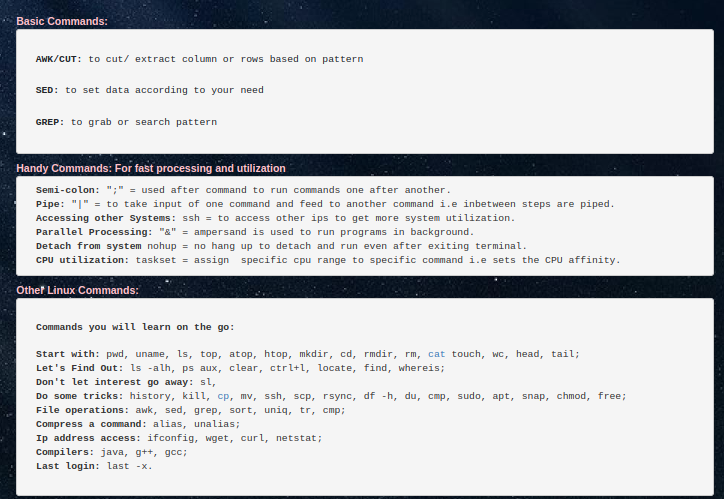
- AWK: A powerful text processing tool used to extract and manipulate data in columns based on patterns.
- CUT: A command to extract specific sections of lines in a file, often used for cutting out fields or columns.
- SED: Stream editor used for parsing and transforming text. It's useful for text substitution, deletion, insertion, and more.
- GREP: A command-line utility for searching plain-text data sets for lines that match a regular expression or pattern.
- Semicolon
;: Used to run multiple commands sequentially. Each command runs after the previous one completes. - Pipe
|: Takes the output of one command and passes it as input to another, allowing for complex command chaining.
- SSH: Securely access remote systems over a network to utilize their resources.
- Ampersand
&: Runs a command in the background, allowing you to continue using the terminal for other tasks. - Nohup: Run a command even after the terminal is closed by detaching it from the session.
- Taskset: Set the CPU affinity for a command, assigning it to specific CPU cores for better resource management.
pwd: Print the current working directory.uname: Show system information (kernel name, version, etc.).ls: List directory contents.top,atop,htop: Monitor system processes and resource usage.
mkdir: Create a new directory.cd: Change the current directory.rmdir,rm: Remove directories and files.cat: Concatenate and display file content.touch: Create an empty file or update the timestamp of an existing file.wc: Count lines, words, and characters in a file.head,tail: Display the beginning or end of a file.
ls -alh: List files with detailed information in human-readable format.ps aux: Display detailed information about active processes.clear,ctrl+l: Clear the terminal screen.locate,find,whereis: Find files or directories on the system.
sl: A fun command to display an animated steam locomotive (install it withsudo apt install sl).history: Display the history of commands entered in the terminal.kill: Terminate processes by ID.cp,mv: Copy and move files or directories.ssh,scp,rsync: Securely transfer files between systems.df -h: Display disk space usage in a human-readable format.du: Estimate file and directory space usage.cmp: Compare two files byte by byte.sudo: Execute commands with superuser privileges.apt,snap: Package management commands for installing, updating, and removing software.chmod: Change file permissions.free: Display memory usage.
awk,sed,grep: Extract, manipulate, and search text data.sort: Sort lines of text files.uniq: Report or omit repeated lines in a file.tr: Translate or delete characters in text.cmp: Compare two files and report differences.
alias,unalias: Create and remove shortcuts for commands.ifconfig: Display or configure network interfaces.wget,curl: Download files from the internet.netstat: Display network connections, routing tables, and interface statistics.
java,g++,gcc: Compile and run Java, C++, and C programs.
last -x: Show the last logins on the system.
This guide provides a solid foundation for navigating and utilizing Linux efficiently. Explore these commands and gradually build your expertise!
Keep on Learning and Executing...🏃🏻
contact@: bioinformaticsfuture@gmail.com