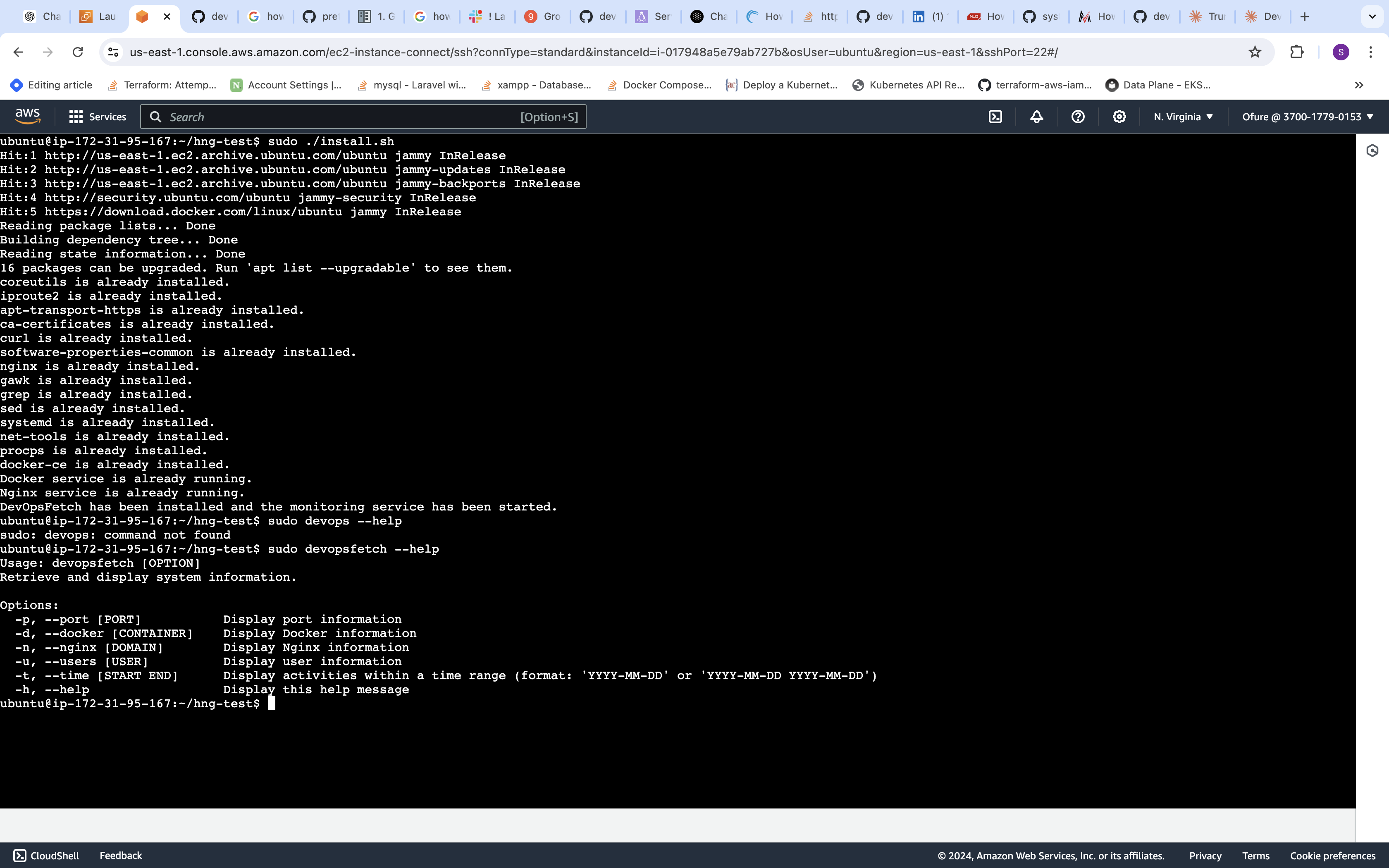
DevOpsFetch is a Bash script that retrieves and displays various system information for DevOps purposes. It provides insights into ports, Docker containers, Nginx configurations, user information, and system activities within specified time ranges.
- Clone this repo
git clone https://github.com/Sarahligbe/server-information-retrieval- cd into the directory with the script and run the
install.shas a root or a user with sudo privileges.
./install.sh- The script checks for and installs necessary packages using apt, including core utilities, Docker, and Nginx. It adds the Docker repository if not already present.
- The main DevOpsFetch script (devopsfetch.sh) is copied to /usr/local/bin/devopsfetch and made executable.
The installation process automates the setup of both DevOpsFetch and its monitoring service, ensuring that system information is continuously logged for later analysis. The log rotation setup helps manage log file sizes over time.
- No explicit configuration is required for DevOpsFetch itself.
- The script ensures that Docker and Nginx services are enabled and running.
DevOpsFetch must be run with root privileges. Use sudo when executing the script:
sudo devopsfetch [OPTION] [ARGUMENT]-p, --port [PORT] Display port information"
-d, --docker [CONTAINER] Display Docker information"
-n, --nginx [DOMAIN] Display Nginx information"
-u, --users [USER] Display user information"
-t, --time [START END] Display activities within a time range (format: 'YYYY-MM-DD' or 'YYYY-MM-DD YYYY-MM-DD')"
-h, --help Display this help message"- Help:
sudo devopsfetch -hThis will display the help message with usage information.
- Port Information:
sudo devopsfetch -p [PORT]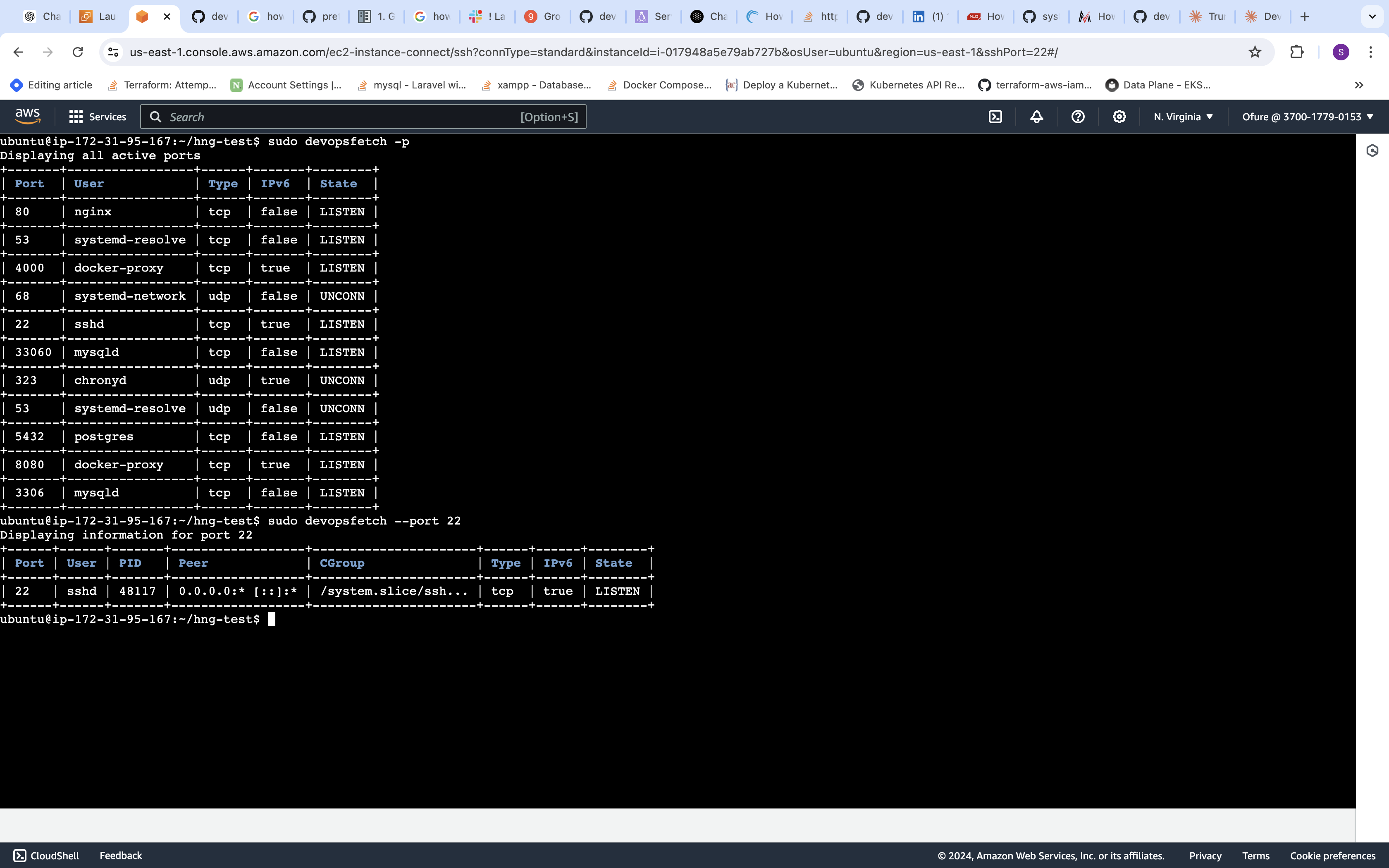 This will display information about port 22. If no port is specified, it will show information for all active ports.
This will display information about port 22. If no port is specified, it will show information for all active ports.
- Docker Information:
sudo devopsfetch -d [CONTAINER]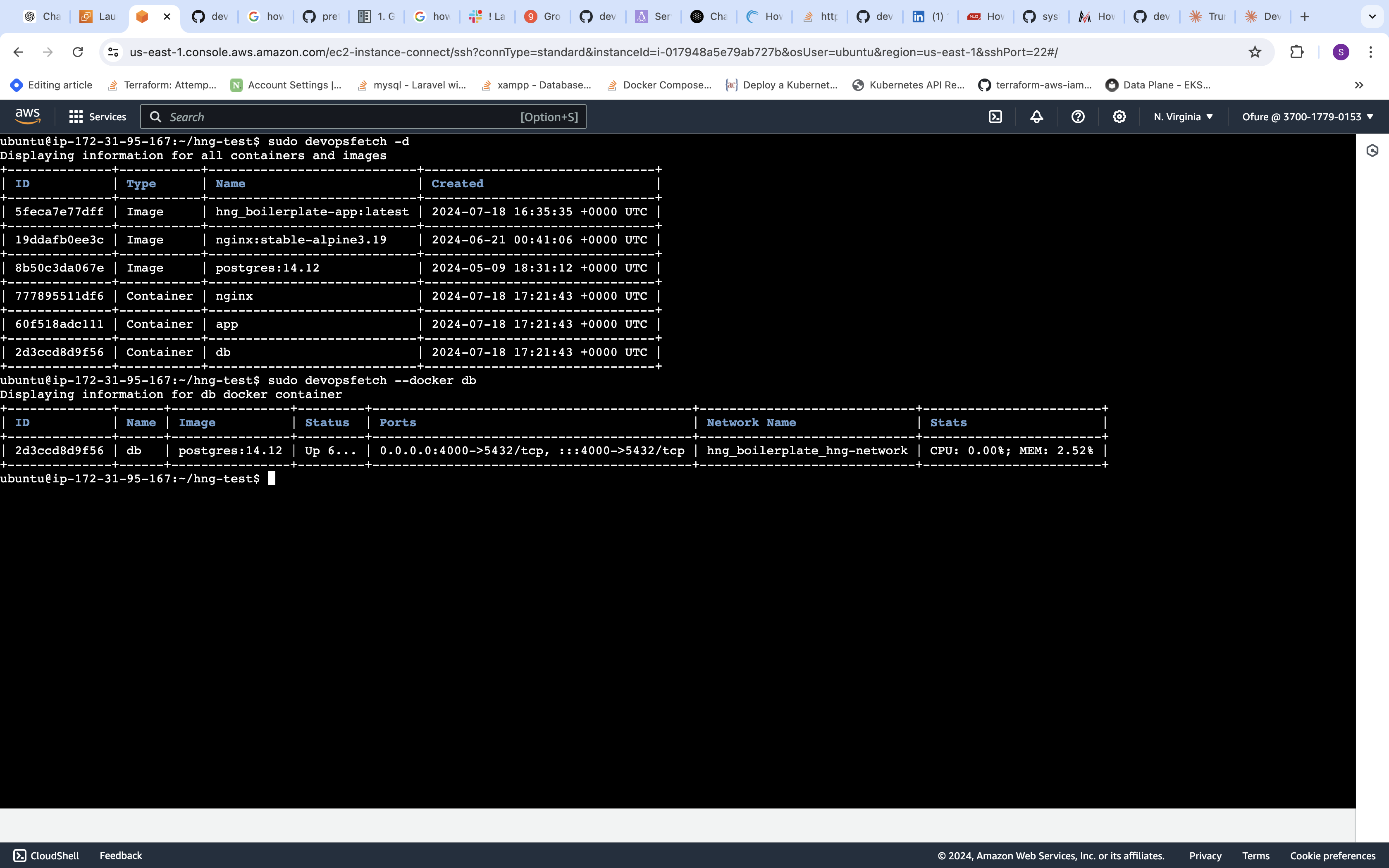 This will display information about the specified Docker container. If no container is specified, it will show information for all containers and images.
This will display information about the specified Docker container. If no container is specified, it will show information for all containers and images.
- Nginx Information:
sudo devopsfetch -n [DOMAIN]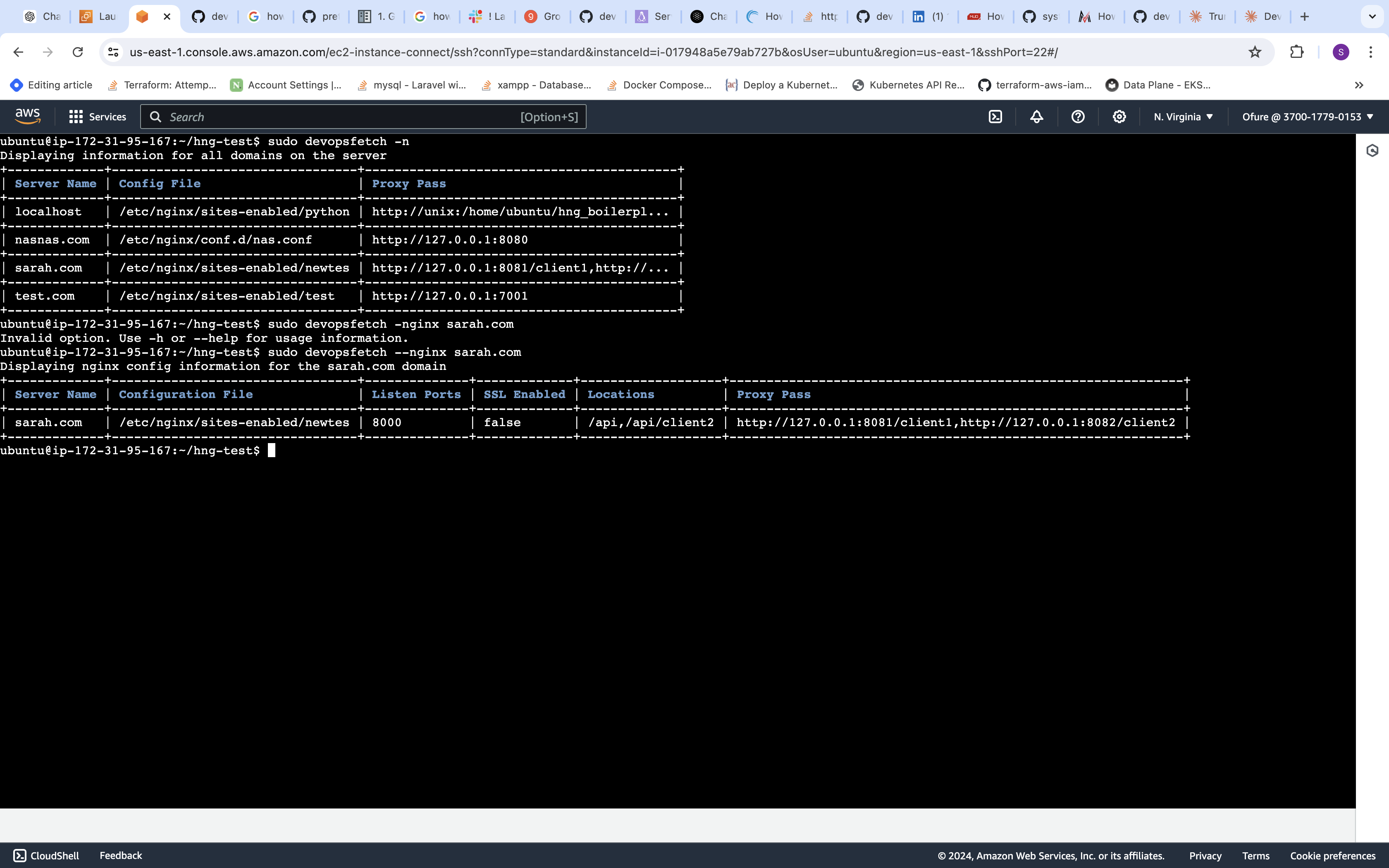 This will display Nginx configuration information for the specified domain. If no domain is specified, it will show information for all domains on the server.
This will display Nginx configuration information for the specified domain. If no domain is specified, it will show information for all domains on the server.
- User Information:
sudo devopsfetch -u [USER]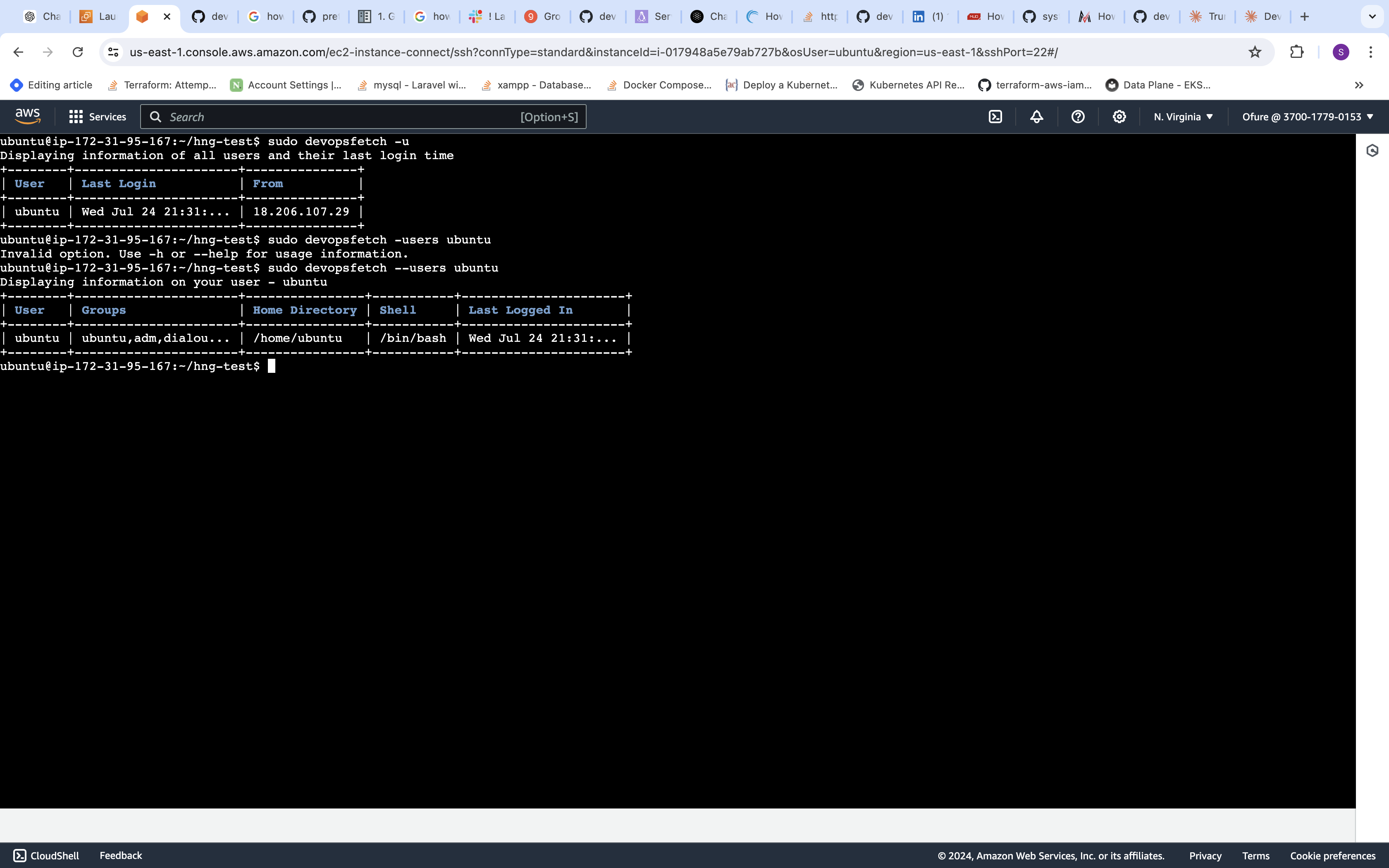 This will display detailed information about the specified user. If no user is specified, it will show information for all regular users on the system.
This will display detailed information about the specified user. If no user is specified, it will show information for all regular users on the system.
- Time Range Activities:
sudo devopsfetch -t [START_DATE] [END_DATE]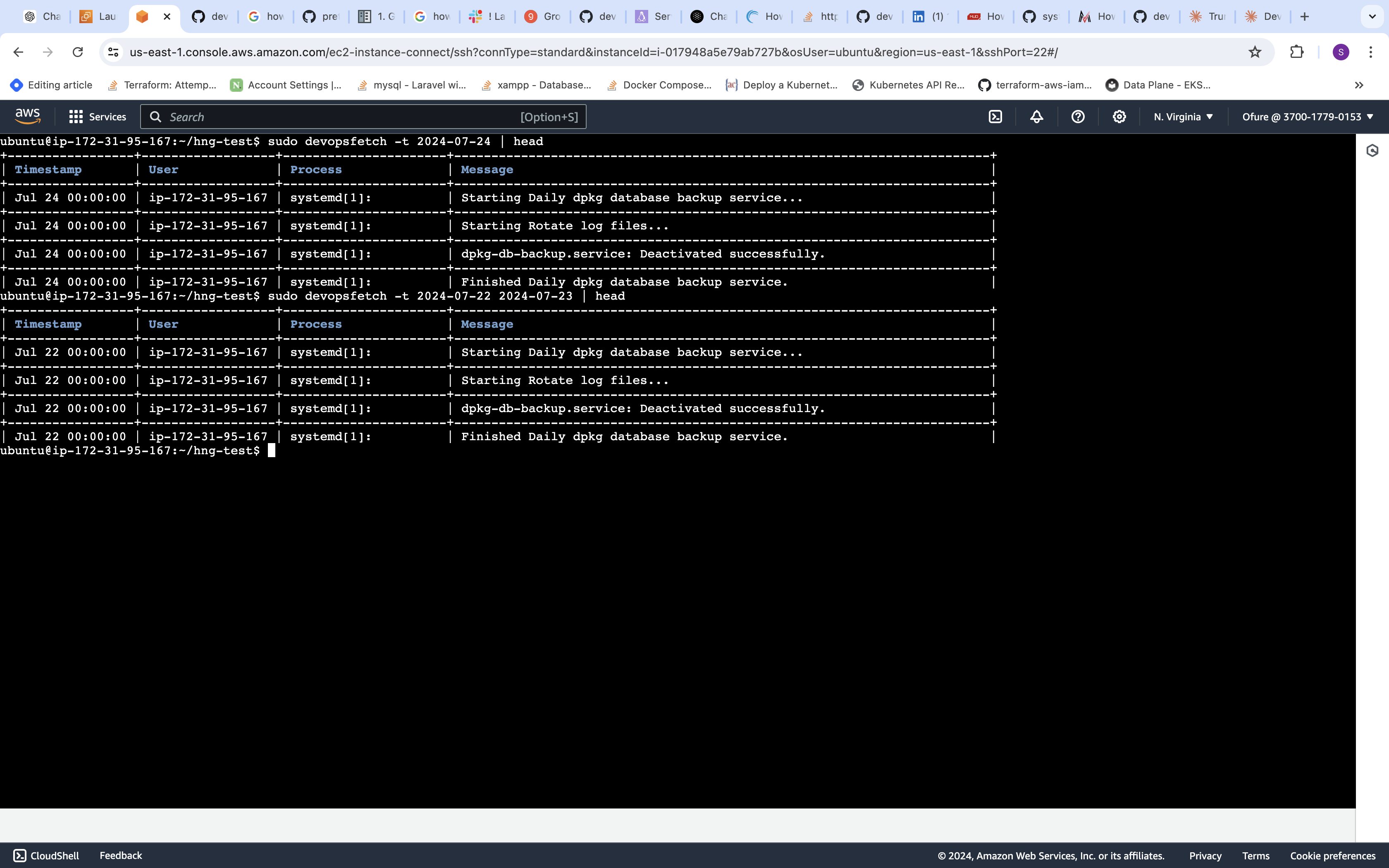 This will display system activities within the specified date range. If only one date is provided, it will show activities for that specific day.
This will display system activities within the specified date range. If only one date is provided, it will show activities for that specific day.
- A log file is created at /var/log/devopsfetch.log via the installation script
- Log rotation is set up using logrotate:
- Logs are rotated daily
- 7 rotated logs are kept
- Rotated logs are compressed
- Missing log files are ignored
- Empty log files are not rotated
- A monitoring script (devopsfetch_monitor.sh) is created in /usr/local/bin/ via the installation script. This script runs DevOpsFetch commands every 3000 seconds (50 minutes) and logs the output. It captures information about ports, Docker, Nginx, and users.
- A systemd service (devopsfetch.service) is created to run this monitoring script continuously. The service is enabled to start on boot and is immediately started after installation.