This project implements an LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) model for predicting the future trends of the NASDAQ 100 index. The model is trained using various combinations of hyperparameters to determine the optimal configuration for accurate predictions.
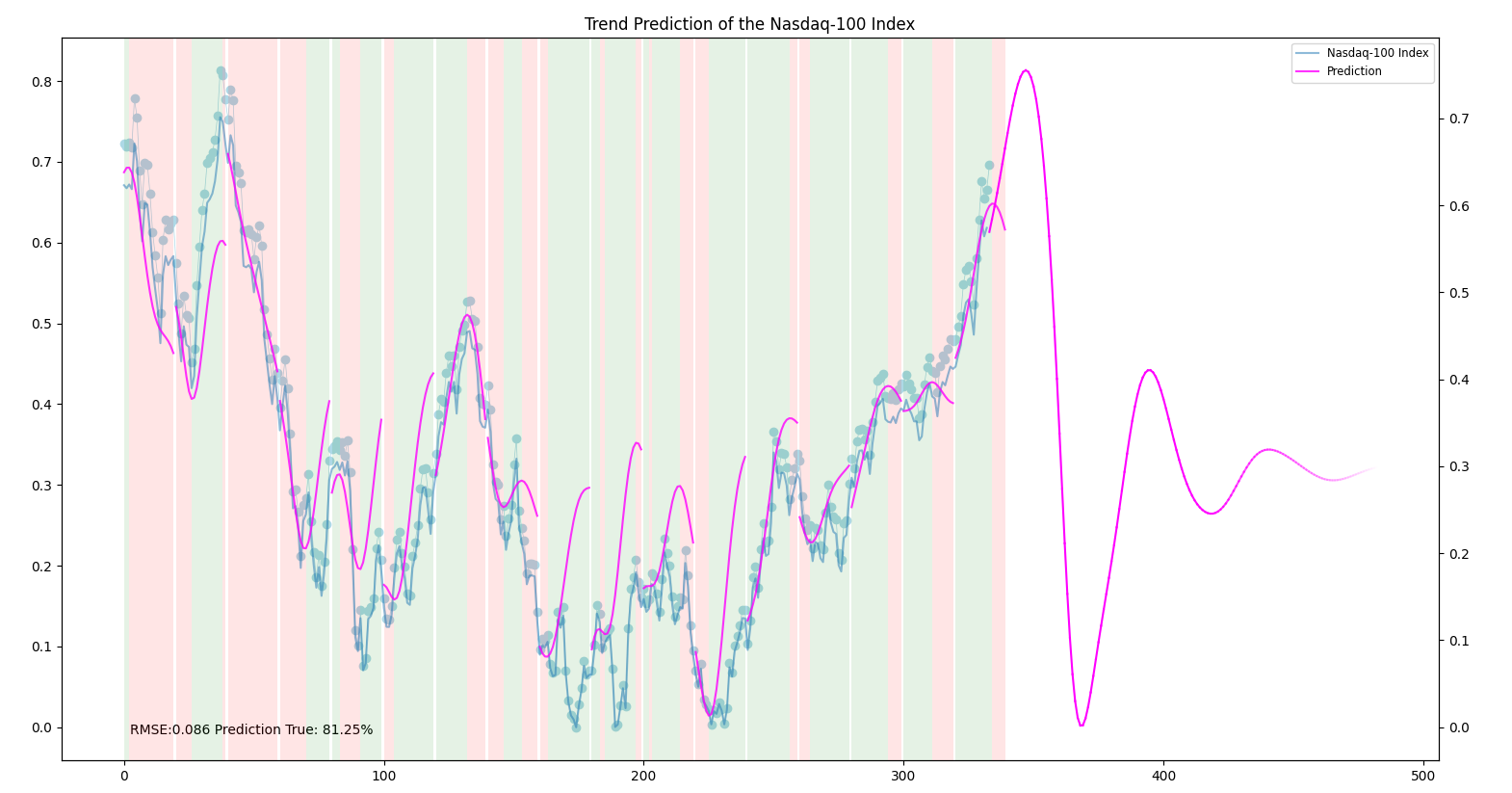
Note that you can utilize this code to forecast the trends of any stocks or other financial products.
The LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) is a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture that is well-suited for sequence prediction tasks, such as time series forecasting. It addresses the limitations of traditional RNNs by introducing specialized memory cells that can selectively store and retrieve information over long periods of time. LSTMs are particularly effective when dealing with sequences that exhibit long-term dependencies and complex patterns.
In this code, the LSTM model is used for predicting stock prices in the NASDAQ 100 index. Let's dive into the key components and parameters of the LSTM model:
The LSTM model consists of one or more LSTM layers. Each layer contains multiple LSTM units, also known as memory cells. These cells have the ability to retain and utilize information over extended sequences, allowing the model to capture long-term dependencies. The number of LSTM layers is controlled by the lstm_layers parameter in the configuration file.
The neurons_per_lstm_layer parameter determines the number of neurons (memory cells) in each LSTM layer. Increasing the number of neurons can enhance the model's capacity to capture complex patterns, but it also increases the computational requirements. The range of neurons_per_lstm_layer is specified in the configuration file, allowing you to experiment with different values.
The input shape of the LSTM layers is determined by the input_timesteps and input_dim parameters. input_timesteps corresponds to the number of time steps in each input sequence, while input_dim represents the number of features or variables included in the input data. The input shape is defined as (input_timesteps, input_dim).
Dropout is a regularization technique used to prevent overfitting in neural networks. It randomly sets a fraction of input units to 0 during training, which helps to reduce the model's reliance on specific features and improves its generalization ability. A dropout layer is inserted after each LSTM layer with a dropout rate.
The final layer of the LSTM model is a dense layer with a linear activation function. This layer maps the output of the preceding LSTM layers to a single output value, representing the predicted stock price.
Before training the LSTM model, it needs to be compiled by specifying the loss function and optimizer. In your code, the mean squared error (mse) is used as the loss function, which measures the discrepancy between the predicted and actual values. The Adam optimizer is chosen for updating the model's weights during training.
By varying the hyperparameters such as the number of LSTM layers, neurons per layer, and training configurations, you can experiment with different combinations to find the optimal LSTM model for predicting stock prices in the NASDAQ 100 index.
Please note that this explanation assumes some familiarity with deep learning concepts. If you need further clarification or have specific questions about any part of the LSTM implementation, feel free to ask!
run.py: This script is the main entry point of the program. It loads the configuration, prepares the data, trains the model with various hyperparameter combinations, and saves the results.model.py: This module defines theModelclass, which handles the building, training, and prediction of the LSTM model.data_processor.py: This module contains theDataLoaderclass, responsible for loading and preprocessing the data.config.json: This JSON file contains the configuration parameters for data processing, training, and model architecture.
Note: This project requires Python 3.11.
- Make sure you have the required dependencies installed. You can install them by running the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txt. - Place your data file named
nasdaq100.csvin thedatadirectory. - Adjust the hyperparameter ranges and other settings in the
config.jsonfile if needed. - Run the code using the command:
python run.py. - The program will train the LSTM model with different hyperparameter combinations and save the results in the
saved_modelsdirectory. - The final model properties will be saved in a JSON file named
model_properties.json, which includes the RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) and trend prediction accuracy for each model configuration.
The LSTM model architecture is defined in the model.py file. It consists of the following layers:
- LSTM Layers: The number of LSTM layers can be configured in the
config.jsonfile. Each LSTM layer has a specified number of neurons, input timesteps, and input dimensions. - Dropout Layers: A dropout layer is added after each LSTM layer to prevent overfitting. The dropout rate can be adjusted in the
config.jsonfile. - Hidden LSTM Layers: This layer is added to stack multiple LSTM layers together, improving the model's capacity to capture complex patterns.
- Dense Layer: A dense layer with linear activation is added as the output layer, predicting a single value.
The config.json file allows you to specify various hyperparameters for data processing, training, and model architecture. Here are the explanations of some important hyperparameters used in the LSTM model:
epochs: The range of epochs to train the model for. The training process will iterate over this range, evaluating each configuration.batch_size: The range of batch sizes to use during training. Different batch sizes will affect the learning dynamics and training time.neurons_per_lstm_layer: The range of the number of neurons in each LSTM layer. Higher numbers can increase the model's capacity to capture complex patterns but may also lead to overfitting.lstm_layers: The range of the number of LSTM layers in the model. Increasing the number of LSTM layers can improve the model's ability to learn hierarchical representations.
An epoch is a complete pass through the entire training dataset. In other words, the number of epochs is the number of times the algorithm has seen the entire dataset during training.
Training a neural network involves iteratively updating the model's weights using different batches of data. After each batch, the weights are adjusted slightly to reduce
the error. An epoch is completed when the algorithm has iterated through all batches of the training dataset.
Multiple epochs are usually required to train a model effectively, as they allow the network to learn from the entire dataset multiple times, refining its internal representations and improving its performance.
Batch Size: The number of training examples used in a single update of the model's weights.
Epoch: One complete pass through the entire training dataset. Multiple epochs allow the model to learn from the data multiple times, improving its performance over time.
After running the code, the program will generate a model_properties.json file in the saved_models directory. This file contains the properties of each trained model configuration, including the RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) and trend prediction accuracy. You can analyze these results to find the best hyperparameter combination for your prediction task.
Additionally, the program generates plots showing the true data, predicted data, and price evolution for each model configuration. These plots can be useful for visualizing the model's performance.
Feel free to adjust the hyperparameters
Please note that the code provided in this repository is intended for educational and learning purposes only. It should not be used as a basis for making investment decisions or as financial advice. The predictions generated by the LSTM model may not accurately reflect future stock prices or market behavior.
Investing in the stock market involves inherent risks, and past performance is not indicative of future results. It is important to conduct thorough research, consult with a qualified financial advisor, and carefully consider your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and financial situation before making any investment decisions.