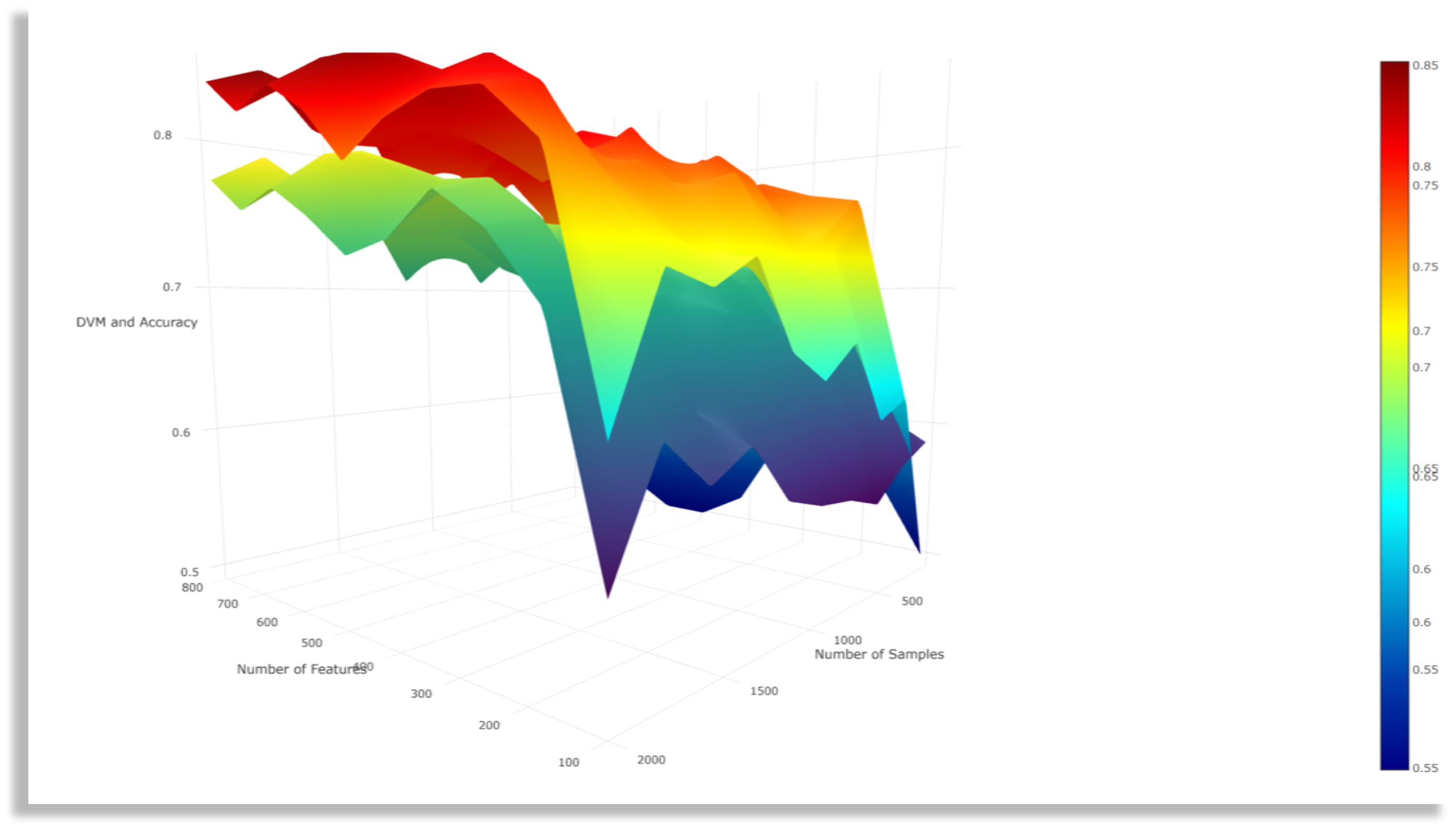
Data Value Metric (DVM)
This SOCR project is focused on developing a new measure, called Data Value Metric (DVM), that quantifies the energy, or information content, of large and complex datasets, which can be used as a yardstick to determine if appending, expanding, or otherwise augmenting the data size or complexity may be beneficial in specific application domains.
DVM is an open science project and provides the complete python code, case studies, examples, simulations, and results under LGPL license. Details are in the code folder.
Interactive 2D and 3D DVM surface plots illustrating the results of several experiment are available online. These graphs show the behavior of the DVM metric spanning the domain of possible number of cases and number of features for the real and simulated datasets.
Ivo D. Dinov, Morteza Noshad, Jerome Choi and Yuming Sun.
This work is supported in part by NIH grants P20 NR015331, P50 NS091856, P30 DK089503, P30AG053760, UL1TR002240, and NSF grants 1734853, 1636840, 1416953, 0716055 and 1023115. Students, trainees, scholars, and researchers from SOCR, BDDS, MNORC, MIDAS, MADC, MICHR, and the broader R-statistical computing and Python communities have contributed ideas, code, and support.
- Noshad, M, Choi, J, Sun, Y, Hero, A, Dinov, ID. (2021) A data value metric for quantifying information content and utility, Journal of Big Data, DOI: 10.1186/s40537-021-00446-6, in print.