Introduction
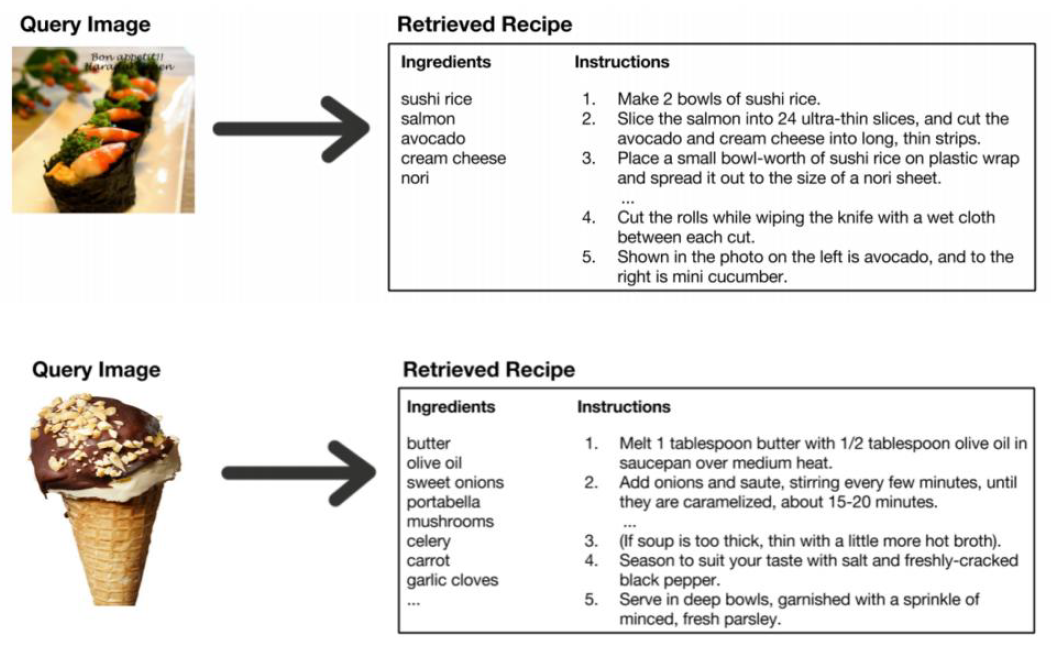
Availability of recipe dataset with matching images and recipe instructions along with ingredients makes possible interesting approaches for cross-modal retrieval. There are large number of user uploaded pictures of food and large number of online recipe collections. One part of the problem is that if a recipe image is provided as a reference and recipe instructions along with ingredients can be retrieved by the system (Image2Recipe). Second part of the problem is that recipe ingredients or name can be used to search and recipe images along with instructions are retrieved (Recipe2Image).
Background
The advent of deep learning has made great strides towards better visual understanding, and generating rich descriptions of visual data. A critical task for the applications such as bi-directional image and text retrieval [2] and image captioning [3] is to learn joint embedding that entails mapping from two or more domains into common latent vector space in which semantically associated inputs are mapped to similar locations.
In 2017, Salvador et al. [1] introduced Recipe1M, a new large-scale, structured corpus of over 1m cooking recipes and 800k food images. As the largest publicly available collection of recipe data, Recipe1M affords the ability to train high capacity models on aligned, multi-modal data. Salvador et al. trained a neural network to find a joint embedding of recipes and images that yields impressive results on an image-recipe retrieval task. Recall@1, Recall@5 and Recall@10 are used as evaluation metric for image-text retrieval task. This project was motivated by the research done at MIT. (http://pic2recipe.csail.mit.edu/)
In this project, I study image-sentence retrieval task i.e. given an input image, the goal is to find the best matching sentences from a list of given sentences in the recipe domain.
Dataset
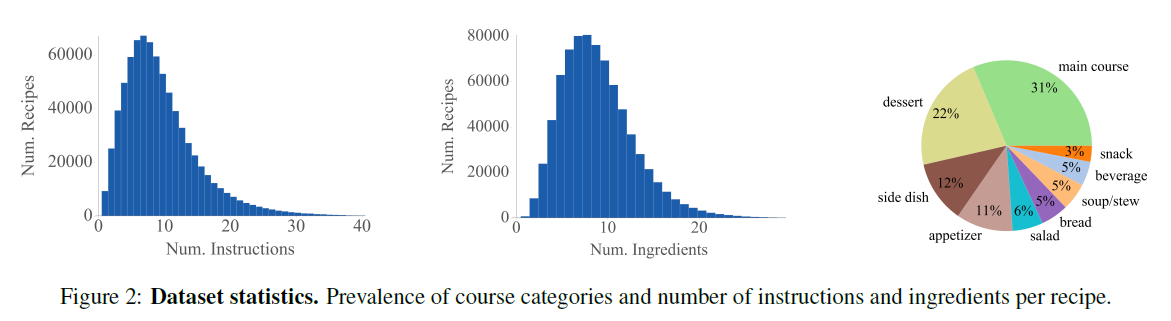
This project is based on Recipe1M dataset released by MIT which includes 402,760 recipes with 887, 536 associated images. Besides the training images, the Recipe1M dataset was split into two dataframes. The 1st dataframe contained the id, ingredients, title, instructions, and original url location of all 1M recipes in the Recipe1M set. The second dataframe contained the ids of only the recipes in Recipe1M set as well as a list of their associated image ids. I preprocessed the dataset to match the image id to its respective recipe title. Pandas python library came handy for data preprocessing task.
Many thanks to Javier Marin (author of the Recipe1M paper) for sharing the dataset for this project.
Hardware
RAM and compute both were challenges with the Recipe1M dataset. The data comprised of 200GB of images and 2GB of recipe information. Initially I used Google Colab for running the code but its RAM(12 GB) was not sufficient. Then I moved to Kaggle Kernel to run my code which provided GPU access, and 16 GB of RAM. Due to hardware limitations I followed an incremental training approach, training on 1000 images in one go.
Model
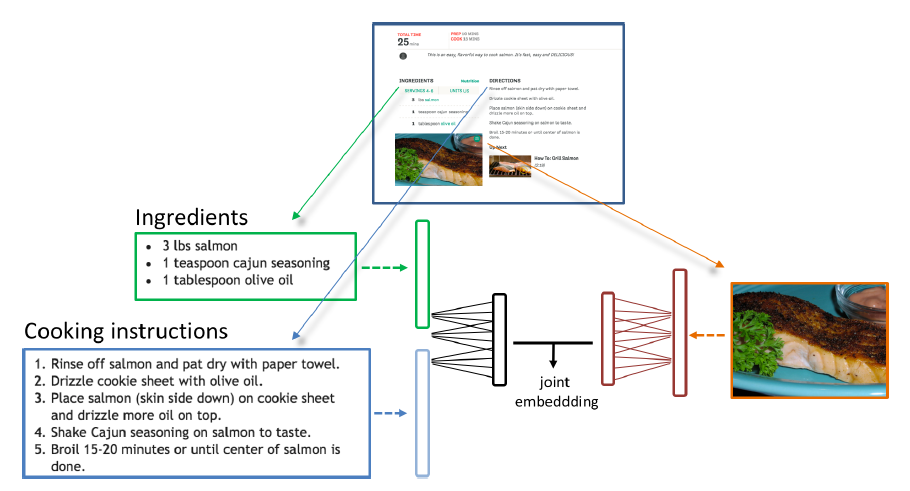
I built a model that projects recipe titles and recipe images in the same representation space, so that an image is close to its title in that space, and far away from dissimilar titles and dissimilar images. This space can be used to label unseen images by searching for the most similar title to its representation.
Image Embeddings
To create image representations, I used ResNet-50 CNN model. The last layer of this model was removed and the activations were taken as input image representation.
Text Embeddings
For text representation, I initially trained Word2Vec model. I started with writing the neural network code for Word2Vec from scratch but the code was not optimized for parallel processing. Later, I switched to Gensim library for Word2Vec computation which provided multi-core option and enabled me to use it on personal laptop (8GB RAM, OctaCore i5 8thGen). For the first state of experimentation, I used a recurrent neural network with GRU units, and in particular the value of the last hidden state after reading the whole recipe title. The embedding layer was initialized with GloVe embeddings [4].
Loss Function
A loss function was needed to tell the classifier to learn to transform the image representation and the text representation so that they end-up at the same location. The dot product between the image and text representations should be high when the title and image match, and low when they don't. My model computes the dot product of the representations of two pairs, a matched (or positive) pair and a mismatched (or negative) pair. It is trained with a maximum margin loss which makes sure the positive pair has a (dot product) value higher than one plus the value of the negative pair. The code to train the model was written in Keras.
Training and Result
I trained on 3000 images and tested on 1000 images. Recall@10 was 27/1000 = 0.027
Then, I trained on 10000 images and tested again on same 1000 images. Recall@10 came out to be 53/1000 = 0.053.
Further Work
- Enhance glove embeddings by retraining using word2vec on Recipe1M dataset
- Use Densenet instead of Resnet-50
- Experiment with another loss function
References/Citations
- Salvador, Amaia, Hynes, Nicholas, Aytar, Yusuf, Marin, Javier, Ofli, Ferda, Weber, Ingmar, and Torralba, Antonio. Learning cross-modal embeddings for cooking recipes and food images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328332173_Recipe1M_A_Dataset_for_Learning_Cross-Modal_Embeddings_for_Cooking_Recipes_and_Food_Images
- Liwei Wang, Yin Li, and Svetlana Lazebnik. Learning two-branch neural networks for imagetext matching tasks. CoRR, abs/1704.03470, 2017.
- Andrej Karpathy and Li Fei-Fei. Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 39(4):664–676, April 2017.
- Jeffrey Pennington, Richard Socher, and Christopher D. Manning. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In In EMNLP, 2014.