MSc final thesis project by Vincenzo Riccio and Giancarlo Sorrentino.
This project is a Self-Adaptive System made of:
- a managed system, SEFA, which is the software object of adaptation.
- a reusable managing system, RAMSES, which is the software responsible of adapting the managed system.
- some simulated third party services used by the managed system
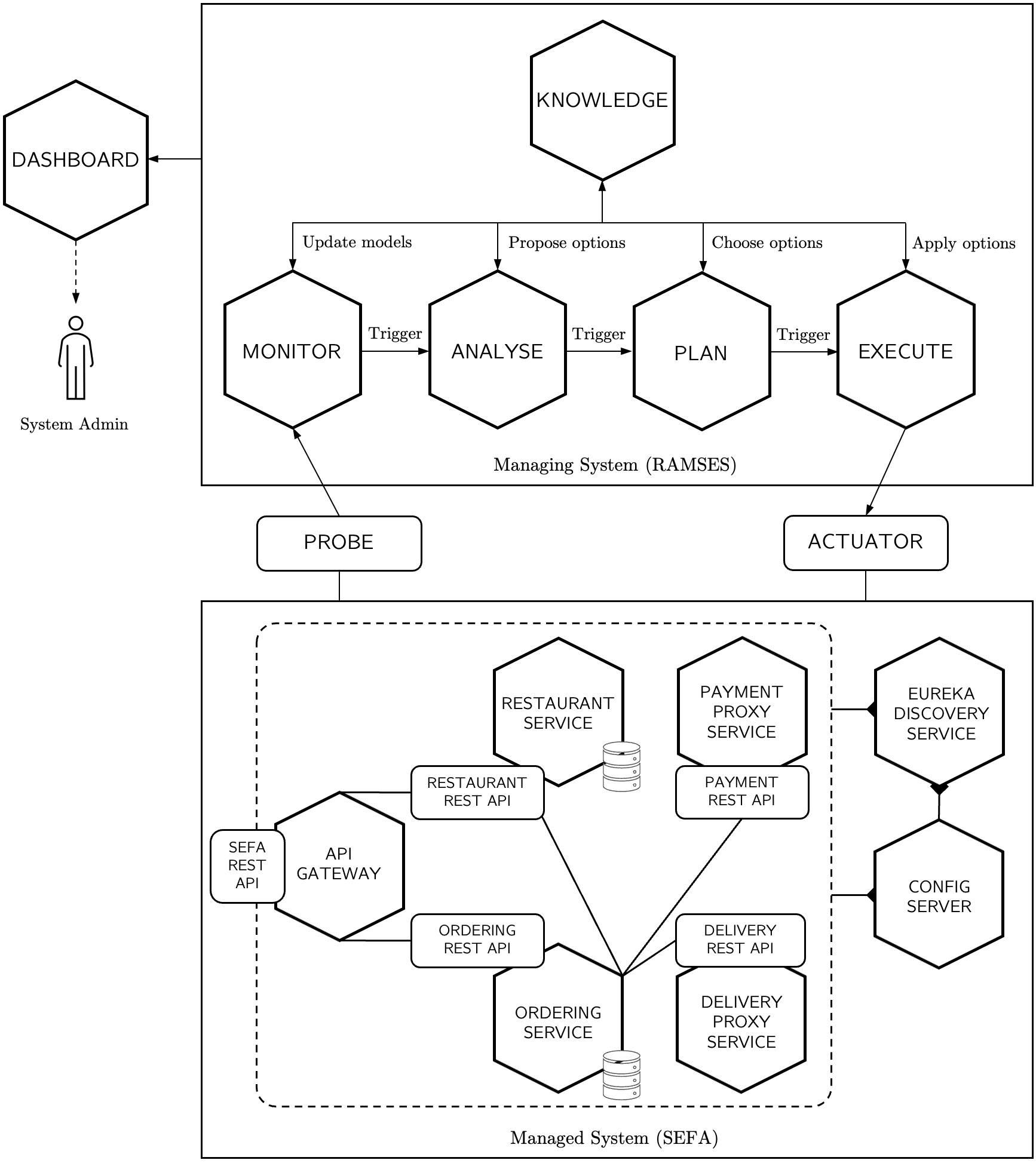
The high-level software architecture is represented below.
Together with the actual code of both RAMSES and SEFA, we also provide a set of ready-to-use docker images. By following the next steps, you can set up and run both systems on the same machine.
To begin with, install Docker on your machine and run it. After the installation, we suggest to configure it with the following minimum requirements:
- CPU: 6
- Memory: 8GB
- Swap: 1GB
The whole Self-Adaptive System was developed, run and tested on a 2020 Apple MacBook Air with the following specifications:
- SoC: Apple M1 (8-core CPU, 7-core GPU)
- RAM: 16GB LPDDR4
- Storage: 256GB on NVMe SSD
- OS: macOS Monterey 12.6
- IDE: Intellij IDEA
- Docker v20.10.17 (allocating 6 CPUs, 10GB Memory, 1.5GB Swap)
The Java version used by the project is version 16.0.2.
The next step involves the creation of a GitHub repository (if you don’t have one yet) to be used by the Managed System Config Server as the configuration repository. You can do so by forking our repository. Check that the application.properties file does not include any load balancer weight. If so, simply delete those lines and push on your repository. Once you have created your configuration repository, create an environmental variable storing its URL by running the following command, after replacing <YOUR_REPO_URL> with the URL of the repository you just created:
$ export GITHUB_REPOSITORY_URL=<YOUR_REPO_URL>
The GITHUB_REPOSITORY_URL variable should look like https://github.com/ramses-sas/config-server.git
Now, generate a GitHub personal access token to grant the Managed System the permission to push data on your repository. You can do so by following this guide.
Once again, create an environmental variable storing your access token by running the following command, after replacing <YOUR_TOKEN> with the token you just created:
$ export GITHUB_OAUTH=<YOUR_TOKEN>
The GITHUB_OAUTH variable should look like an alphanumeric string.
Finally, run the SEFA+RAMSES_setup.sh bash script if you want to run RAMSES together with SEFA. Otherwise, run the SMS+RAMSES_setup.sh bash script to run RAMSES together with the Simple Managed System.
- Use option
-ato specify the system architecture. The available ones areamd64andarm64. The latter is the default one. - Use option
-lto run only the load generator (use this option only after having the entire SAS running).
Once all the containers have been launched you can start interacting with both systems.
To easily interact with SEFA you can open your browser and go to the URL exposed by the sefa-web-service container, which is visible in Docker.
From there, you can interact with the app both as an admin, by adding and editing restaurants, or as a user, by placing orders.
To interact with the RAMSES dashboard, open your browser and go to the URL exposed by the ramses-dashboard container. From there you can navigate through the 3 subsections, accessible from the menu bar.
- All the managed services are under the Home page, where you can see their configuration and a link to the details of each service.
- The list of the applied adaptation options is under the Adaptation page,
- You can modify the hyperparameters of RAMSES from the Configuration page, as well as starting/stopping the monitor routine and enabling/disabling the adaptation. Notice that the monitor routine and the adaptation are initially disabled.
From the Home page you can track the availability and the average response time of each service and of their instances. Notice that these values are available only if new requests are made to the services. To generate artificial requests to SEFA, you can use our automatic load generator. If you did not launch it when asked by the setup script, you can instanciate it by running again the same script with the -l option.
A known issue on macOS involves the Actuator component, that sometimes cannot directly contact the Docker interface to run or stop containers. This results in the Instances Manager container to fail its booting process. To solve this issue, install socat using this guide and run the command
$ socat -d TCP-LISTEN:2375,range=0.0.0.0/0,reuseaddr,fork UNIX:/var/run/docker.sock