Software vulnerabilities damage the functionality of software systems. Recently, many deep learning-based approaches have been proposed to detect vulnerabilities at the function level by using one or a few different modalities (e.g., text representation, graph-based representation) of the function and have achieved promising performance. However, some of these existing studies have not completely leveraged these diverse modalities, particularly the underutilized image modality, and the others using images to represent functions for vulnerability detection have not made adequate use of the significant graph structure underlying the images.
In this paper, we propose MVulD, a multi-modal-based function-level vulnerability detection approach, which utilizes multi-modal features of the function (i.e., text representation, graph representation, and image representation) to detect vulnerabilities. Specifically, MVulD utilizes a pre-trained model (i.e., UniXcoder) to learn the semantic information of the textual source code, employs the graph neural network to distill graph based representation, and makes use of computer vision techniques to obtain the image representation while retaining the graph structure of the function. We conducted a large-scale experiment on 25,816 functions. The experimental results show that MVulD improves four state-of-the-art baselines by 30.8%-81.3%, 12.8%-27.4%, 48.8%-115%, and 22.9%-141% in terms of F1-score, Accuracy, Precision, and PR-AUC respectively.
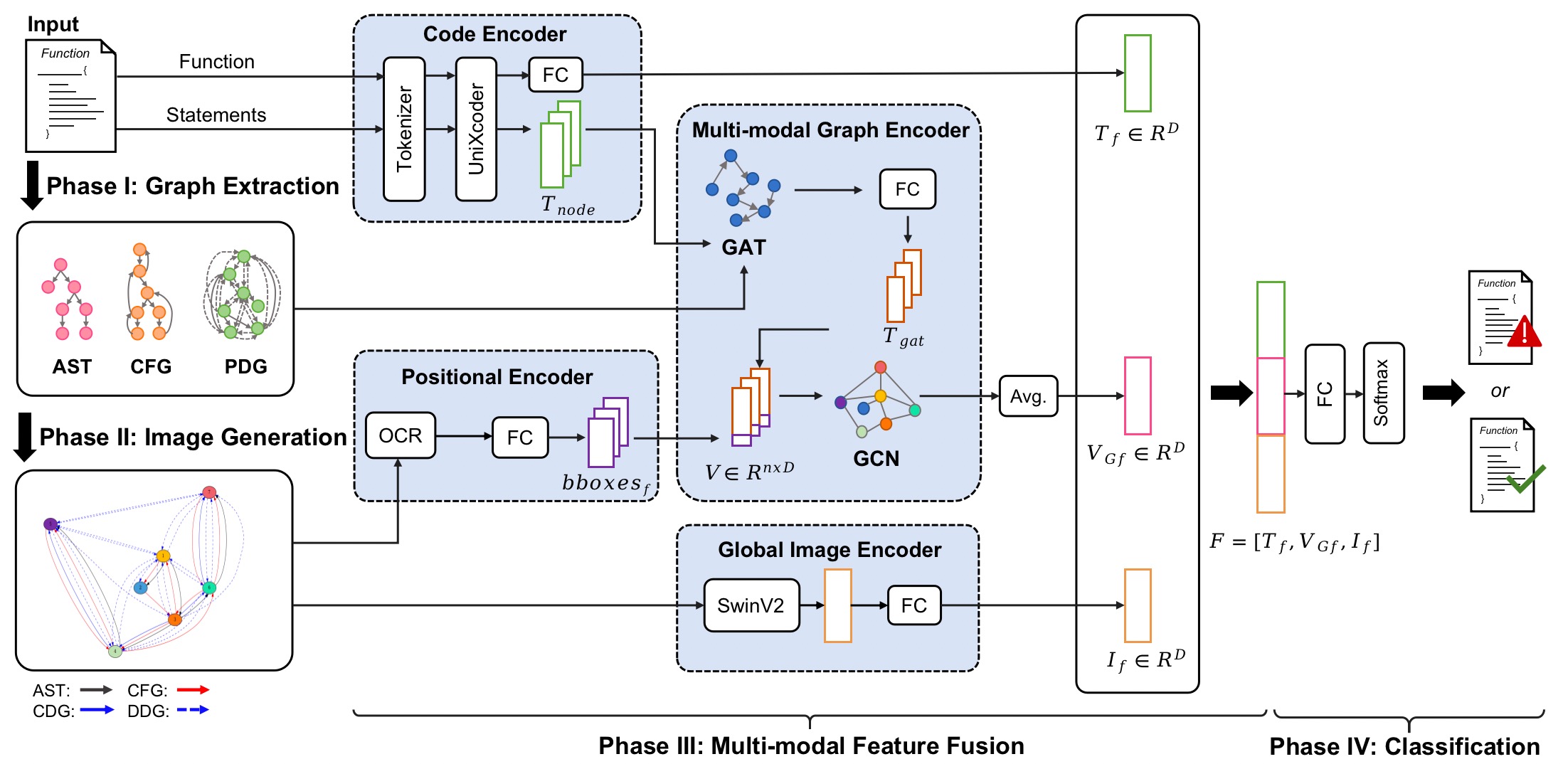
An overview architecture of MVulD
-
Graph Extraction: obtain the structure representation of the function.
-
Image generation: helps to transform the structural graph into graphical representation.
-
Multi-modal feature fusion: builds the relationship of various modalities to obtain enriched code representations.
-
Classification: applied to detect whether a function is vulnerable or not.
In our experiment, we choose the Big-Vul dataset provided by Fan, which is one of the largest vulnerability datasets collected from 348 open-source GitHub projects spanning 91 different vulnerability types.
And we normalize the source code by performing three filtering steps on the Big-Vul dataset.
Our final dataset contains 25,816 functions in total, including 4,069 vulnerable functions and 21,747 non-vulnerable functions.
You can download the Big-Vul dataset and process it refer to baselines/README.md, or you can also download the preprocessed dataset from HERE and unzip it.
Create Conda environment
$ conda env create -f environment.yml
Activate the environment
$ conda activate MVulD
We provide dataset processing scripts (including Graph Extraction and Image generation), please refer to baselines/README.md
The global image features were extracted by the SwinV2 model.
For more details, please refer to our paper. Here we train the swinV2 model.
swinv2_base_patch4_window12to24_192to384_22kto1k_ft.pth can be download from https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer.
To train and test SwinV2 model, using the following commands.
cd MVulD
# train and finetune swinv2 using our generated images
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 1 --master_port 12826 main.py --cfg configs/mySwin/swinv2_base_patch4_window24to28_384to448_1ktoMYDATA_ft.yaml --pretrained swinv2_base_patch4_window12to24_192to384_22kto1k_ft.pth --batch-size 4
# test swinv2
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 1 --master_port 24093 main.py --cfg configs/mySwin/swinv2_base_patch4_window24to28_384to448_1ktoMYDATA_ft.yaml --batch-size 4 --test 1
We train UniXcoder model to obtain the semantic information of the source code, please refer to baselines/README.md.
For convenience, we share a UniXcoder model here trained by using our studied dataset.
To obtain the positional feature embedding, we use OCR techniques to detect texts and positions from images, please refer to OCR/README.txt
To train and test MVulD model, using the following commands.
cd MVulD
# train
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 1 --master_port 10055 main_bigvul.py --cfg configs/mySwin/swinv2_base_patch4_window24to28_384to448_1ktoMYDATA_ft.yaml --batch-size 4
# test
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 1 --master_port 21129 main_bigvul.py --cfg configs/mySwin/swinv2_base_patch4_window24to28_384to448_1ktoMYDATA_ft.yaml --batch-size 4 --test 1