Please give this repo a ⭐ if you like it. Thanks. 😊
Source (GeeksForGeeks)
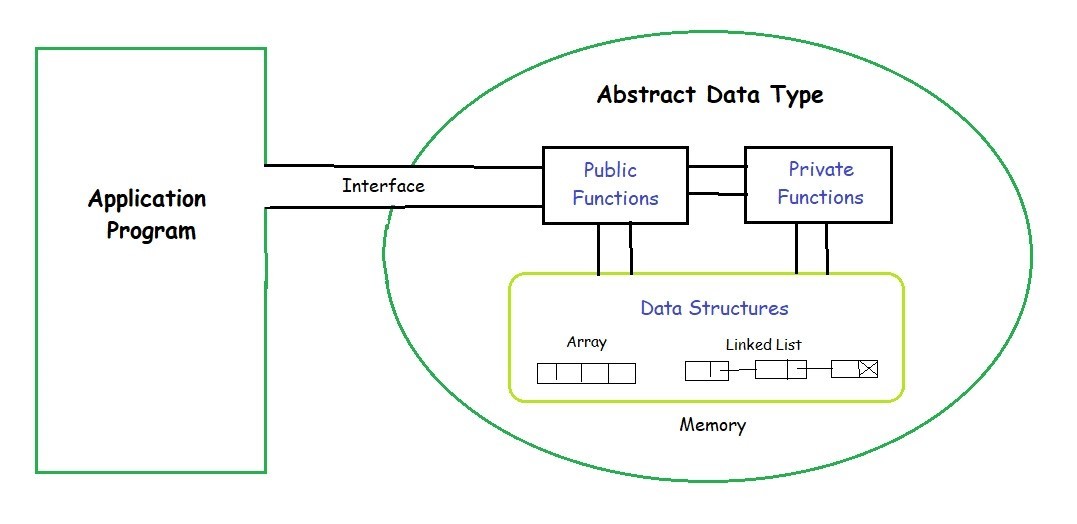
ADT is a class of object whose behaviour is specified by a set of values and a set of operations. It does not specify how data will be stored in memory or which algorithms will be utilised to carry out the actions. It is named "abstract" because it provides a view that is independent of implementation.
- ArrayADT
The array is a basic abstract data type that holds an ordered collection of items accessible by an integer index. These items can be anything from primitive types such as integers to more complex types like instances of classes. Since it's an ADT, it doesn't specify an implementation, but is almost always implemented by an array (data structure) or dynamic array.
class ArrayADT
{
private:
int capacity,lastindex;
int *ptr;
public:
void append();
void insert();
void deleteElement();
void display();
void display();
void edit();
int getData();
int size();
}; - StackADT
Stack is a linear data structure in which the insertion and deletion operations are performed at only one end. In a stack, adding and removing of elements are performed at a single position which is known as "top". That means, a new element is added at top of the stack and an element is removed from the top of the stack. In stack, the insertion and deletion operations are performed based on LIFO (Last In First Out) principle.
class stackADT{
private:
int top;
int capacity;
int* arr;
public:
void push();
void pop();
int peek();
int size();
bool isEmpty();
}; - ListADT
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers.
class listADT{
private:
listADT* next;
int data;
public:
void insertAtHead();
void insertAtTail();
void insertAtLocation();
void deleteFromHead();
void deleteFromTail();
void displayList();
}; These were few examples of ADTs.
Features of ADT:
- Abstraction: The user does not need to know the implementation of the data structure.
- Better Conceptualization: ADT gives us a better conceptualization of the real world.
- Robust: The program is robust and has the ability to catch errors.