- Open source job scheduling library
- It can be used to create simple to complex schedules for executing tens, hundreds, or even ten thousands of jobs
- Jobs - tasks defined as standard Java components that may execute anything we program them to do
- Freely usable and licensed under Apache 2.0 license.
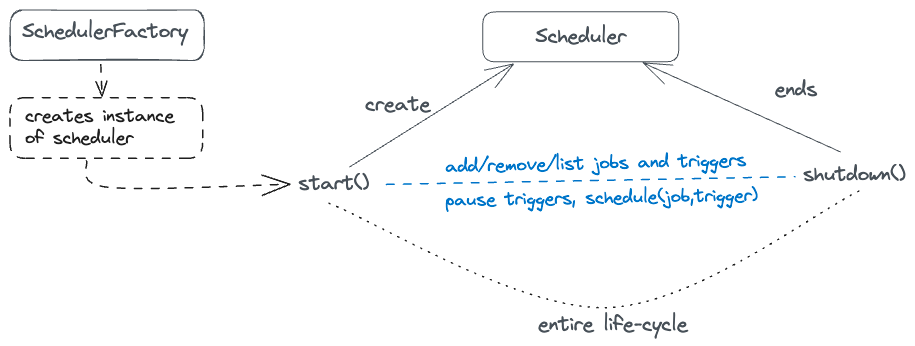
A scheduler should be instantiated before it can be used. It's instantiated using the SchedulerFactory.
Once the scheduler is instantiated it can be started, put in standby-mode and shutdown. Once shutdown, schedulers
need to be re-instantiated before restarting. Triggers cannot be fired until the scheduler is started or
is in pause mode.
- responsible for managing runtime environment
- maintains everything required for scheduling jobs, managing listeners, clustering, transactions and job persistence.
- maintains registry of JobDetails, Listeners and Triggers
- executes Job and Listeners when their associated Trigger is fired
- factory interface for creating instance of Scheduler based on configured environment
- can be configured via properties, yml or java code
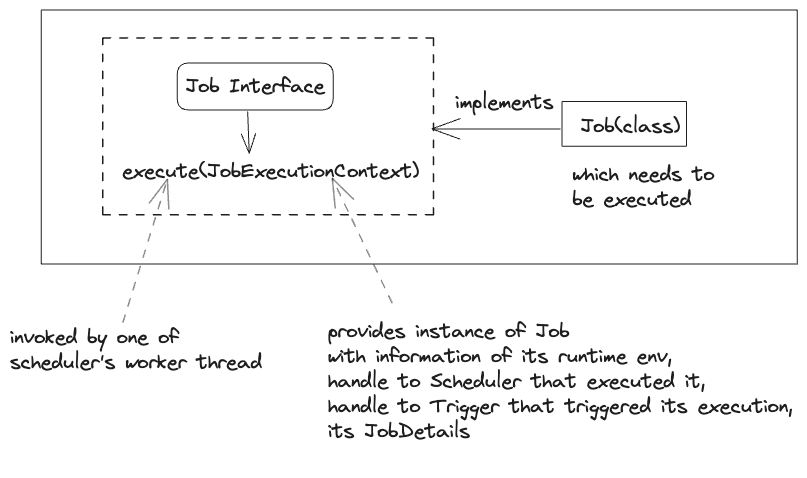
- interface which is implemented by the class that contains the application code to execute on a trigger is fired.
- Interface implemented by the class which contains the execution-specific information about a job.
- scheduler registers the instance of Triggers with JobDetails.
- When trigger is fired, scheduler picks a thread from thread pool and uses the properties from JobDetails to execute the Job on that thread.
- typical properties: job name, job class, job data map, isConcurrentExecutionDisallowed etc.
- Builder pattern used to construct instance of JobDetail
- Configuration to decide when/how-long/how-many-times to run a Job.
- Quartz ships with a handful of different trigger types, but the most commonly used types are SimpleTrigger and CronTrigger.
- SimpleTrigger is handy if you need ‘one-shot’ execution (just single execution of a job at a given moment in time), or if you need to fire a job at a given time, and have it repeat N times, with a delay of T between executions.
- CronTrigger is useful if you wish to have triggering based on calendar-like schedules - such as “every Friday, at noon” or “at 10:15 on the 10th day of every month.”
- builder pattern to create an instance of Trigger
- pool of threads reserved by Quartz to run jobs
- When started, the framework initializes a set of worker threads that are used by the Scheduler to execute Jobs
- place where scheduler keeps information about job/trigger etc
- Used when using a JDBCJobSore.
- receive information related to triggers, if configured
- receive notification of events within scheduler itself, like addition/removal of a job/trigger
Ref : Quartz Scheduler with SpringBoot
1.Add dependencies Gradle Dependencies:
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-quartz'
// FOR QUARTZ POOL
// https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.mchange/c3p0
implementation 'com.mchange:c3p0:0.9.5.5'Maven Dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-quartz</artifactId>
</dependency>2.Properties
server.port=9091
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.hibernate.show-sql=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/local_crm
spring.datasource.username=expressuser
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
#============================================================================
# Configure JobStore - JDBC
#============================================================================
# store type either in-memory or jdbc to store in D
spring.quartz.job-store-type=jdbc
# to create tables used to store job and other scheduling activities
spring.quartz.jdbc.initialize-schema=always
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.misfireThreshold=1000
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.useProperties=true
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.tablePrefix=QRTZ_
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.class=org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.JobStoreTX
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.driverDelegateClass=org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.PostgreSQLDelegate
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.dataSource=quartzDS
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.dataSource.quartzDS.URL=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/local_crm
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.dataSource.quartzDS.user=expressuser
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.dataSource.quartzDS.password=password
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.dataSource.quartzDS.driver=org.postgresql.Driver
#============================================================================
# Configure Main Scheduler Properties
#==========================================================================
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.scheduler.instanceName=agencyheight
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.scheduler.instanceId=AUTO
#============================================================================
# Configure ThreadPool
#============================================================================
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.threadPool.class=org.quartz.simpl.SimpleThreadPool
# if you want to provide multiple threads to run jobs
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.threadPool.threadCount=1
#spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.threadPool.threadPriority=5
#============================================================================
# Configure Cluster properties
#============================================================================
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.isClustered=true
# Frequency (in milliseconds) at which this instance checks-in to cluster.
# Affects the rate of detecting failed instances.
# Defaults to 7500 ms.
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.clusterCheckinInterval=1000
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.scheduler.collectionPrefix=yourCluster
# Time in millis after which a trigger can be considered as expired.
# Defaults to 10 minutes:
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.scheduler.triggerTimeoutMillis=1200000
# Time in millis after which a job can be considered as expired.
# Defaults to 10 minutes:
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.scheduler.jobTimeoutMillis=1200000
# Time limit in millis after which a trigger should be treated as misfired.
# Defaults to 5000 ms.
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.scheduler.misfireThreshold=10000
# When using jdbc job store to avoid lock issues
spring.quartz.properties.org.quartz.jobStore.acquireTriggersWithinLock = true
3.Configuration
import java.util.Properties;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.quartz.spi.TriggerFiredBundle;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzProperties;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.SchedulerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.SpringBeanJobFactory;
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SchedulerConfiguration {
private final QuartzProperties quartzProperties;
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private Properties getQuartzProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.putAll(quartzProperties.getProperties());
return properties;
}
/**
* When Spring will use SchedulerFactoryBean to create Scheduler, SchedulerFactoryBean will set
* this SpringBeanJobFactory in the Scheduler. Then upon each trigger fire, createJobInstance of
* this SpringBeanJobFactory will be called And we're explicitly weaving the beans from
* application context. * @return
*/
@Bean
public SpringBeanJobFactory createSpringBeanJobFactory() {
return new SpringBeanJobFactory() {
@Override
protected Object createJobInstance(TriggerFiredBundle bundle) throws Exception {
final Object job = super.createJobInstance(bundle);
applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().autowireBean(job);
return job;
}
};
}
/**
* we create only SchedulerFactoryBean and spring implicitly uses it to create Scheduler
*
* @return SchedulerFactoryBean
*/
@Bean
public SchedulerFactoryBean createSchedulerFactoryBean(SpringBeanJobFactory jobFactory) {
jobFactory.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
SchedulerFactoryBean schedulerFactory = new SchedulerFactoryBean();
schedulerFactory.setQuartzProperties(getQuartzProperties());
schedulerFactory.setAutoStartup(Boolean.TRUE);
schedulerFactory.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
schedulerFactory.setJobFactory(jobFactory);
schedulerFactory.setApplicationContextSchedulerContextKey("applicationContext");
return schedulerFactory;
}
}4.Job Service
After we have configured our scheduler, we create a service that uses the configured scheduler and creates(update, replace and so on) job.
package com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.service;
import static org.quartz.JobKey.jobKey;
import com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.builder.JobBuilderUtil;
import com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.builder.TriggerBuilderUtil;
import com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.model.JobDescriptor;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Set;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.quartz.JobBuilder;
import org.quartz.JobDataMap;
import org.quartz.JobDetail;
import org.quartz.Scheduler;
import org.quartz.SchedulerException;
import org.quartz.Trigger;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author : sabu.shakya
* @created : 2023-06-28
**/
@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class JobService {
private final Scheduler scheduler;
private final JobBuilderUtil jobBuilder;
private final TriggerBuilderUtil triggerBuilder;
/**
* @param jobDescriptor CREATES JOB BASED ON JOB DESCRIPTOR AND SCHEDULES AS PER THE TRIGGER
* DESCRIPTION
*/
public void createJob(JobDescriptor jobDescriptor) {
JobDetail jobDetail = jobBuilder.buildJobDetail(jobDescriptor);
Set<Trigger> triggers = triggerBuilder.buildTriggers(jobDescriptor);
try {
log.info("Scheduling job with key : {}", jobDetail.getKey());
scheduler.scheduleJob(jobDetail, triggers, Boolean.FALSE);
log.info("Job with key : {} scheduled ", jobDetail.getKey());
} catch (SchedulerException e) {
log.error("Could not schedule job with key : {}, error:{}", jobDetail.getKey(),
e.getLocalizedMessage(), e);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
}
// FOR DETAILS LOOK INTO REPO
}5.Create Job
The above jobService can now be used to create jobs. We need to construct the a job class that contains that contains the execution code when scheduler triggers the job.
We will be creating a job that sends a simple text email.
package com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.job;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.quartz.JobDataMap;
import org.quartz.JobExecutionContext;
import org.quartz.JobExecutionException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.mail.SimpleMailMessage;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author : sabu.shakya
* @created : 2023-07-06
**/
@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SendEmail extends AbstractJob {
@Value("${spring.mail.username}")
private String email;
private final JavaMailSender javaMailSender;
@Override
public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
this.log(context);
JobDataMap jobDataMap = this.getJobDataMap(context);
this.sendEmail(
(String) jobDataMap.get("toEmail"),
(String) jobDataMap.get("subject"),
(String) jobDataMap.get("message"));
}
public void sendEmail(String toEmail, String subject, String message) {
log.info("Preparing to send email to : {} ", toEmail);
SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage();
mailMessage.setTo(toEmail);
mailMessage.setSubject(subject);
mailMessage.setText(message);
mailMessage.setFrom(email);
javaMailSender.send(mailMessage);
log.info("Completed sending email.");
}
}6.Schedule Job We can now schedule this job whenever required. For now we'll schedule the email job after 30 seconds of invocation through api.
package com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.service;
import static com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.constants.JobConstants.EMAIL_JOB;
import com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.model.JobDescriptor;
import com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.model.MailRequest;
import com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.model.TriggerDescriptor;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MailService {
private final JobService jobService;
public void sendEmail(MailRequest mailRequest) {
Map<String, Object> data = buildData(mailRequest);
JobDescriptor jobDescriptor = buildJobDescriptor(data);
jobService.createJob(jobDescriptor);
}
private static JobDescriptor buildJobDescriptor(Map<String, Object> data) {
JobDescriptor jobDescriptor = new JobDescriptor();
jobDescriptor.setGroup("email");
// NEEDS TO BE UNIQUE
jobDescriptor.setName("mailTo:"+ data.get("toEmail")+ UUID.randomUUID());
jobDescriptor.setData(data);
jobDescriptor.setType(EMAIL_JOB);
jobDescriptor.setDescription("Schedule send email.");
TriggerDescriptor triggerDescriptor = buildTrigger();
jobDescriptor.setTriggerDescriptors(Collections.singletonList(triggerDescriptor));
return jobDescriptor;
}
private static TriggerDescriptor buildTrigger() {
TriggerDescriptor triggerDescriptor = new TriggerDescriptor();
triggerDescriptor.setFireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(30));
return triggerDescriptor;
}
private static Map<String, Object> buildData(MailRequest mailRequest) {
Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>();
data.put("toEmail", mailRequest.getToEmail());
data.put("subject", mailRequest.getSubject());
data.put("message", mailRequest.getMessage());
return data;
}
}package com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.controller;
import com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.model.MailRequest;
import com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.service.MailService;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/schedule")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MailController {
private final MailService mailService;
@PostMapping("/mail")
public ResponseEntity<?> triggerEmailJob(@RequestBody @Valid MailRequest mailRequest) {
mailService.sendEmail(mailRequest);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
}Mail Configuration
package com.sabu.schedulerquartzpoc.configuration;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSenderImpl;
@Configuration
public class MailConfiguration {
@Value("${spring.mail.username}")
private String email;
@Value("${spring.mail.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public JavaMailSender getJavaMailSender() {
JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender = new JavaMailSenderImpl();
mailSender.setHost("smtp.gmail.com");
mailSender.setPort(587);
mailSender.setUsername(email);
mailSender.setPassword(password);
Properties props = mailSender.getJavaMailProperties();
props.put("mail.transport.protocol", "smtp");
props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true");
props.put("mail.smtp.starttls.enable", "true");
props.put("mail.debug", "true");
return mailSender;
}
}Add these to properties file:
spring.mail.host=smtp.gmail.com
spring.mail.port=587
spring.mail.username=your@email.com
spring.mail.password=password
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.auth=true
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.starttls.enable=trueReferences: