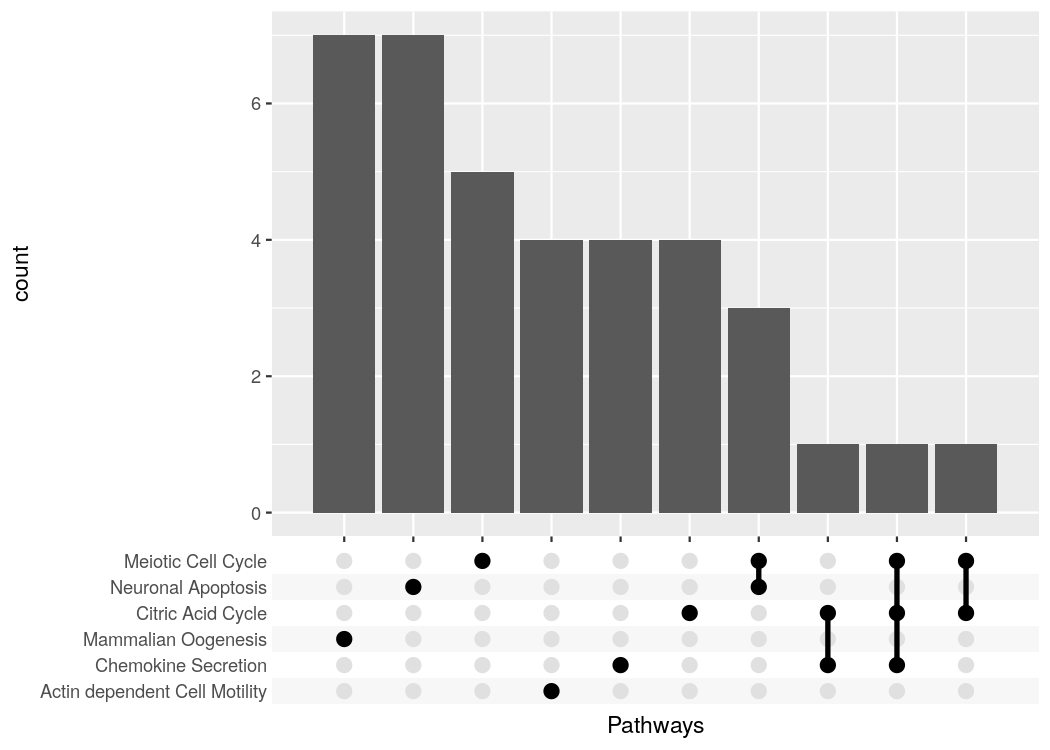
#> # ... with 27 more rowstidy_pathway_member %>%
group_by(Gene) %>%
summarize(Pathways = list(Pathway)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = Pathways)) +
geom_bar() +
scale_x_upset()The first important idea is to realize that a list column is just as good as a character vector with the list elements collapsed
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
mutate(Genres_collapsed = sapply(Genres, function(x) paste0(sort(x), collapse = "-"))) %>%
select(title, Genres, Genres_collapsed)
#> # A tibble: 5,000 x 3
#> title Genres Genres_collapsed
#> <chr> <list> <chr>
#> 1 Ei ist eine geschissene Gottesgabe, Das <chr [1]> Documentary
#> 2 Hamos sto aigaio <chr [1]> Comedy
#> 3 Mind Benders, The <chr [0]> ""
#> 4 Trop (peu) d'amour <chr [0]> ""
#> 5 Crystania no densetsu <chr [1]> Animation
#> 6 Totale!, La <chr [1]> Comedy
#> 7 Visiblement je vous aime <chr [0]> ""
#> 8 Pang shen feng <chr [2]> Action-Animation
#> 9 Not as a Stranger <chr [1]> Drama
#> 10 Autobiographia Dimionit <chr [1]> Drama
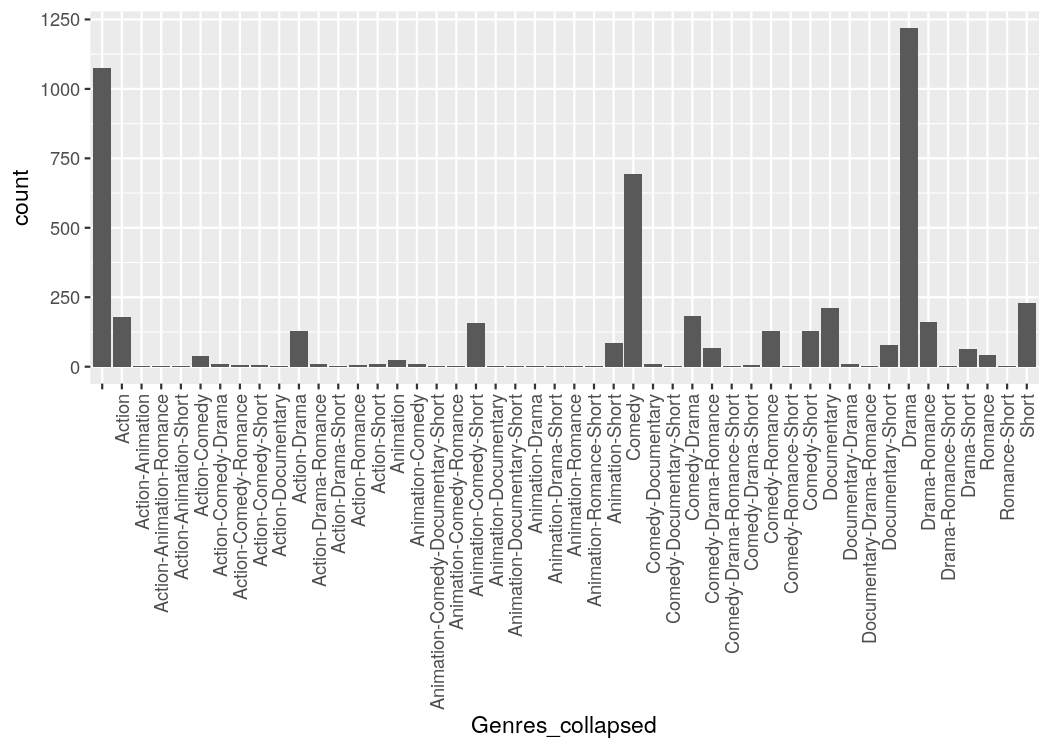
#> # ... with 4,990 more rowsWe can easily make a plot using the strings as categorical axis labels
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
mutate(Genres_collapsed = sapply(Genres, function(x) paste0(sort(x), collapse = "-"))) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Genres_collapsed)) +
geom_bar() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle=90, hjust=1, vjust=0.5))Because the process of collapsing list columns into delimited strings is fairly generic, I provide a new scale that does this automatically (scale_x_mergelist()).
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
geom_bar() +
scale_x_mergelist(sep = "-") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle=90, hjust=1, vjust=0.5))But the problem is that it can be difficult to read those labels. Instead I provide a third function that replaces the axis labels with a combination matrix (axis_combmatrix()).
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
geom_bar() +
scale_x_mergelist(sep = "-") +
axis_combmatrix(sep = "-")One thing that is only possible with the scale_x_upset() function is to automatically order the categories and genres by freq or by degree.
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
geom_bar() +
scale_x_upset(order_by = "degree")
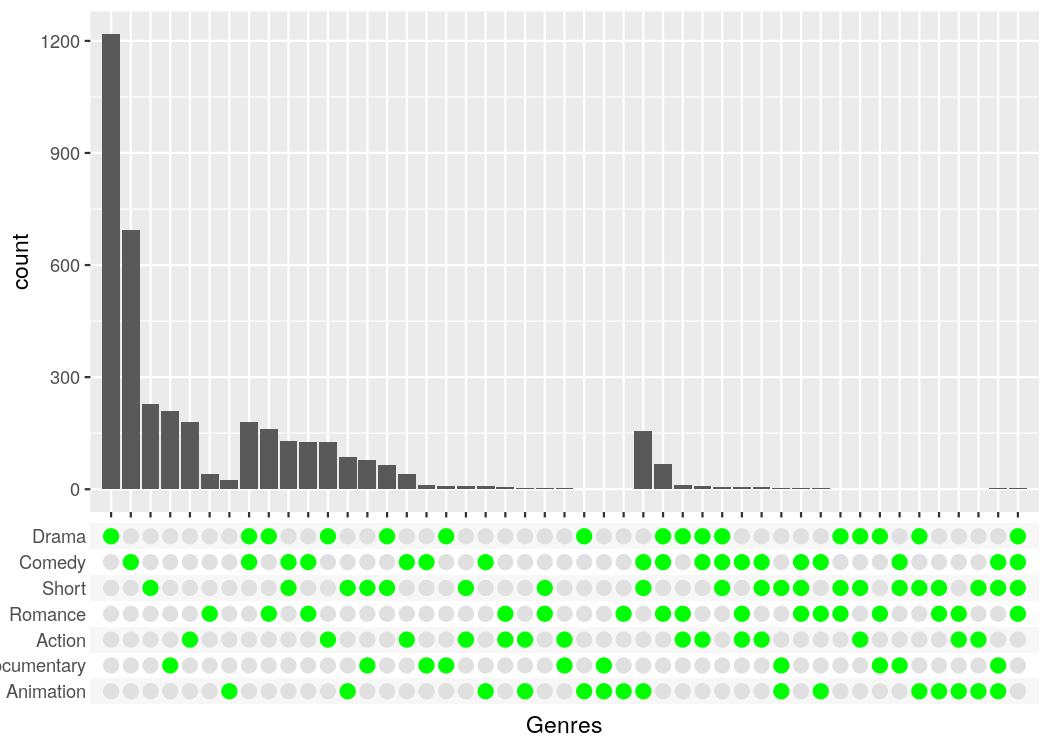
#> Warning: Removed 1076 rows containing non-finite values (stat_count).To make publication ready plots, you often want to have complete control how each part of a plot looks. This is why I provide an easy way to style the combination matrix. Simply add a theme_combmatrix() to the plot.
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
geom_bar() +
scale_x_upset(order_by = "degree") +
theme_combmatrix(combmatrix.panel.point.color.fill = "green",
combmatrix.panel.line.size = 0,
combmatrix.label.make_space = FALSE)
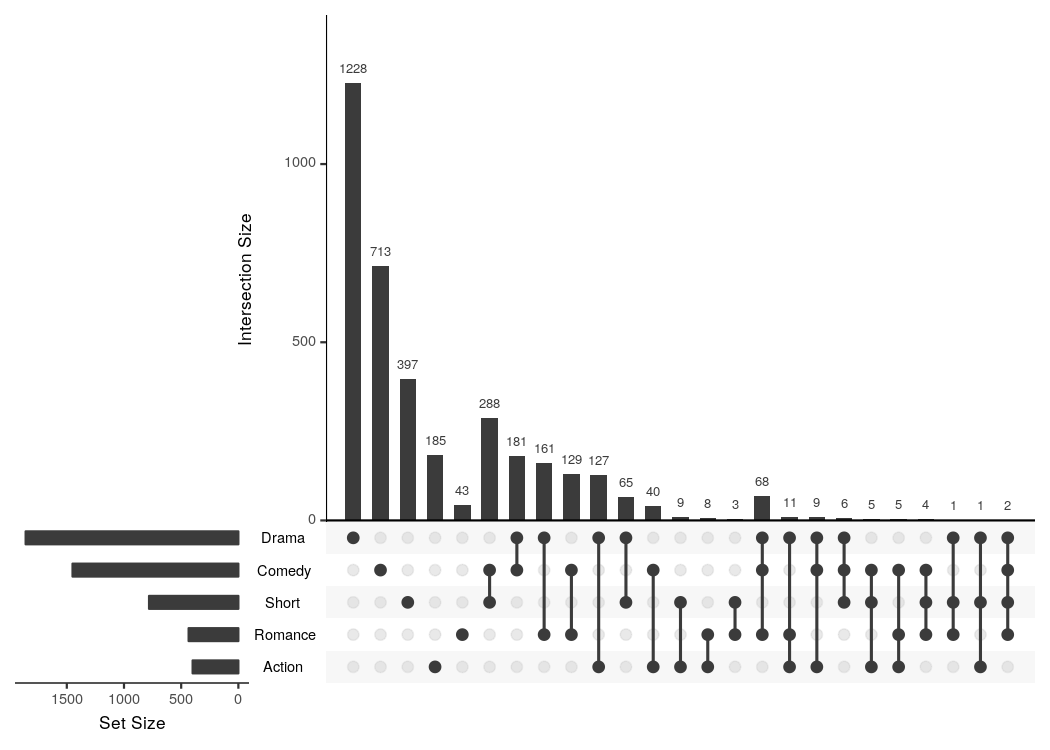
#> Warning: Removed 1076 rows containing non-finite values (stat_count).There is already a package called UpSetR (GitHub, CRAN) that provides very similar functionality and that heavily inspired me to write this package. It produces a similar plot with an additional view that shows the overall size of each genre.
# UpSetR
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
unnest() %>%
mutate(GenreMember=1) %>%
spread(Genres, GenreMember, fill=0) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
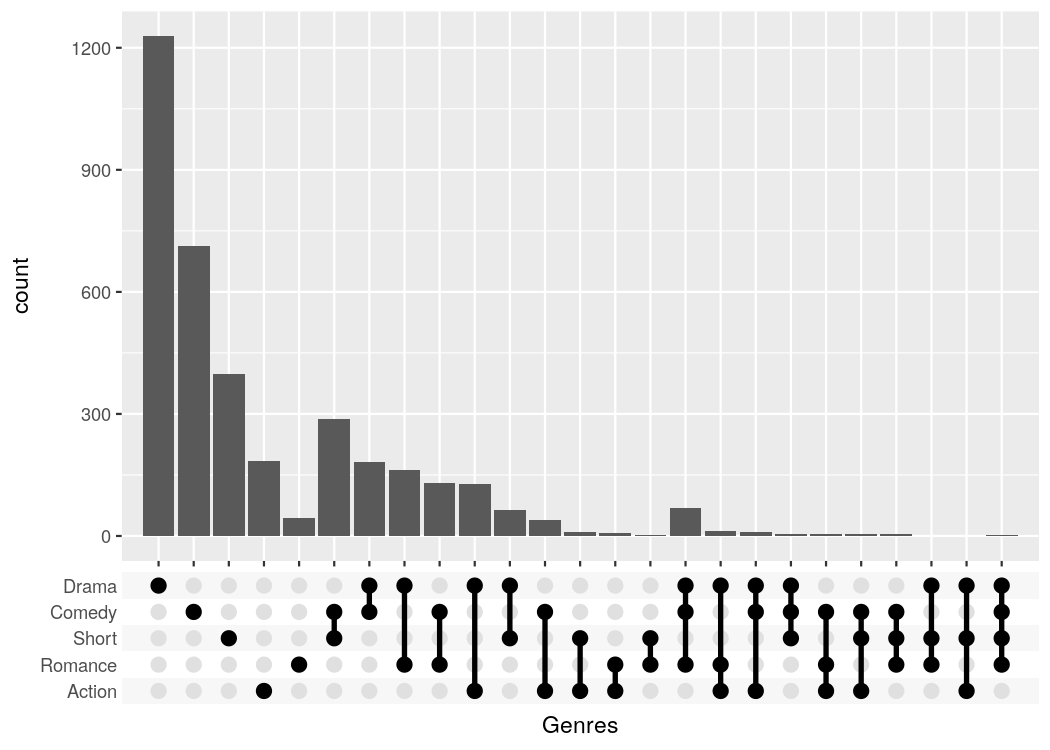
UpSetR::upset(sets = c("Action", "Romance", "Short", "Comedy", "Drama"), keep.order = TRUE)# ggupset
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
geom_bar() +
scale_x_upset(order_by = "degree", n_sets = 5)
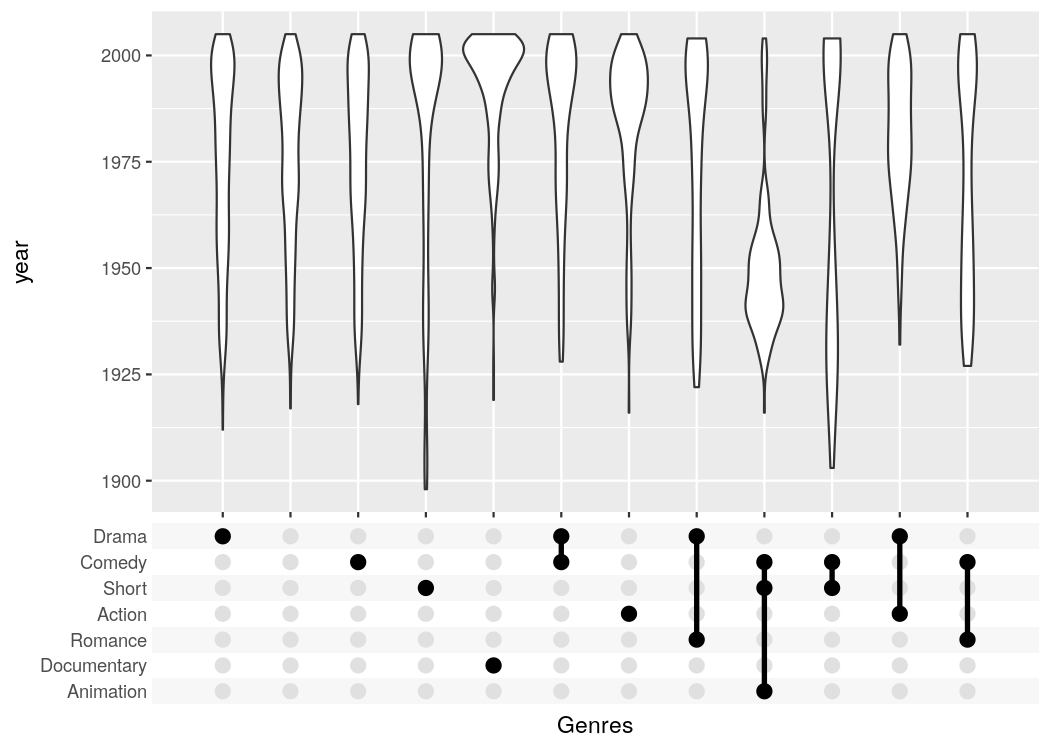
#> Warning: Removed 1311 rows containing non-finite values (stat_count).The UpSetR package provides a lot convenient helpers around this kind of plot; the main advantage of my package is that it can be combined with any kind of ggplot that uses a categorical x-axis. This additional flexibility can be useful if you want to create non-standard plots. The following plot for example shows when movies of a certain genre were published.
tidy_movies %>%
distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Genres, y=year)) +
geom_violin() +
scale_x_upset(order_by = "freq", n_intersections = 12)
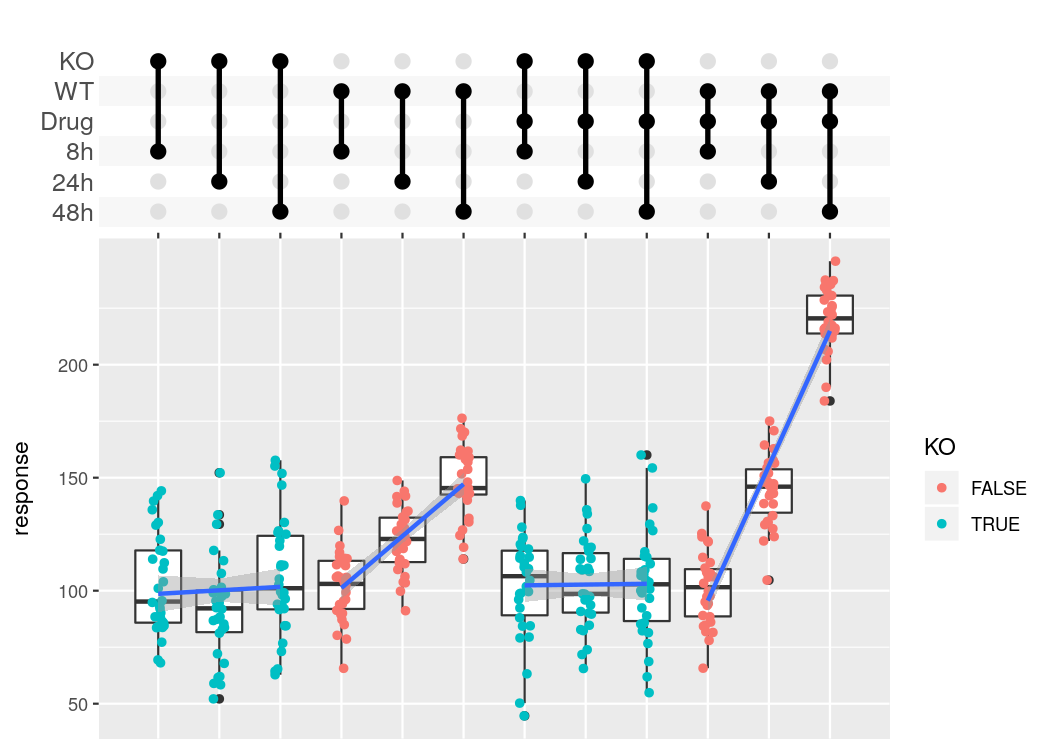
#> Warning: Removed 513 rows containing non-finite values (stat_ydensity).The combination matrix axis can be used to show complex experimental designs, where each sample got a combination of different treatments.
df_complex_conditions
#> # A tibble: 360 x 4
#> KO DrugA Timepoint response
#> <lgl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 TRUE Yes 8 84.3
#> 2 TRUE Yes 8 105.
#> 3 TRUE Yes 8 79.1
#> 4 TRUE Yes 8 140.
#> 5 TRUE Yes 8 108.
#> 6 TRUE Yes 8 79.5
#> 7 TRUE Yes 8 112.
#> 8 TRUE Yes 8 118.
#> 9 TRUE Yes 8 114.
#> 10 TRUE Yes 8 92.4
#> # ... with 350 more rows
df_complex_conditions %>%
mutate(Label = pmap(list(KO, DrugA, Timepoint), function(KO, DrugA, Timepoint){
c(if(KO) "KO" else "WT", if(DrugA == "Yes") "Drug", paste0(Timepoint, "h"))
})) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=Label, y=response)) +
geom_boxplot() +
geom_jitter(aes(color=KO), width=0.1) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", aes(group = paste0(KO, "-", DrugA))) +
scale_x_upset(order_by = "degree",
sets = c("KO", "WT", "Drug", "8h", "24h", "48h"),
position="top", name = "") +
theme_combmatrix(combmatrix.label.text = element_text(size=12),
combmatrix.label.extra_spacing = 5)dplyr currently does not support list columns as grouping variables. In that case it makes sense to collapse it manually and use the axis_combmatrix() function to get a good looking plot.
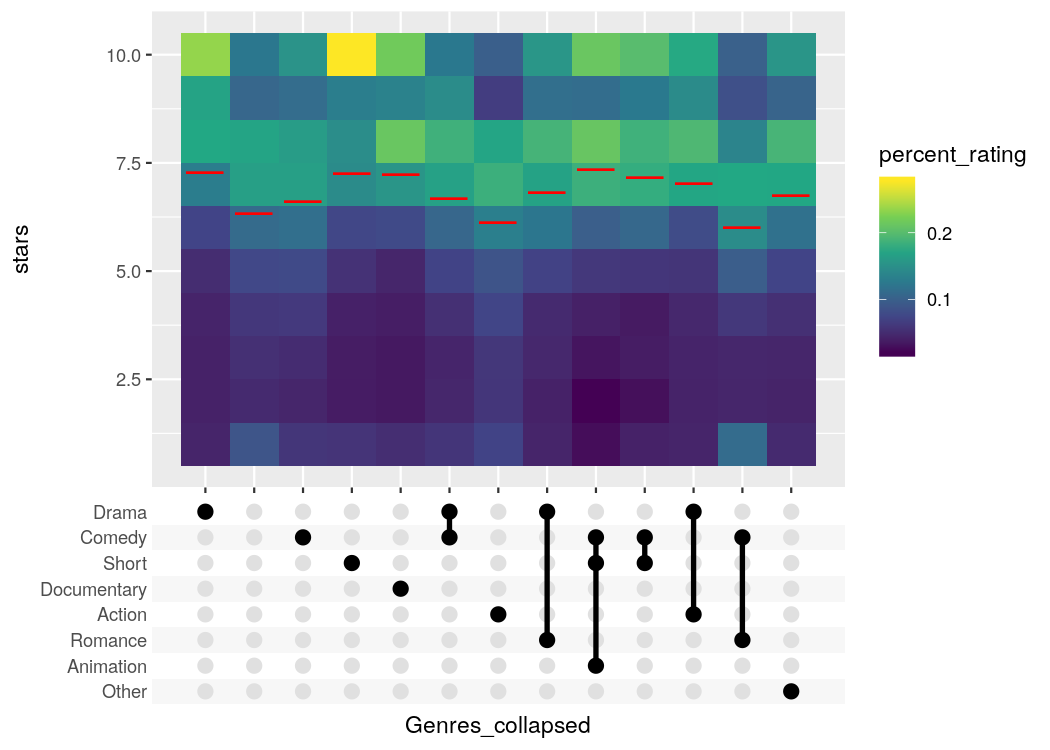
# Percentage of votes for n stars for top 12 genres
avg_rating <- tidy_movies %>%
mutate(Genres_collapsed = sapply(Genres, function(x) paste0(sort(x), collapse="-"))) %>%
mutate(Genres_collapsed = fct_lump(fct_infreq(as.factor(Genres_collapsed)), n=12)) %>%
group_by(stars, Genres_collapsed) %>%
summarize(percent_rating = sum(votes * percent_rating)) %>%
group_by(Genres_collapsed) %>%
mutate(percent_rating = percent_rating / sum(percent_rating)) %>%
arrange(Genres_collapsed)
avg_rating
#> # A tibble: 130 x 3
#> # Groups: Genres_collapsed [13]
#> stars Genres_collapsed percent_rating
#> <dbl> <fct> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Drama 0.0437
#> 2 2 Drama 0.0411
#> 3 3 Drama 0.0414
#> 4 4 Drama 0.0433
#> 5 5 Drama 0.0506
#> 6 6 Drama 0.0717
#> 7 7 Drama 0.129
#> 8 8 Drama 0.175
#> 9 9 Drama 0.170
#> 10 10 Drama 0.235
#> # ... with 120 more rows
# Plot using the combination matrix axis
# the red lines indicate the average rating per genre
ggplot(avg_rating, aes(x=Genres_collapsed, y=stars, fill=percent_rating)) +
geom_tile() +
stat_summary_bin(aes(y=percent_rating * stars), fun.y = sum, geom="point",
shape="—", color="red", size=6) +
axis_combmatrix(sep = "-", levels = c("Drama", "Comedy", "Short",
"Documentary", "Action", "Romance", "Animation", "Other")) +
scale_fill_viridis_c()