This is the official code repository Code for the Pytorch implementation of RemoCap More details in Project page
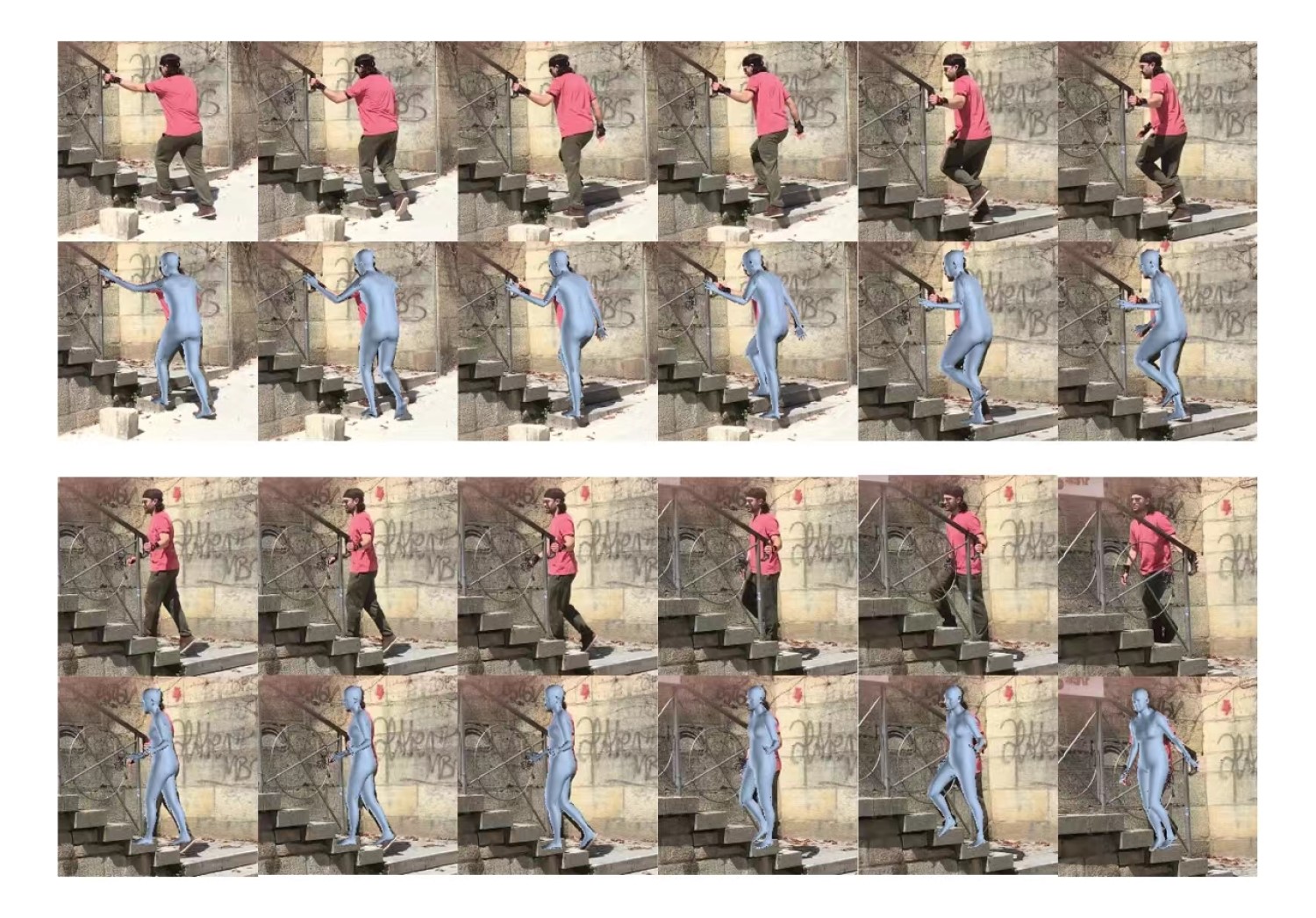
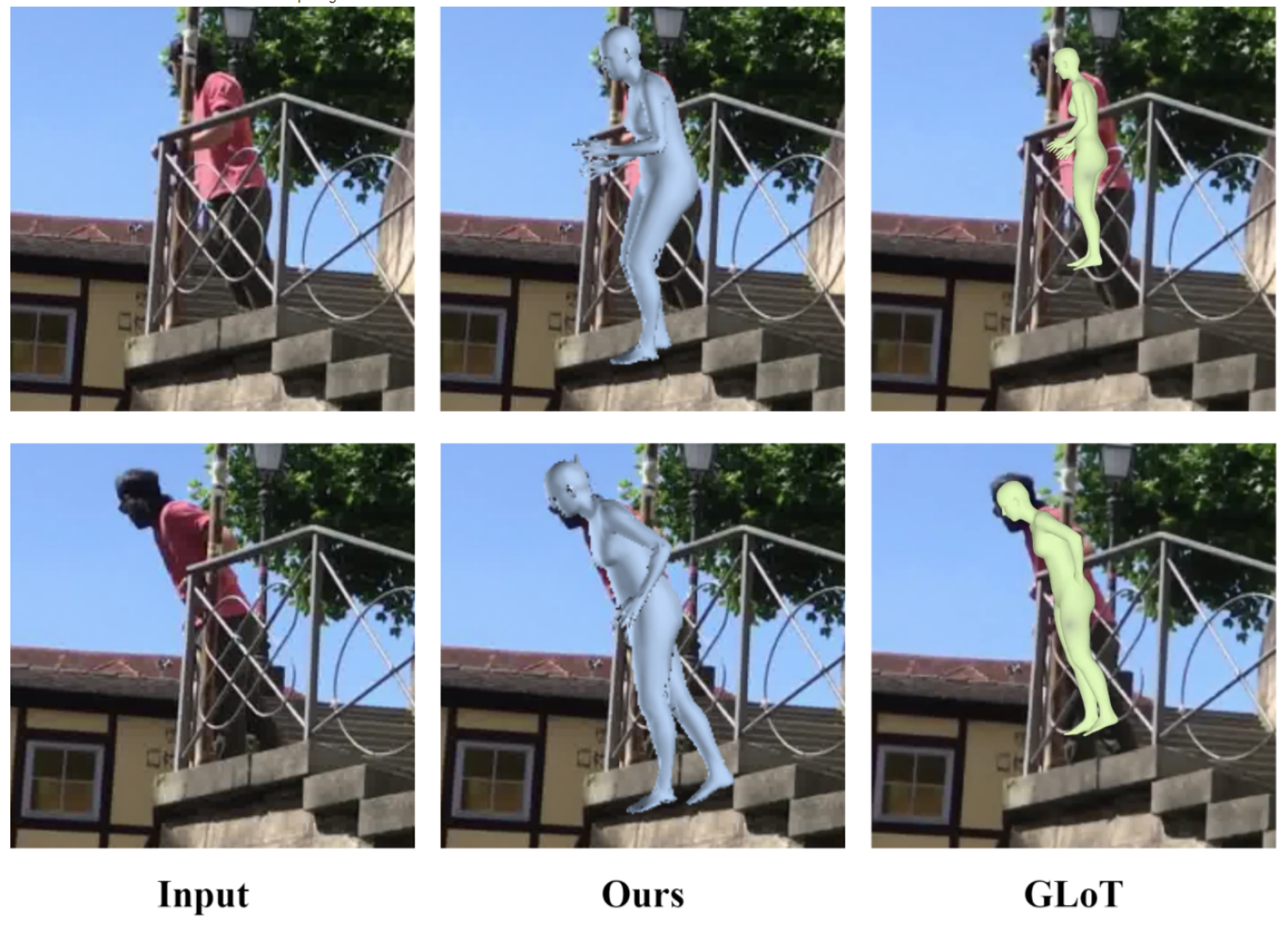
Here are the results of our reconstruction comparing the current SOTA methods GloT.
The base codes are largely borrowed from FasterMETRO and PointHMR.
# We suggest to create a new conda environment with python version 3.8
conda create --name STDF python=3.8
# Activate conda environment
conda activate STDF
# Install Pytorch that is compatible with your CUDA version
# CUDA 10.1
conda install pytorch==1.7.1 torchvision==0.8.2 cudatoolkit=10.1 -c pytorch
# CUDA 10.2
conda install pytorch==1.7.1 torchvision==0.8.2 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
# CUDA 11.1
conda install pytorch==1.8.0 torchvision==0.9.0 cudatoolkit=11.1 -c pytorch -c conda-forge
# Install apex
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/apex.git
cd apex
python setup.py install --cuda_ext --cpp_ext
cd ..
# Install OpenDR
pip install matplotlib
pip install git+https://gitlab.eecs.umich.edu/ngv-python-modules/opendr.git
# Install STDFormer
git clone --recursive https://github.com/STDFormer-3D-Human-Mesh-Recovery/STDFormer.git
cd STDFormer
Unzip the file STDFormer/src/model.zip
python setup.py build develop
# Install requirements
pip install -r requirements(1).txt
pip install ./manopth/.
pip install --upgrade azureml-core
Please refer to PointHMR. directly for dataset download and processing.
python /HOME/your......path/STDFormer/src/tools/run_STDFormer_bodymesh_dp_3dpw.pyPlease download the STDFormer 3DPW Datatset weights we provide to /STDFormer/3dpw_checkpoint/state_dict.bin STDFormer_checkponit_3DPW
#You need change yourself path
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#########################################################
# Data related arguments
#########################################################
parser.add_argument("--data_dir", default='datasets', type=str, required=False,
help="Directory with all datasets, each in one subfolder")
parser.add_argument("--train_yaml", default='/HOME/HOME/data/PointHMR/datasets/3dpw/train.yaml', type=str, required=False,
help="Yaml file with all data for training.")
parser.add_argument("--val_yaml", default='/HOME/HOME/data/PointHMR/datasets/3dpw/test_has_gender.yaml', type=str, required=False,
help="Yaml file with all data for validation.")
..........................
..............................
#########################################################
# Loading/Saving checkpoints
#########################################################
parser.add_argument("--output_dir", default='/HOME/............./output_3DPWZ_result', type=str, required=False,
help="The output directory to save checkpoint and test results.")
parser.add_argument("--saving_epochs", default=1, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--resume_checkpoint", default="/HOME/.........../STDFormer/3dpw_checkpoint/state_dict.bin", type=str, required=False,
help="Path to specific checkpoint for resume training.")Before the stage involving the participation of the transformer encoder and decoder in reconstruction, when extracting features from the target, one often encounters the following situations, especially in uncertain outdoor environments:
- Multiple individuals appearing in the frame, interacting and correlating with the target person.
- The foreground and background in the frame are highly complex, with the foreground obscuring the target object, and low distinguishability between the background and the target object.
- For video tasks, the previously mentioned scenarios may involve motion, including the movement of the target object and the camera's own pose. Both stationary and moving non-target objects, or strong motion, can interfere with the extraction of target features. Particularly in video tasks, disturbances in motion features accumulate over the temporal axis, resulting in increased noise.
The above three points are categorized by us as spatiotemporal feature coupling, which is the primary reason for the inaccurate extraction of target features.
Therefore, the key to solving the feature coupling problem lies in decoupling the coupled features from both spatial and temporal perspectives to address the three points mentioned above.
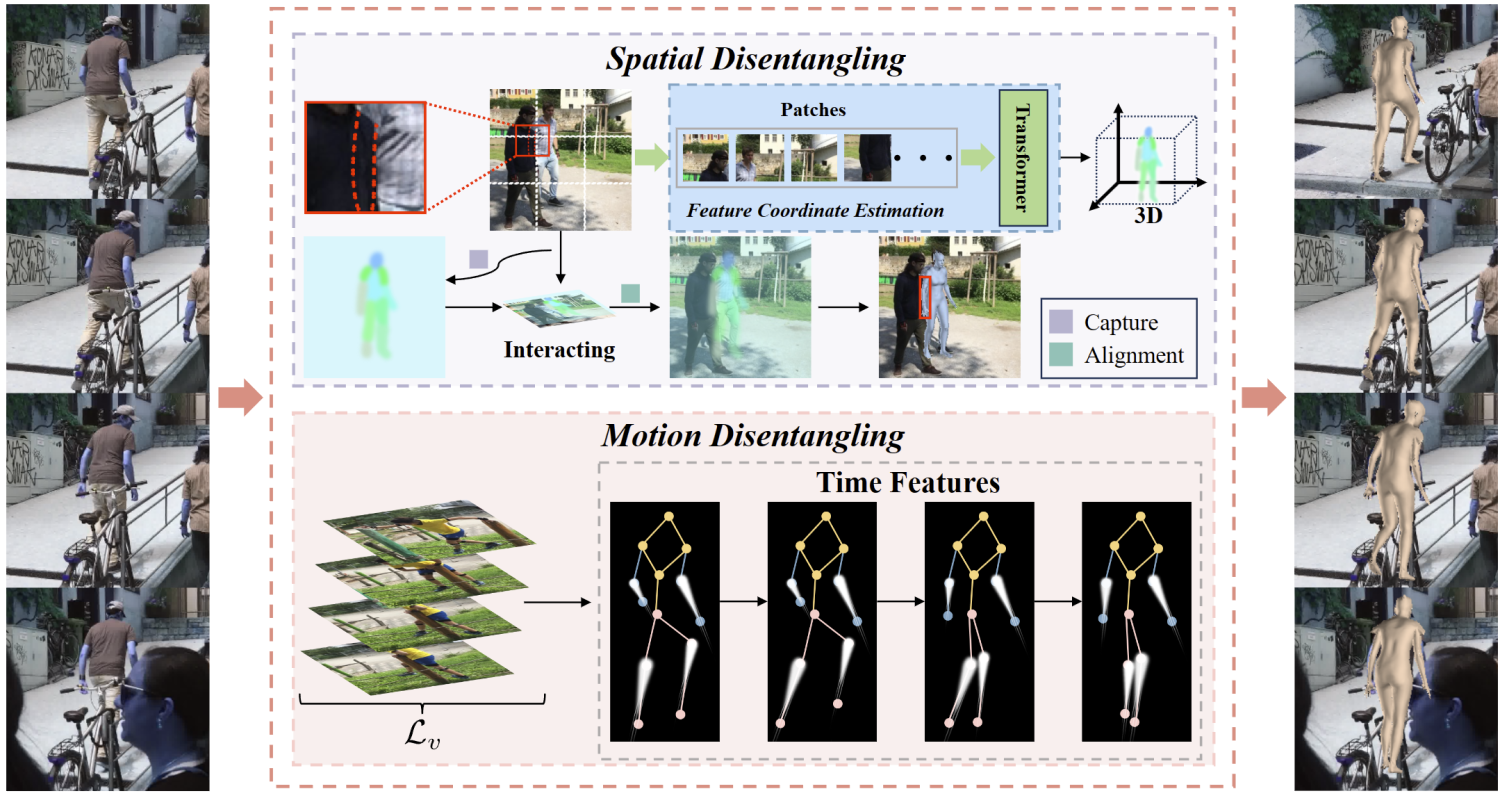
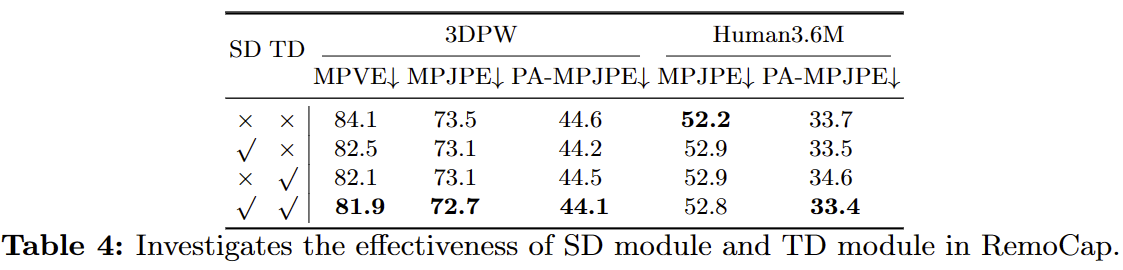
Spatial disentanglement refers to, within a frame, using cross-channel attention learning to supervise target features and non-target features through different channel pooling and loss functions. After discretization, attention is concentrated on the channel where the target features are located, thereby enhancing the learning of target features within the frame and reducing attention to non-target features.
Temporal disentanglement involves forming a feature space based on sequential inputs, then learning the differences in features on the temporal sequence level through cross-channel learning. According to the attention weights of different channels, temporal decoupling is performed in the feature space to separate target features and non-target features on the temporal sequence level, which includes motion-related non-target features.
In the future we consider being able to transfer our task to the reconstruction of the hand task, as our approach is model-free should give good results. On the other hand, we will continue to explore the advantages of the model-free approach over the parametric model approach in video tasks. For example, the model-free approach is able to adequately match the silhouette features, gender, and age of the target person when reconstructing the human body.
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.