Opencvは画像処理についていろいろな関数がありますが、多くの関数は、8bit(256)をベースに作られています。研究用途の画像データでは、より解像度の高い16bitが用いられています。
opencvでは実装されていない16bit Grayscaleのヒストグラム平坦化処理について覚えとして記載します。
を参考に16bit版を作成しました。
windows 10 Pro
Anaconda
Python 3.9
opencv 4.5
画像データをopencvで読み込むとnumpyのarray形式になります。
データのタイプは通常の画像ファイルですとuint8(符号なし8ビット整数型)になります。
# モジュールをインポートして、題材としてLennaさんを読み込みます。
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# from PIL import Image
# 画像をグレースケールで読み込む
file_name = 'Lenna_gray.png'
img = cv2.imread(file_name, cv2.IMREAD_ANYDEPTH)
# img = cv2.imread(file_name, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE | cv2.IMREAD_ANYCOLOR)
print(img.dtype)
# I = Image.open(file_name)
# img = np.array(I)
# >>> uint8# 16bitのデータに変換します。
img_16 = img.copy()
img_16 = img_16.astype('uint16')
# img_16 = img_16*256
print(img_16.dtype)
print(img_16.max())
# >>> uint16
# >>> 245### 8bit版(チュートリアルと同じ)チュートリアルを再現してみます。
def equalize_hist8(img, info=True):
img2 = img.copy()
hist,bins = np.histogram(img.flatten(),256,[0,256])
cdf = hist.cumsum()
cdf_normalized = cdf * hist.max()/ cdf.max()
if info:
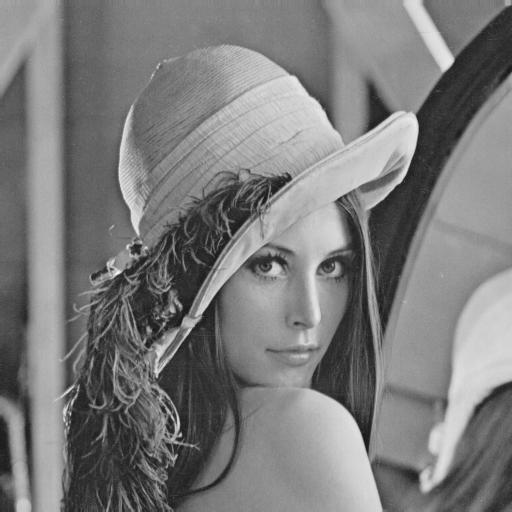
plt.imshow(img, cmap = "gray")
plt.title('Original')
plt.show()
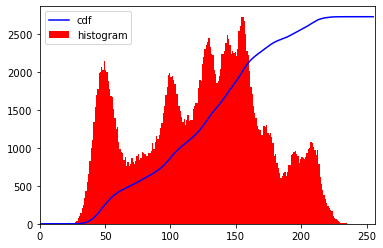
plt.plot(cdf_normalized, color = 'b')
plt.hist(img.flatten(),256,[0,256], color = 'r')
plt.xlim([0,256])
plt.legend(('cdf','histogram'), loc = 'upper left')
plt.show()
cdf_m = np.ma.masked_equal(cdf,0)
cdf_m = (cdf_m - cdf_m.min())*255/(cdf_m.max()-cdf_m.min())
cdf_m2 = np.ma.filled(cdf_m,0).astype('uint8')
img2 = cdf_m2[img]
hist2,bins2 = np.histogram(img2.flatten(),256,[0,256])
cdf2 = hist2.cumsum()
cdf2_normalized = cdf2 * hist2.max()/ cdf2.max()
if info:
plt.imshow(img2,cmap = "gray")
plt.title('EqualizeHist')
plt.show()
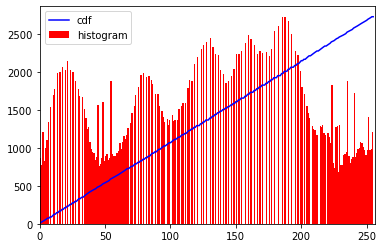
plt.plot(cdf2_normalized, color = 'b')
plt.hist(img2.flatten(),256,[0,256], color = 'r')
plt.xlim([0,256])
plt.legend(('cdf','histogram'), loc = 'upper left')
plt.show()
return img2
_ = equalize_hist8(img, info=True)### 16bit版
# - 8bitの256を16bitの65536に変更
# - 配列のデータタイプをuint16に変更
# - 少し時間がかかります。(2分ぐらい) histgramの計算に時間がかかります。
def equalize_hist16(img, info=True):
img2 = img.copy()
hist,bins = np.histogram(img.flatten(),65536,[0,65536])
cdf = hist.cumsum()
cdf_normalized = cdf * hist.max()/ cdf.max()
if info:
plt.imshow(img,cmap = "gray")
plt.title('Original')
plt.show()
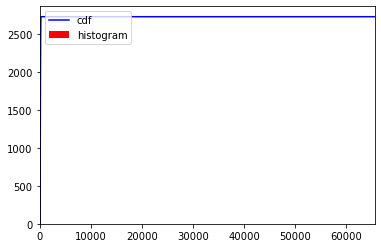
plt.plot(cdf_normalized, color = 'b')
plt.hist(img.flatten(),65536,[0,65536], color = 'r')
plt.xlim([0,65536])
plt.legend(('cdf','histogram'), loc = 'upper left')
plt.show()
cdf_m = np.ma.masked_equal(cdf,0)
cdf_m = (cdf_m - cdf_m.min())*65535/(cdf_m.max()-cdf_m.min())
cdf_m2 = np.ma.filled(cdf_m,0).astype('uint16')
img2 = cdf_m2[img]
hist2,bins2 = np.histogram(img2.flatten(),65536,[0,65536])
cdf2 = hist2.cumsum()
cdf2_normalized = cdf2 * hist2.max()/ cdf2.max()
if info:
plt.imshow(img2,cmap = "gray")
plt.title('EqualizeHist')
plt.show()
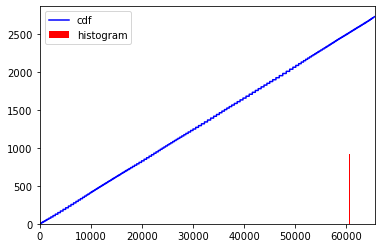
plt.plot(cdf2_normalized, color = 'b')
plt.hist(img2.flatten(),65536,[0,65536], color = 'r')
plt.xlim([0,65536])
plt.legend(('cdf','histogram'), loc = 'upper left')
plt.show()
return img2
_ = equalize_hist16(img_16, info=True)### 自動でDataTypeを確認して計算(8、16の両方に対応できるように変更)
def equalize_hist(img, info=True):
img2 = img.copy()
dataType = img.dtype
print(dataType)
if dataType == 'uint8':
tval = 256
elif dataType == 'uint16':
tval = 65536
hist,bins = np.histogram(img.flatten(),tval,[0,tval])
cdf = hist.cumsum()
cdf_normalized = cdf * hist.max()/ cdf.max()
if info:
plt.imshow(img,cmap = "gray")
plt.title('Original')
plt.show()
plt.plot(cdf_normalized, color = 'b')
plt.hist(img.flatten(),tval,[0,tval], color = 'r')
plt.xlim([0,tval])
plt.legend(('cdf','histogram'), loc = 'upper left')
plt.show()
cdf_m = np.ma.masked_equal(cdf,0)
cdf_m = (cdf_m - cdf_m.min())*(tval-1)/(cdf_m.max()-cdf_m.min())
cdf_m2 = np.ma.filled(cdf_m,0).astype(dataType)
img2 = cdf_m2[img]
if info:
plt.imshow(img2,cmap = "gray")
plt.title('EqualizeHist')
plt.show()
hist2,bins2 = np.histogram(img2.flatten(),tval,[0,tval])
cdf2 = hist2.cumsum()
cdf2_normalized = cdf2 * hist2.max()/ cdf2.max()
plt.plot(cdf2_normalized, color = 'b')
plt.hist(img2.flatten(),tval,[0,tval], color = 'r')
plt.xlim([0,tval])
plt.legend(('cdf','histogram'), loc = 'upper left')
plt.show()
return img2
_ = equalize_hist(img_16, info=True)ヒスグラムの計算で時間がかかってしまっていますが、16bitに対応するヒストグラム平坦化処理のコードを作成しました。
opencv、SciPyのndimageなどは、基本8bit対応ですので、16bitのイメージを入れるとエラーが出たり、8bitにキャストされてしまうことがあるので注意してください。