This repo provides tutorials and a library to help CV researchers to generate synthetic data using Blender.
The tutorial covers basic operations in Blender.
The library provides functions help generating images from different viewpoints.
Blender is good for single image rendering; it provides complete python interface and good support for shapenet models.
Game engine based software (Unreal, Unity) provides a virtual world for simulation, which is better for agents to interact with the environment; a lot of VR assets to buy in the market.
This tutorial is for Blender 2.7.9
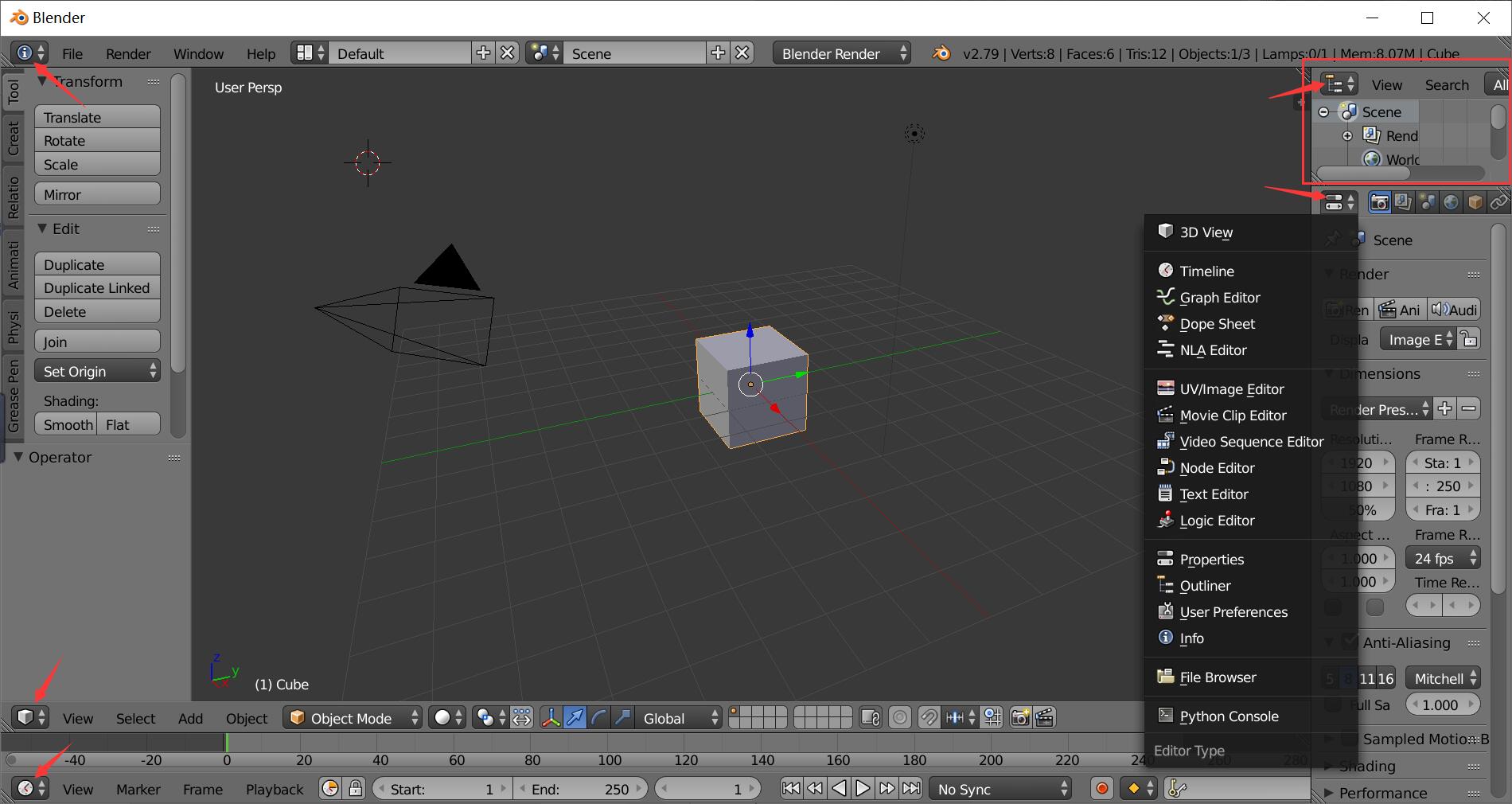
The whole interface is divided into several panels, each panel has type and the type can be changed (3D view, Timeline, etc).
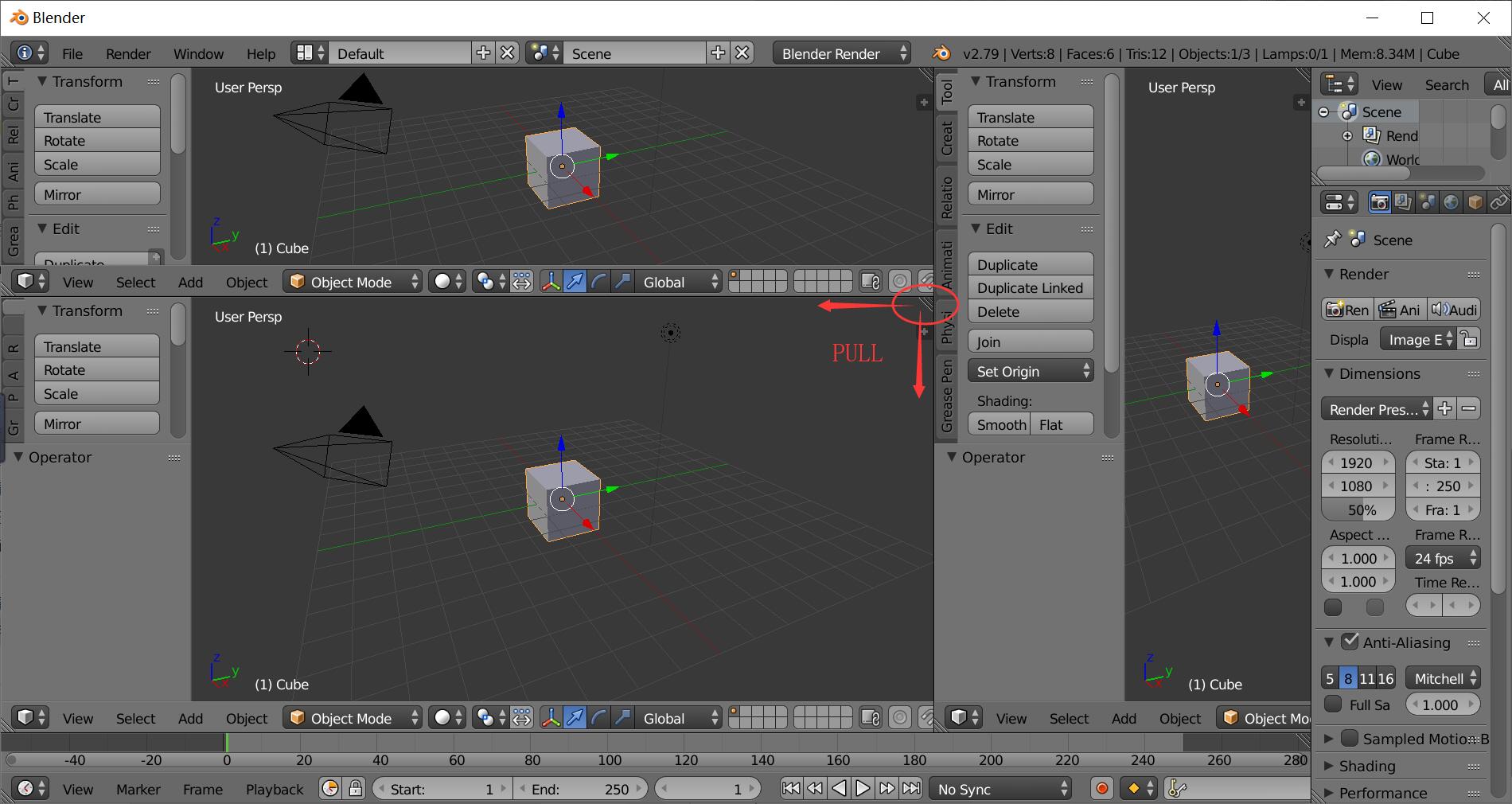
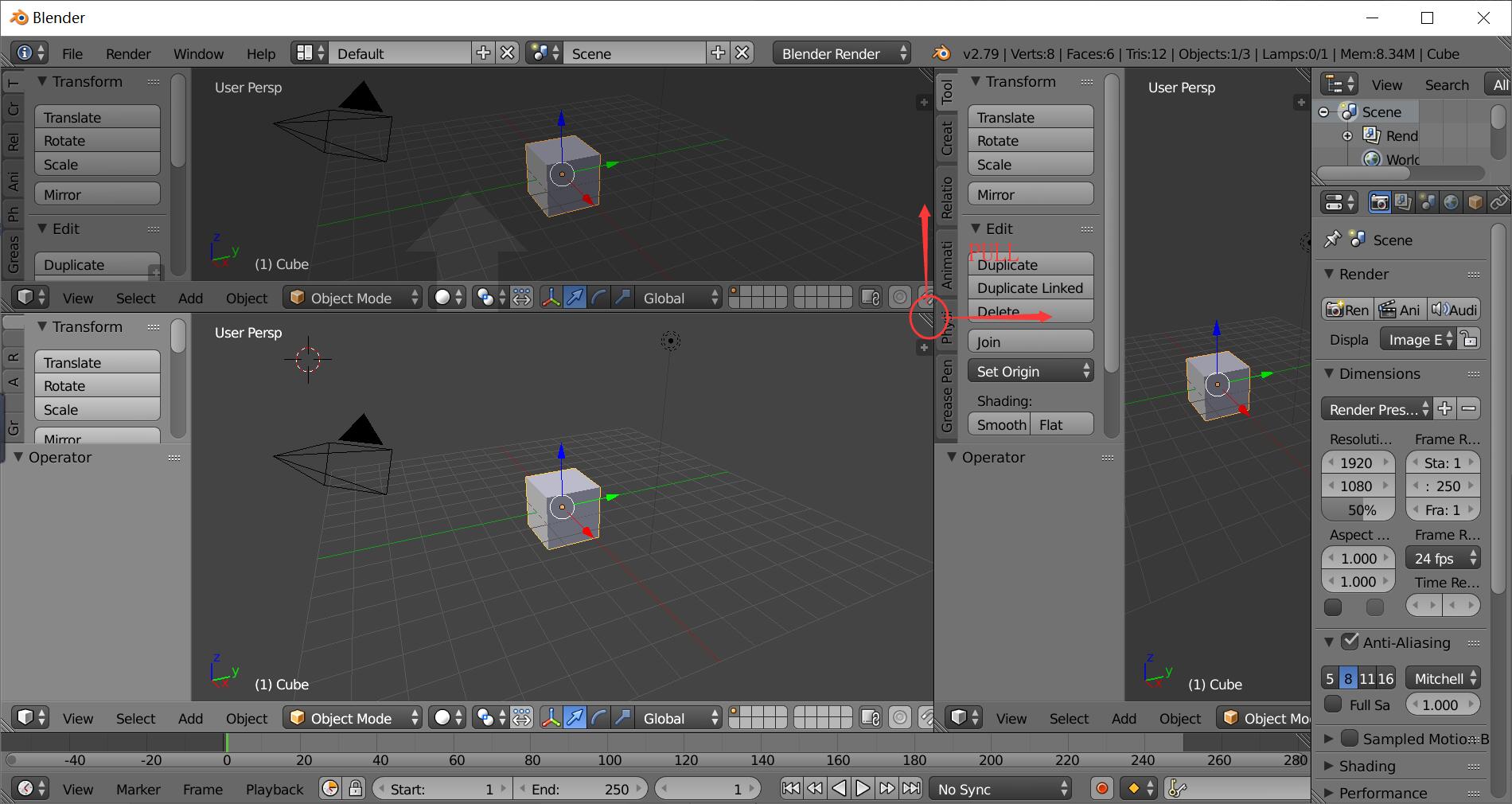
To create more panels, drag the triangle on the right top of the main panel, and pull towards left or down, a new panel will appear.
To merge two panels, drag the triangle and pull towards top or right to merge the corresponding panel.
left click - pivot point
right click - select
wheel - zoom in / out
File -> import -> .obj
Press F12 to render the image (see the objects from camera point)
Press F11 to go back
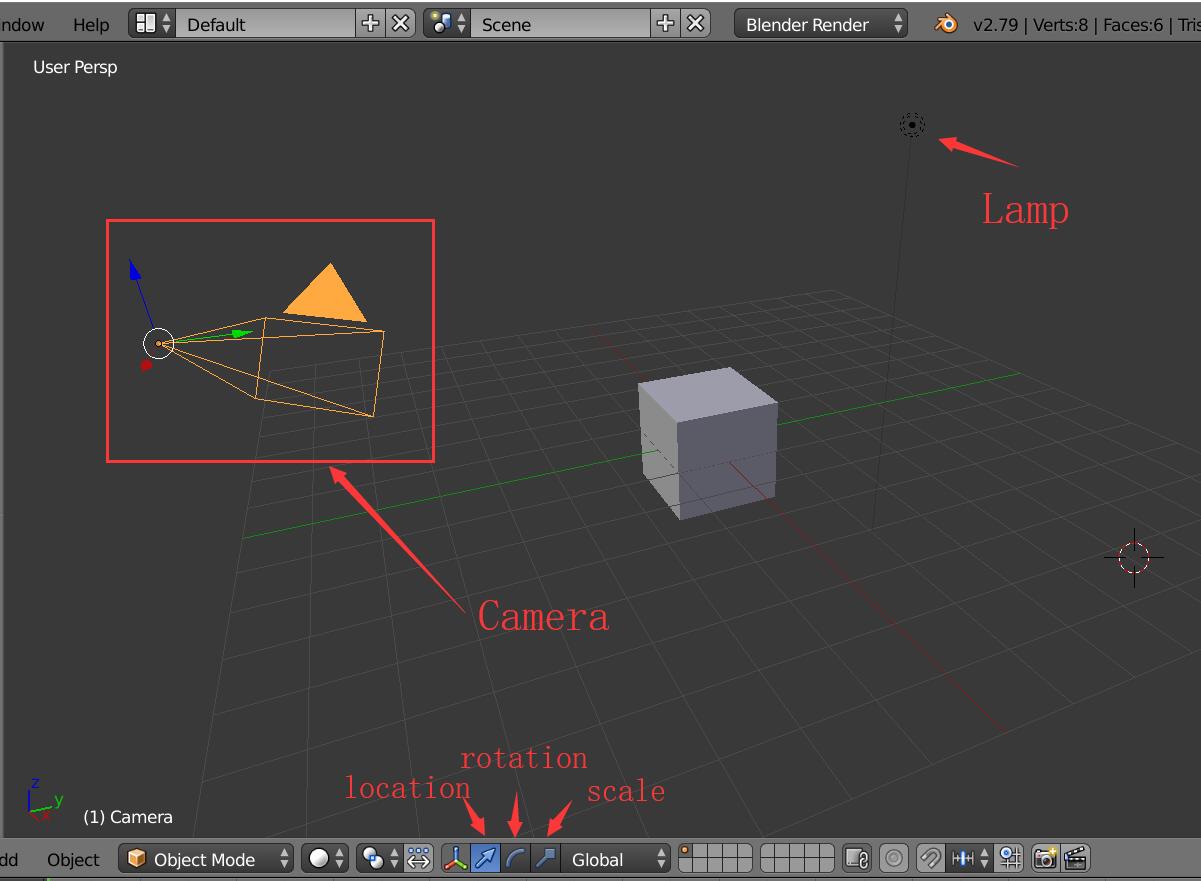
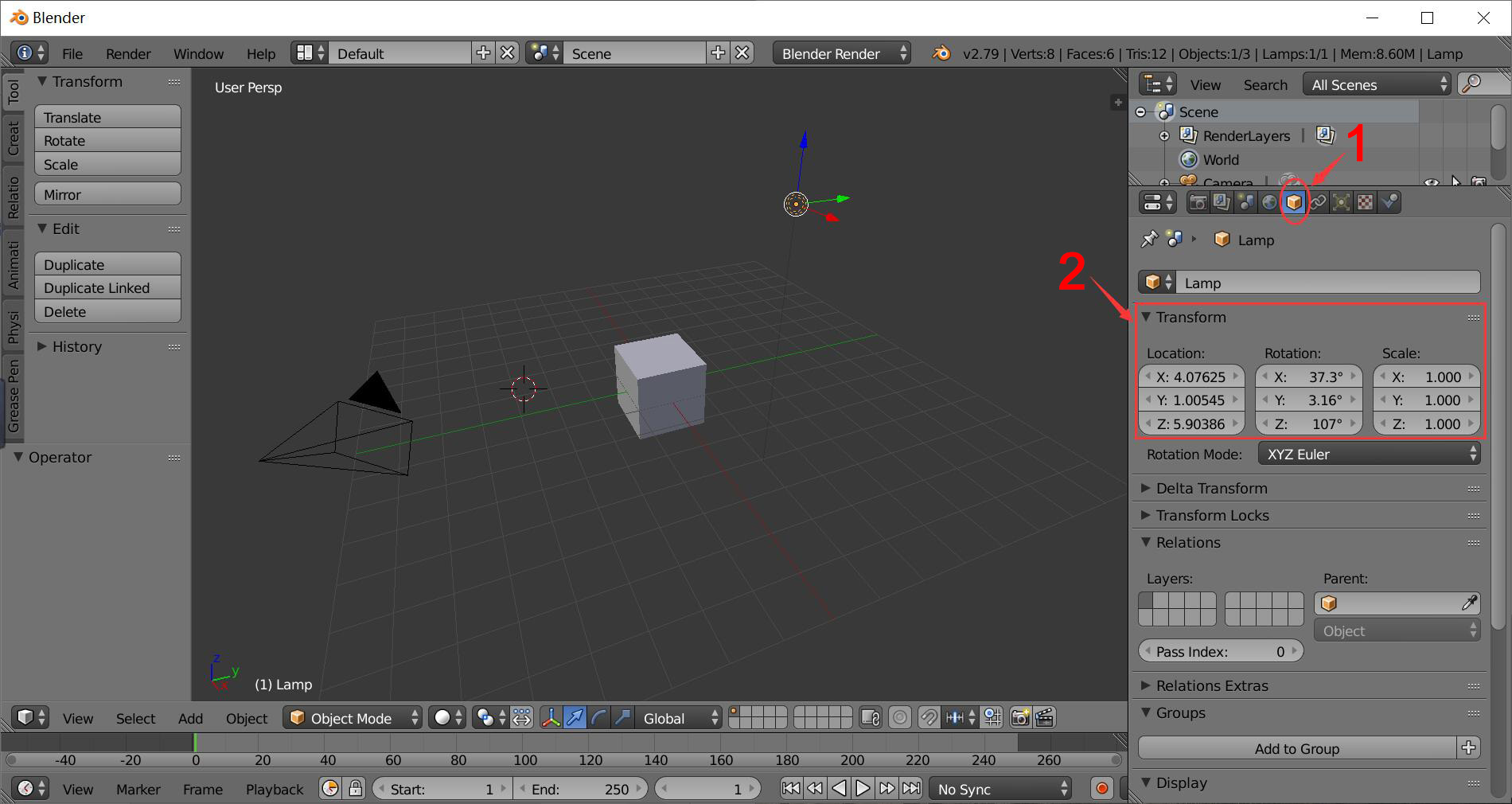
Directly move the camera and point light in the 3D viewpoint scene. Use the options below to change the location, rotation and scale.
Select the object panel and change the number of these objects.
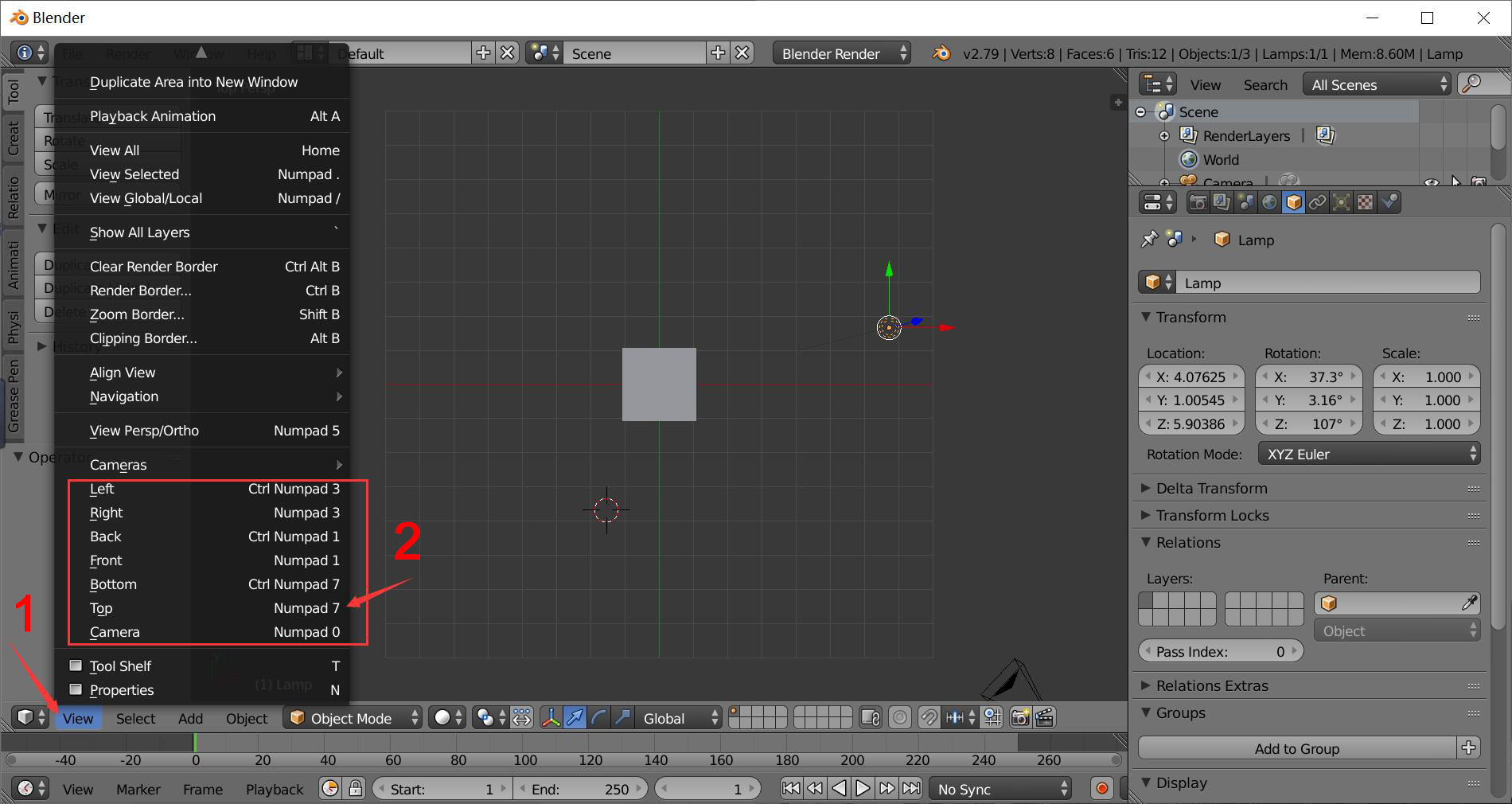
Use the view menu to toggle to other views. (The example below shows the top view)
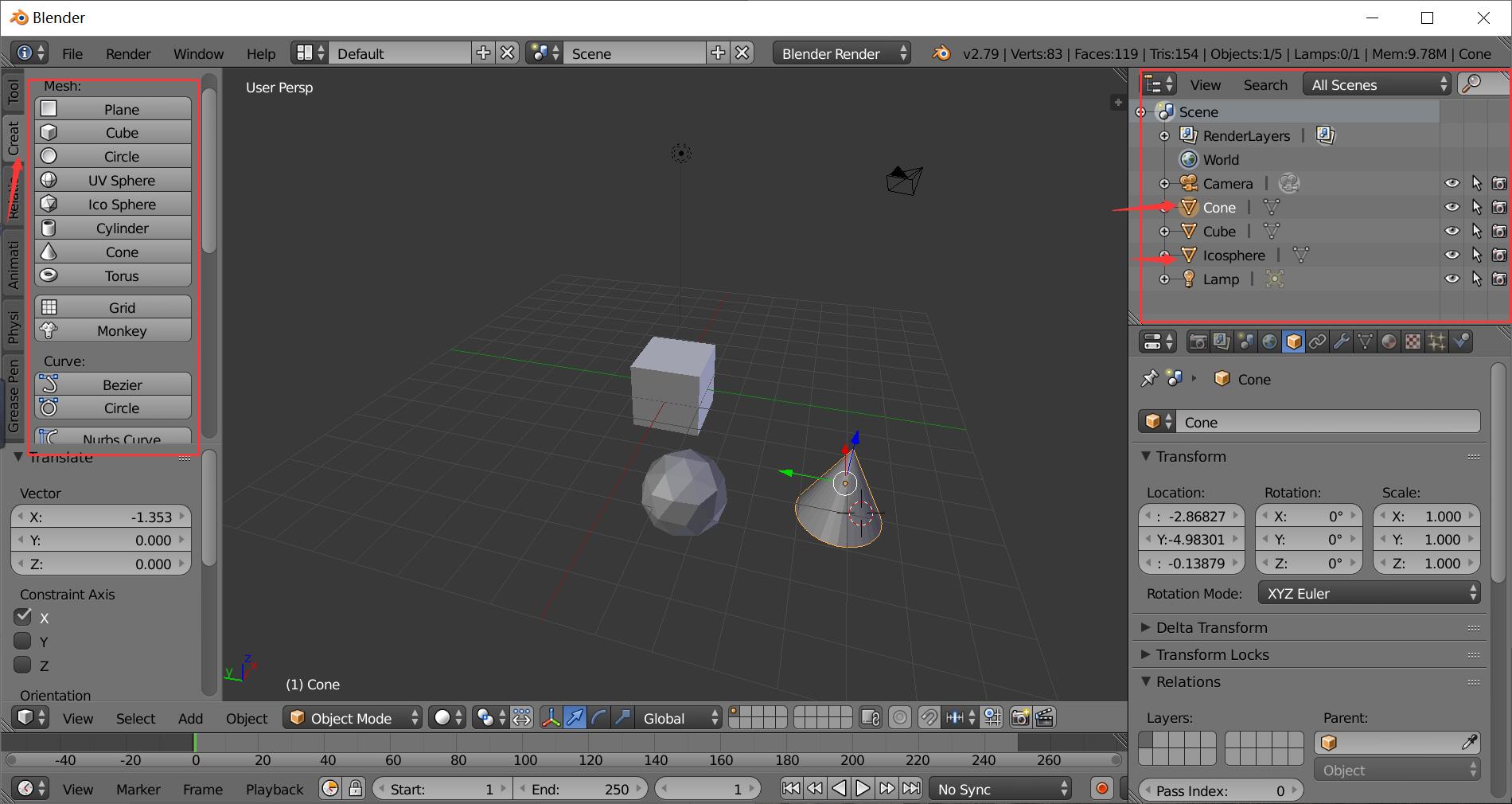
From the left panel Create to find objects to put into the scene.
All the objects in the scene are shown in the Outliner panel.
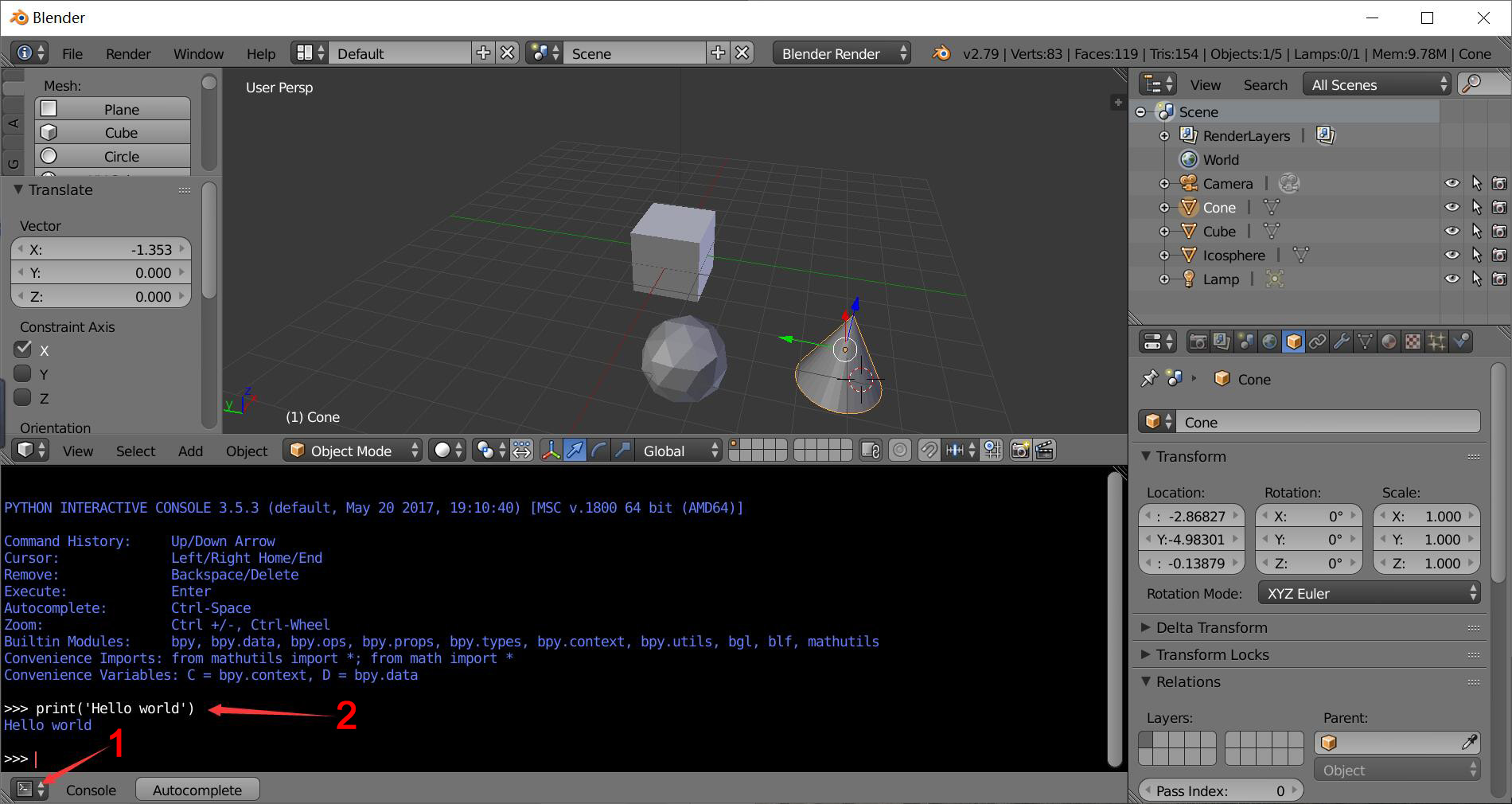
Switch the bottom panel to python console
Try to print hello world
But how to control objects in the scene by python?
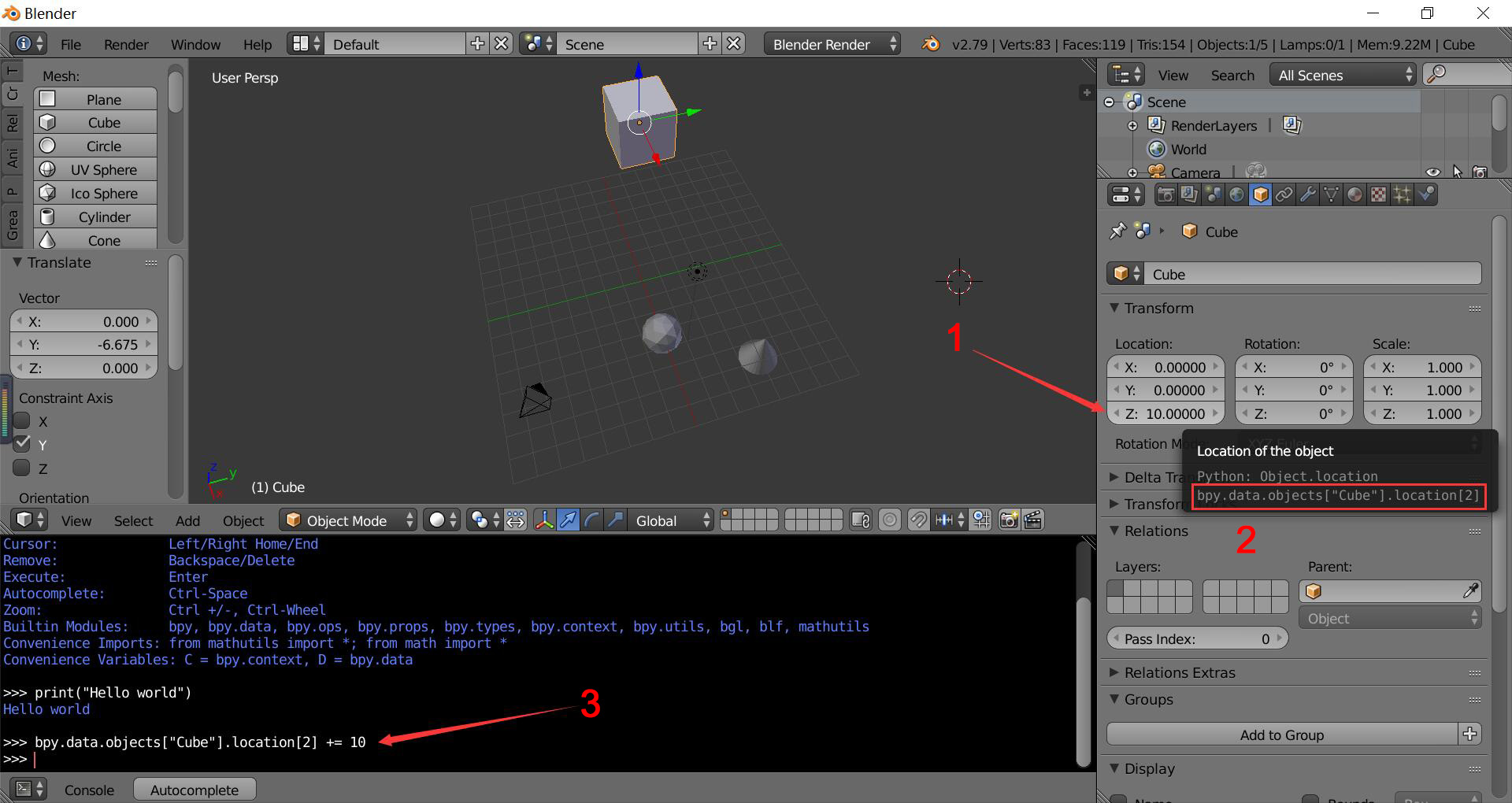
Use the bpy module provided by Blender to access the scene.
Hover over text field to get the object's python value and change it in python console using python grammar.
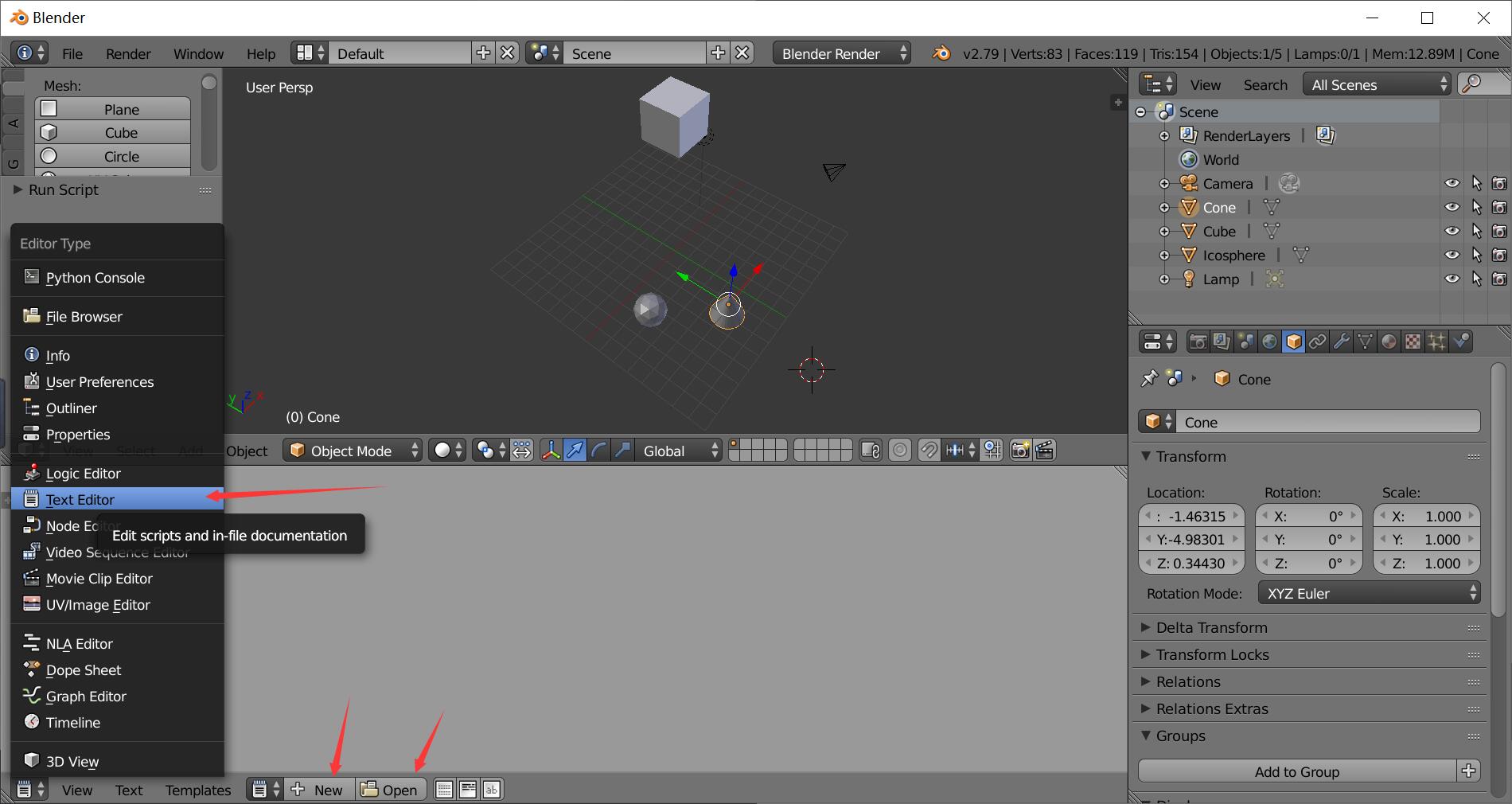
Switch the panel type to text editor, new or open a file and write python script in it.
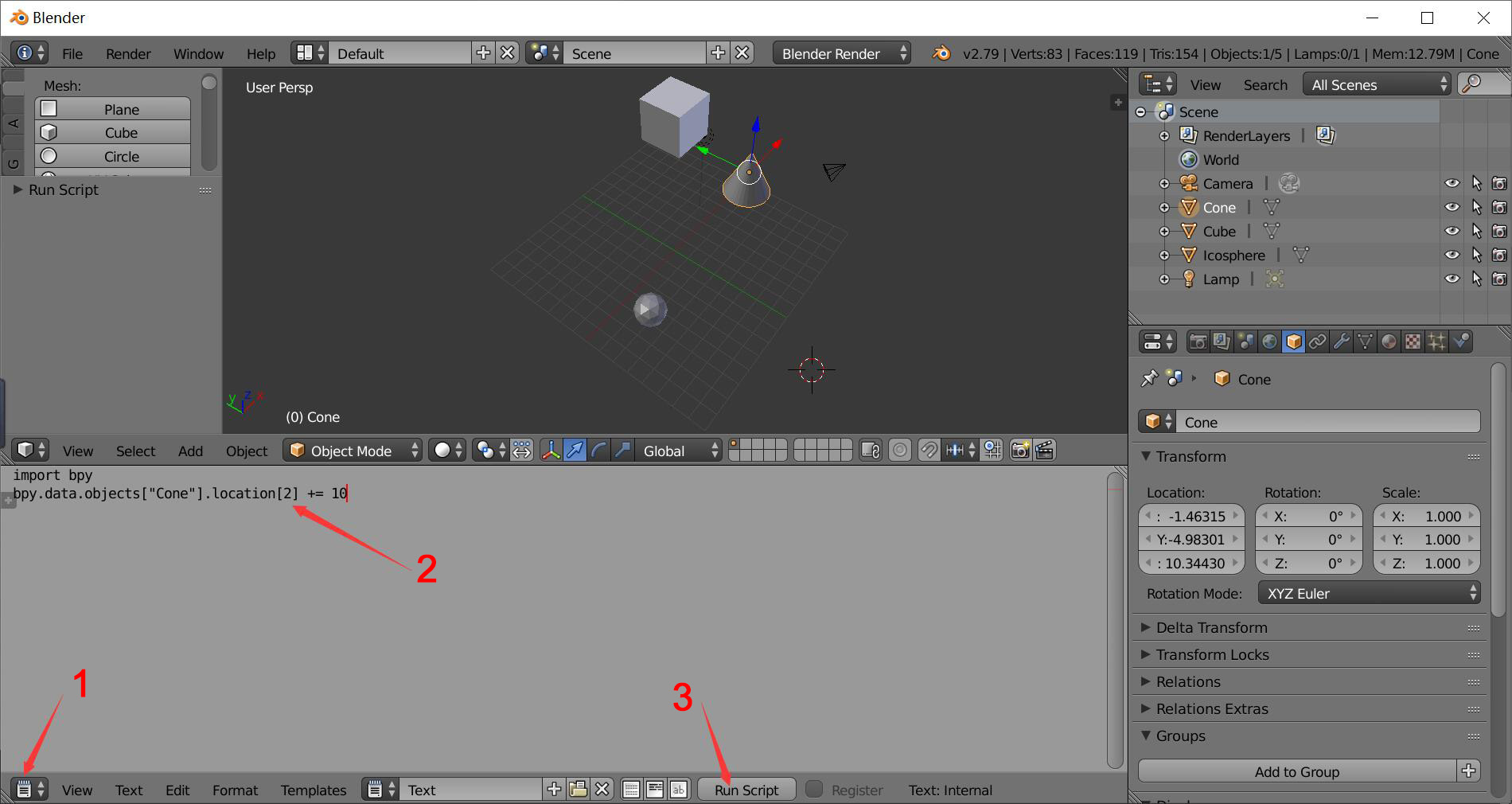
Finish your script then click Run script to see the difference.
Be aware that while writing in the file, you need to import bpy first, or there may be error.
In the last section, we introduce the way of running script within Blender, but usually we would like to run it in the command line.
This section tells how to write scripts to achieve generating images automatically.
To start Blender in the command line, we can use blender --script xxx.py to run xxx.py in Blender
- Outside to call Blender (You can also use shell not python)
- Inside Blender to control Blender
This repo provides a simple package blcv that can put models into scene and get images from different viewpoints.
You can use pip install blcv to install the package.
Note that we should use blcv in Blender's bundled Python, so you need to install the package in Blender's Python environment.
Use the following commands:
$ cd /blender-path/2.xx/python/bin/
/blender-path/2.xx/python/bin$ python.exe get-pip.py
/blender-path/2.xx/python/bin$ python.exe -m pip install blcv
If you encounter more problems installing blcv in Blender environment, you can refer to this answer.
blcv
- call_blender(render_code, blender_executable_path, blank_blend_file_path, io_redirect='', background=True): activate Blender and call the script
- render_code: directory to Blender script
- blender_executable_path: directory to Blender.exe
- blank_blend_file_path: Blender file
- io_redirect: redirect the output into a file, use '' to show the output in command lines
- background: whether run the Blender in background, default as 'True'
blcv.tools
- BcObject: operate an existed object in the scene
- init(self, id): input the name of the object
- destroy(self): delete the object
- set_loc(self, x, y, z): set the object's location
- get_loc(self, x, y, z): get the object's location
- set_rot(self, x, y, z, w=None, mode='XYZ'): set the object's rotation; the mode includes 'AXIS_ANGLE', 'QUATERNION' and 'XYZ'
- get_rot(self, mode='XYZ', w=None): set the object's rotation; the mode includes 'AXIS_ANGLE', 'QUATERNION' and 'XYZ'
- set_scale(self, x, y, z): set the object's scale
- get_scale(self, ): get the object's scale
- BcCamera(BcObject): operate an camera in the scene
- init(self, id): input the name of the camera
- set_camera_to_center(self, dist, azimuth_deg, elevation_deg, theta_deg): given the camera's rotation, set the camera in the position towards the center point [0, 0, 0]
- BcScene:
- init(self)
- set_render_mode(self, mode): set the background mode
- get_img(self, filepath): save image crop in filaepath
- import_obj(shape_file): import a new model into the scene and return its name
start_blender.py: outside script; set configurations for Blender and call inside script.
blender_script.py: inside script; import models, set viewpoints and get images.
blank.blend: Blender file; save current scene information; you can open it by Blender and modify objects in it, this is the initial scene of demo.
Modify Blender install path in start_blender.py, then:
python start_blender.py
The start_blender.py will automatically activate Blender and run blender_script.py in it.
The demo generates airplane images from circle viewpoints using the models in examples folder, the results will be saved in images folder.
If you have any questions or encounter any problems, feel free to contact me by sarahwei0210@gmail.com.