PL/SQL Cop supports custom validators. A validator must implement the PLSQLCopValidator Java interface and has to be a direct or indirect descendant of the PLSQLJavaValidator class.
You may use these validators as is or amend/extend them to suit your needs.
This project provides the following four custom validators in the package com.trivadis.tvdcc.validators:
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| TrivadisGuidelines3Plus | Checks Naming Conventions of the Trivadis PL/SQL & SQL Coding Guidelines |
| GLP | Checks naming of global and local variables and parameters |
| SQLInjection | Looks for SQL injection vulnerabilities, e.g. unasserted parameters in dynamic SQL |
| OverrideTrivadisGuidelines | Extends TrivadisGuidelines3 and overrides check for G-1050. |
This validator implements 15 guidelines to cover the chapter 2.2 Naming Conventions of the Trivadis PL/SQL & SQL Coding Guidelines.
| Guideline | Message |
|---|---|
| G-9001 | Global variables should start with 'g_'. |
| G-9002 | Local variables should start with 'l_'. |
| G-9003 | Cursors should start with 'c_' |
| G-9004 | Records should start with 'r_'. |
| G-9005 | Collection types (arrays/tables) should start with 't_'. |
| G-9006 | Objects should start with 'o_'. |
| G-9007 | Cursor parameters should start with 'p_'. |
| G-9008 | In parameters should start with 'in_'. |
| G-9009 | Out parameters should start with 'out_'. |
| G-9010 | In/out parameters should start with 'io_'. |
| G-9011 | Record Type definitions should start with 'r_' and end with '_type'. |
| G-9012 | Collection Type definitions (arrays/tables) should start with 't_' and end with '_type'. |
| G-9013 | Exceptions should start with 'e_'. |
| G-9014 | Constants should start with 'co_'. |
| G-9015 | Subtypes should end with 'type'. |
This validator is an extension to the Trivadis PL/SQL & SQL Coding Guidelines. This means that the all guidelines defined in chapter 4. Language Usage are checked as well.
This is a simple validator to check the following naming convention guidelines:
| Guideline | Message |
|---|---|
| G-9001 | Global variables should start with 'g_'. |
| G-9002 | Local variables should start with 'l_'. |
| G-9003 | Parameters should start with 'p_'. |
This validator checks just these three guidelines. It does not extend the Trivadis PL/SQL & SQL Coding Guidelines.
This validator implements the following guideline:
| Guideline | Message |
|---|---|
| G-9501 | Parameter used in string expression of dynamic SQL. Use asserted local variable instead. |
It looks for unasserted parameters used in EXECUTE IMMEDIATE statements and OPEN FOR statements. All parameters used in these statements must be asserted with one of the subprograms provided by DBMS_ASSERT.
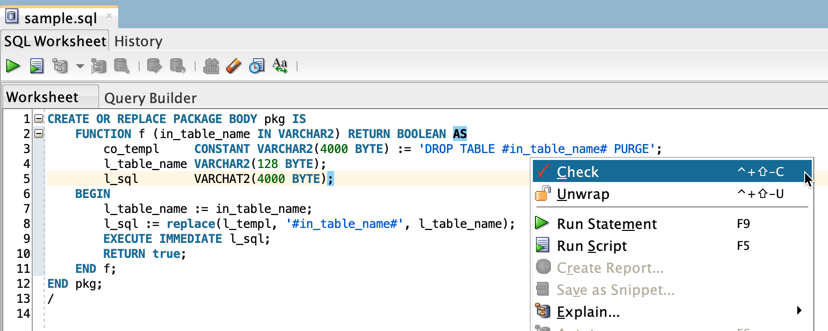
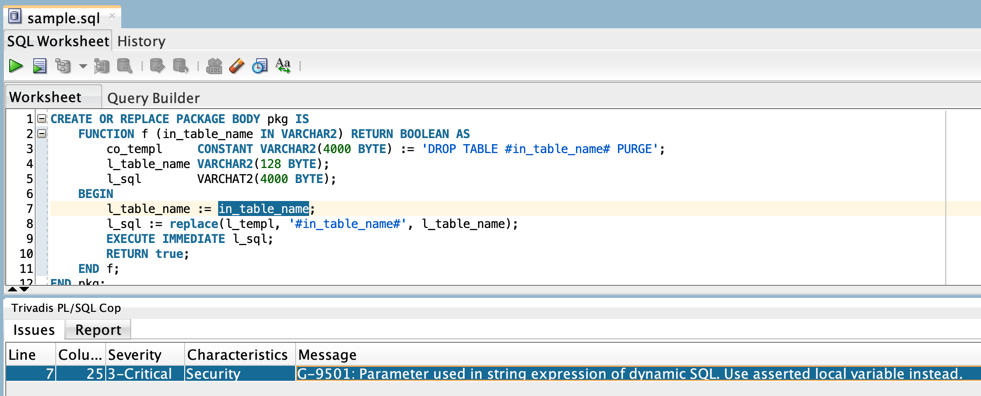
The input parameter in_table_name is copied to the local variable l_table_name and then used without an assert to build the l_sql variable. Hence, the execute immediate statement is considered vulnerable to SQL injection, e.g. by passing DEPT CASCADE CONSTRAINTS.
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY pkg IS
FUNCTION f (in_table_name IN VARCHAR2) RETURN BOOLEAN AS
co_templ CONSTANT VARCHAR2(4000 BYTE) := 'DROP TABLE #in_table_name# PURGE';
l_table_name VARCHAR2(128 BYTE);
l_sql VARCHAR2(4000 BYTE);
BEGIN
l_table_name := in_table_name;
l_sql := replace(l_templ, '#in_table_name#', l_table_name);
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE l_sql;
RETURN true;
END f;
END pkg;SQL injection is not possible, because the input parameter in_table_name is checked/modified with sys.dbms_assert.enquote_name.
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY pkg IS
FUNCTION f (in_table_name IN VARCHAR2) RETURN BOOLEAN AS
co_templ CONSTANT VARCHAR2(4000 BYTE) := 'DROP TABLE #in_table_name# PURGE';
l_table_name VARCHAR2(128 BYTE);
l_sql VARCHAR2(4000 BYTE);
BEGIN
l_table_name := sys.dbms_assert.enquote_name(in_table_name);
l_sql := replace(l_templ, '#in_table_name#', l_table_name);
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE l_sql;
RETURN true;
END f;
END pkg;This validator shows how existing guideline checks can be overridden.
The following guideline is overriden:
| Guideline | Message |
|---|---|
| G-1050 | Avoid using literals in your code. |
Literals as part of a Logger package call are not reported (see also issue 8).
-
Download PL/SQL Cop
Download PL/SQL Cop from here.
-
Install PL/SQL Cop
-
Uncompress the distributed PL/SQL Cop archive file (e.g. tvdcc-2.2.1.zip) into a folder of your choice (hereinafter referred to as
TVDCC_HOME). I use/usr/local/bin/tvdccforTVDCC_HOMEon my MacBook Pro. -
For Windows platforms only: Amend the settings for JAVA_HOME in the tvdcc.cmd file to meet your environment settings. Use at least a Java 7 runtime environment (JRE) or development kit (JDK).
-
Include
TVDCC_HOMEin your PATH environment variable for handy interactive usage. -
Optionally copy your commercial license file into the
TVDCC_HOMEdirectory. For simplicity name the file tvdcc.lic.
-
-
Download Validator
Download
validators.jarfrom here. -
Install Validator
Copy the previously downloaded
validator.jarinto thepluginfolder of yourTVDCC_HOMEfolder. -
Run PL/SQL Cop with Custom Validator
Open a terminal window, change to the
TVDCC_HOMEdirectory and run the following command to all files in$HOME/github/utPLSQL/sourcewith the custom validatorcom.trivadis.tvdcc.validators.SQLInjection:./tvdcc.sh path=$HOME/github/utPLSQL/source validator=com.trivadis.tvdcc.validators.SQLInjectionThe
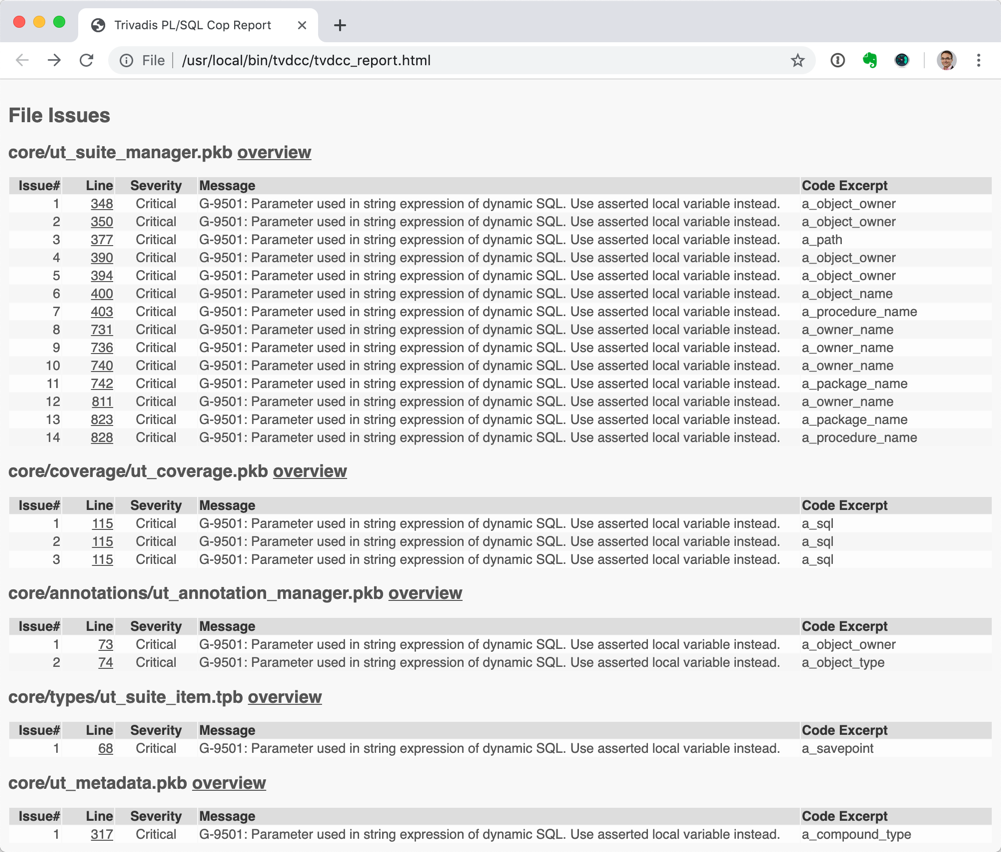
tvdcc_report.htmlfile contain the results. Here's an excerpt:
-
Install PL/SQL Cop
As explained above.
-
Download PL/SQL Cop for SQL Developer
Download PL/SQL Cop for SQL Developer from here.
-
Install PL/SQL Cop for SQL Developer
- Start SQL Developer
- Select
Check for Updates…in the help menu. - Use the
Install From Local File(s)option to install the previously downloadedTVDCC_for_SQLDev-*.zipfile. - Restart SQL Developer
-
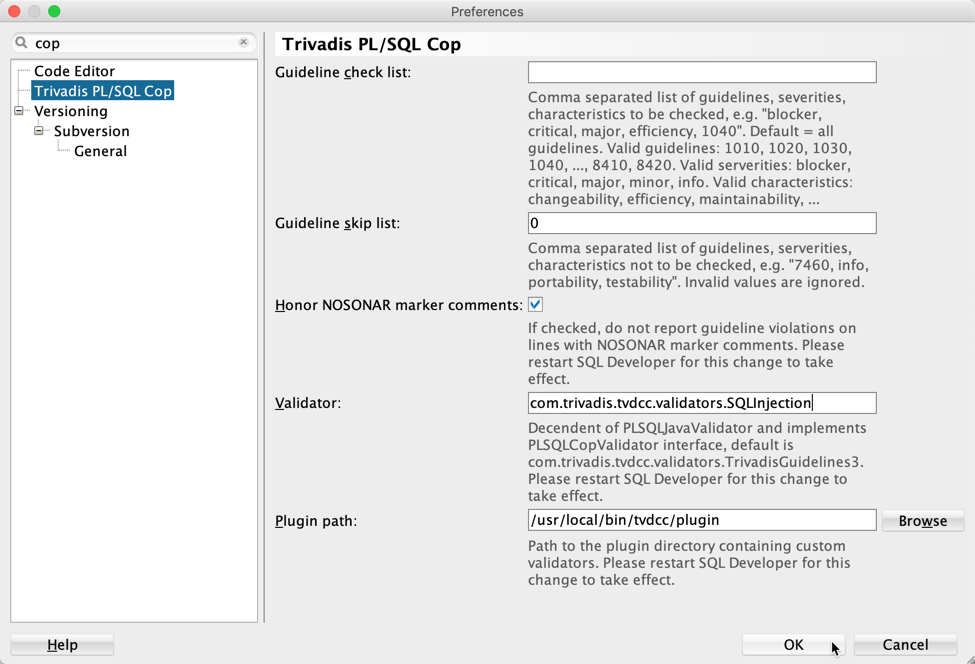
Configure Validator
Configure the validator in SQL Developer as shown in the following screenshot:
-
Check Code
Open the code to be checked in an editor and select
Checkfrom the context menu.The check result is shown by default at the bottom of your SQL Developer workspace.
-
Install PL/SQL Cop
As explained above.
-
Install Maven
Download and install Apache Maven 3.6.1
-
Clone the cop-validators repository
Clone or download this repository.
-
Build
validators.jarOpen a terminal window in the cop-validators root folder and maven build by the following command
mvn -Dtvdcc.basedir=/usr/local/bin/tvdcc clean packageAmend the parameter
tvdcc.basedirto match yourTVDCC_HOMEdirectory. This folder is used to reference PL/SQL Cop jar files which are not available in public Maven repositories
Please file your bug reports, enhancement requests, questions and other support requests within Github's issue tracker.
The PL/SQL Cop Validators are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. You may obtain a copy of the License at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/.