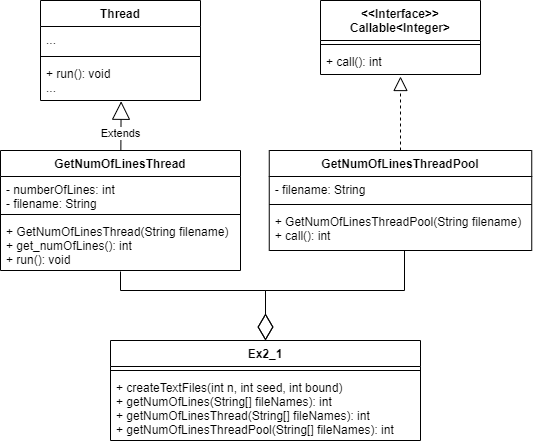
we created numbers of files and compute number lines for each file , by using 3 methods:
- normal method without using thread
- used threads
- used ThreadPool
The following tables show 3 scenarios in each scenario are measured 3 methods on fixed amounts of files In ascending order of lines per file
Ex2_1.createTextFiles(10000, 1, 10);
| 10000 Files | 1000 Files | 100 Files | 10 Files | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
getNumOfLines() |
9 sec 478 ms | 167 ms | 152 ms | 86 ms |
getNumOfLinesThreads() |
1 sec 733 ms | 228 ms | 61 ms | 47 ms |
getNumOfLinesThreadPool() |
2 sec 90 ms | 228 ms | 55 ms | 47 ms |
total lines |
45309 | 4738 | 476 | 57 |
Ex2_1.createTextFiles(10000, 1, 100);
| 10000 Files | 1000 Files | 100 Files | 10 Files | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
getNumOfLines() |
13 sec 709 ms | 1 sec 601 ms | 448 ms | 95 ms |
getNumOfLinesThreads() |
1 sec 632 ms | 255 ms | 78 ms | 48 ms |
getNumOfLinesThreadPool() |
2 sec 8 ms | 210 ms | 65 ms | 48 ms |
total lines |
499039 | 50698 | 4956 | 457 |
Ex2_1.createTextFiles(10000, 1, 1000);
| 10000 Files | 1000 Files | 100 Files | 10 Files | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
getNumOfLines() |
55 sec 304 ms | 6 sec 800 ms | 649 ms | 110 ms |
getNumOfLinesThreads() |
1 sec 835 ms | 289 ms | 100 ms | 42 ms |
getNumOfLinesThreadPool() |
2 sec 251 ms | 286 ms | 103 ms | 54 ms |
total lines |
5005739 | 508498 | 51056 | 6657 |
It can be seen that the more files there are, and the more lines there are in each file,
the more the functions that use threads are significantly faster than the normal function
that does not use threads. Another thing, you can notice that the third function that
uses threadpool, takes a little more time than the second function.
We assume that this is the case because both use more or less the same number of threads,
but we pay the overhead of creating the threadpool and operating it.
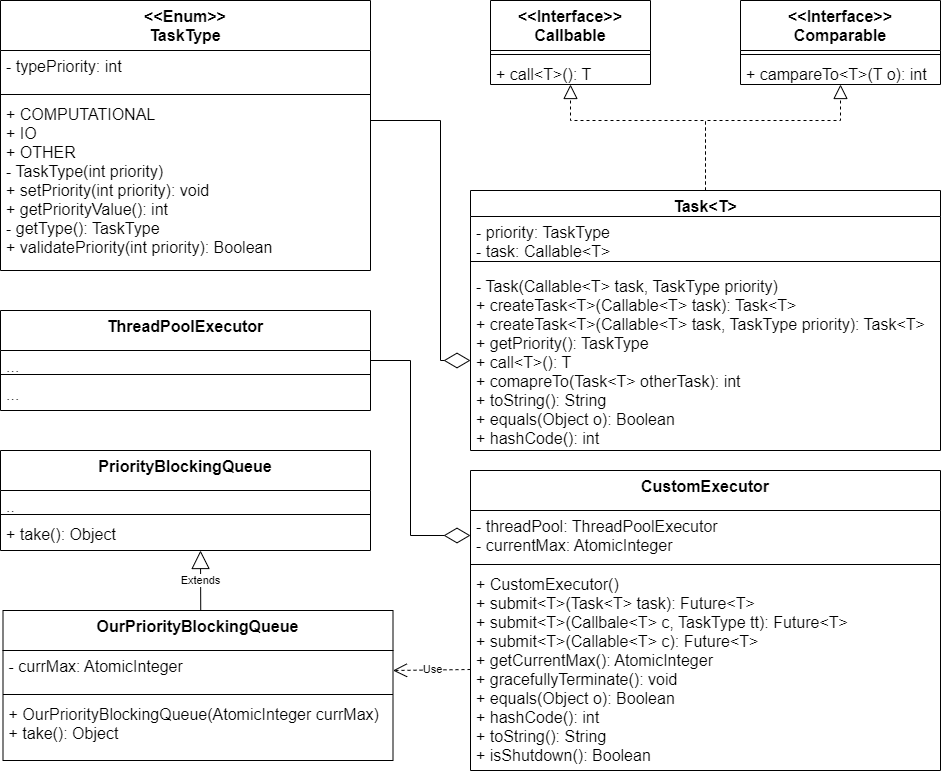
Here we created two new types that extend the functionality of Java's Concurrency Framework
- A generic task with a Type that returns a result and may throw an exception. Each task has a priority used for scheduling inferred from the integer value of the tasks Type.
- A custom thread pool class that defines a method for submitting a generic task as described in the section 1 to a priority queue, and a method for submitting a generic task created by a Callable and a Type, passed as arguments.
- For more details click here