- Modal dialog management.
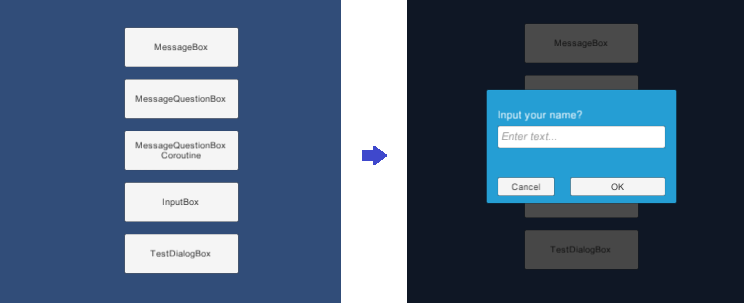
- Common dialog boxes such as MessageBox and InputBox.
This library provides basic modal dialog managements on Unity-GUI. Modal dialog box works like a function which gets input argument, does work, and returns return value. When a modal dialog box shows, input of other windows under showing dialog box will be blocked.
// show up TestDialogBox with an arugment
var handle = UiManager.Instance.ShowModalRoot<TestDialogBox>("Input your name?");
// waits for dialog to finish it's work
yield return StartCoroutine(handle.WaitForHide());
// gets return value from dialog
Debug.Log(handle.ReturnValue);DialogBox should inherit UiDialog.
When dialog box shows up, OnShow handler will be invoked with param is passed by ShowModalRoot.
When work done and there is a return value, Hide method can be used.
//
public class TestDialogBox : UiDialog
{
public override void OnShow(object param)
{
// gets an argument from caller
Message.text = (string)param;
Input.text = "";
}
public void OnOkButtonClick()
{
// returns values to caller
Hide(Input.text);
}
}It's quite simple to show modal dialog boxes but there are several ways for showing dialog box.
ShowModalPrefab: Use the prefab dialog box. Whenever show up new dialog, dialog box will be instantiated.ShowModalTemplate: Use the template dialog box in the scene. Whenever show up new dialog, dialog box will be cloned.ShowModal<T>: Use a passed dialog box whose type is T.ShowModalRoot<T>: Use a named dialog box underCanvas/DialogBoxin the scene.
For getting return value of it, there are two ways.
First one is using Hidden callback.
var handle = UiManager.Instance.ShowModalRoot<TestDialogBox>("Input your name?");
handle.Hidden += (dlg, val) => { Debug,Log(val); };Second one is using coroutine. It's quite useful under modal chaining.
var handle = UiManager.Instance.ShowModalRoot<TestDialogBox>("Input your name?");
yield return StartCoroutine(handle.WaitForHide());
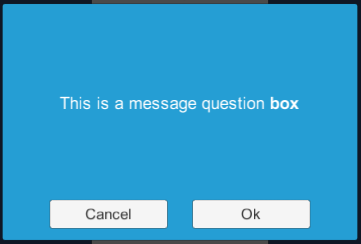
Debug.Log(handle.ReturnValue);UiMessageBox.Show("This is a message question <b>box</b>",
UiMessageBox.QuestionType.OkCancel,
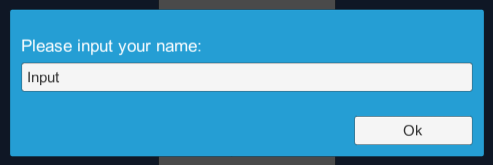
r => { /* Callback */ });UiInputBox.Show("Please input your name:",
"Input",
r => { /* Callback */ });