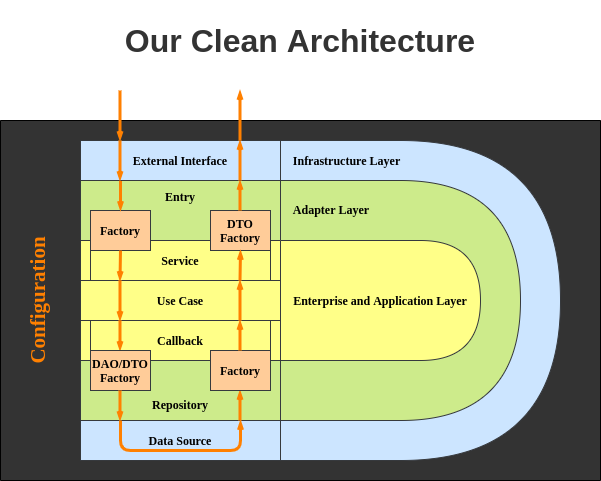
An implementation of Clean Architecture in Scala. We will implement a simple blog application using Clean Architecture in Scala. The bellow image is a schematic of our clean architecture style.
I will walk through the following projects to show the process of creating a Scala Application using Clean Architecture and some frameworks:
Directories and abstraction of contract.service.Service.
For more information about this section visit my blog - Clean Architecture in Scala.
Design of classes and implementation of simple class-related use cases.
For more information about this section visit my blog - Implementing a Clean Architecture Application in Scala - Part 1 .
Signature of services and callbacks.
- Services should extend
c.s.Serviceand have only one public method which isc.s.Service.call. - Callbacks should contain only the abstraction of CRUD operations without any logic.
- Callbacks do not take execution context as a parameter and should take one from their parent module (R.T. #4 Application).
For more information about this section visit my blog - Implementing a Clean Architecture Application in Scala - Part 1 .
Implementation of repositories, use cases, and modules.
- Repositories should implement callbacks and have only public members which their parent has.
- Use cases should implement services and should have only one public member which is
c.s.Service.call. - Use cases should use instances of callbacks (NOT repositories).
- All configurations should be placed in
modulespackage. - There are three essential modules
- Loading the config and validating it happens in
modules.ConfigModule. - Callbacks should be bound to repositories in
modules.CallbackModule. - Services should be bound to use cases in
modules.ServiceModule.
- Loading the config and validating it happens in
- Each type of external data source and entry should have exactly one module.
- All repositories using database should extend
modules.DatabaseModule - All repositories using REST API and a special HTTP client should extend
modules.RESTModule
- All repositories using database should extend
Here are some tips about config files.
- An important security point is NOT to commit config files.
Put some entries to ignore config files in
.gitignorefile.application.confapplication.staging*.confapplication.prodcution*.conf
- Store all config files in one directory i.e. the project root,
resources. I recommend usingresourcesdirectory. - It is essential to specify the template of config file, and I recommend committing
application.template.confwith dummy values. - There are multiple ways to specify the config file which we want to run the application with.
We are using
configlibrary ofcom.typesafeto load configs.- It utilises HOCON files to load configs.
- Expectedly, this library offers
c.t.c.ConfigFactory.parseFilefunction to parse config file. You may set an environment variable to specify the config file and load it using this function. - A more elegant method is to use
-DConfig.fileJVM option and use this functionConfigFactory.load().withFallback(ConfigFactory.defaultApplication()).resolve.
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
RESERVED
RESERVED
Initialized.
RESERVED
Initialized.
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
For more information about this repository, visit my blog.
Please create an issue to suggest a new concept, framework, or library.
Implement current concepts using mentioned frameworks or libraries, and send a PR. PRs are always welcome.