Provide a circuit in bristol format, and you can generate the corresponding taproot address. One transaction is a bitcommitment transaction, while the other is a verification transaction. For testing, it use the circuit from the yellow paper as an example.
| name | description |
|---|---|
| lib.rs | Overall test cases. |
| bitcommitmenttx.rs | Generate bit commitments transaction and address. |
| circuits.rs | Convert the circuit into a list of operations such as wires and gates. Generate preimages and preimage hashes for all wires. |
| gate_templates.rs | Template scripts for gates, used to replace the preimage hash to generate the leaves of the verification transaction. |
| timelock.rs | Generate time lock scripts for other 2 taproot transactions. |
| utils.rs | Some general gadgets: sha256 rand xor inv and. |
| verificationtx | Generate verification transaction and address |
For specific details, please refer to the Yellow Paper.
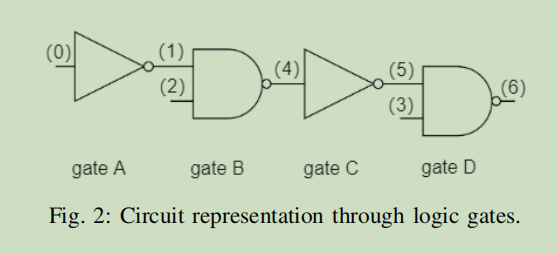
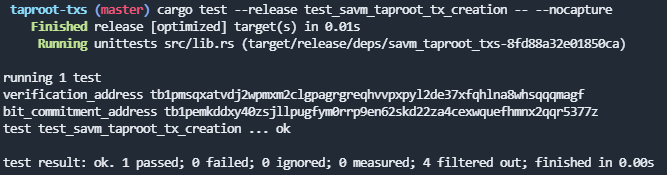
cargo test --release test_savm_taproot_tx_creationAs shown in the figure, this is the logic gate circuit diagram in the yellow paper. The code testing case will use this as input to generate on-chain verification transactions.
This is its corresponding circuit in the Bristol form.
4 7
1 3
1 1
1 1 0 1 INV
2 1 1 3 4 AND
1 1 4 5 INV
2 1 2 5 6 AND
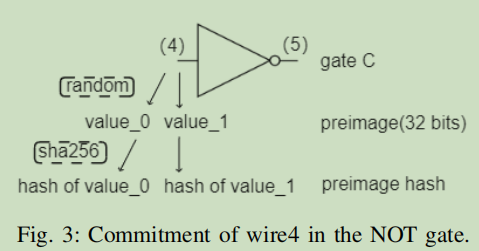
According to the Yellow Paper, next step is to take the parsed data and process each wire as follows.
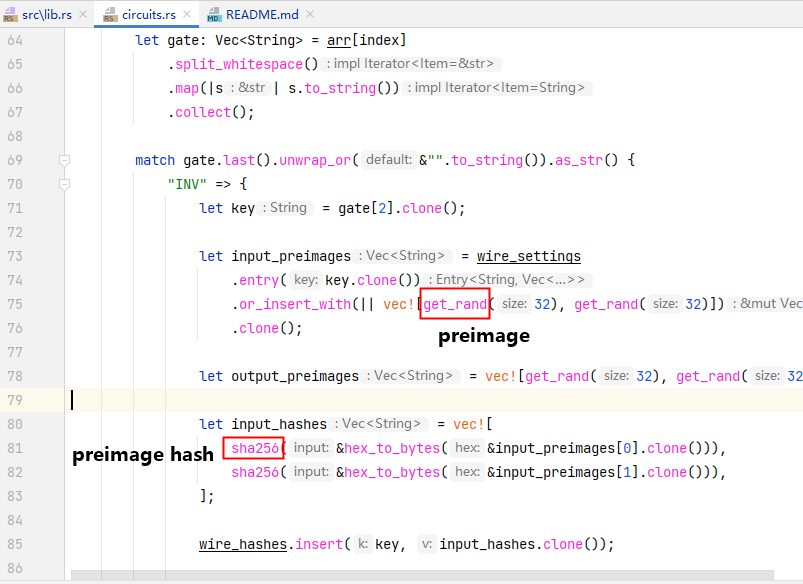
First, generate a corresponding random number preimage for each wire, then use sha256 to generate the preimage hash.
use generate_bit_commitments and generate_bit_subsequent_commitments separate out the preimagehashs and preimages.
Then, using the operations_array and preimagehash data, along with script templates(gate_templates.rs), create all leaf scripts, then place them into taproot to generate a 2-input taproot transaction.