This is a base EFI which should be good to go for most 11th Gen Rocket lake boards.
| Bootloader |
|---|
| OpenCore v0.8.5 |
Dortania Comet Lake Install Guide
- First: Load optimized defaults
- RAM: Default settings recommended, no XMP Profile
- in general no Overclocking is recommended
- Internal Graphics, no iGPU support in macOS since 11th Gen Intel
- Fast Boot
- Secure Boot (see section Secure Boot if you want to enable it)
- USB-Settings: Legacy USB Support
- VT-D (can be enabled if you set DisableIoMapper to YES)
- Compatibility Support Module (CSM).
- Thunderbolt (For initial install, as Thunderbolt can cause issues if not setup correctly)
- Intel SGX (mostly in CPU settings)
- Intel Platform Trust (mostly in CPU settings)
- CFG Lock (MSR 0xE2 write protection) This must be off, if you can't find the option then ENABLE AppleXcpmCfgLock. Your hack will not boot with CFG-Lock enabled.
- VT-X or VT-D
- Above 4G decoding. This must be on, if you can't find the option then add npci=0x2000 to boot-args. Do not have both this option and npci on boot-args enabled at the same time. When enabling Above4G, Resizable BAR Support may become an available on some motherboards.
- USB Settings: EHCI Hand-off
- USB-Settings: XHCI Hand-off
- OS type: Windows 8.1/10 UEFI Mode or OTHER
- SATA Mode: AHCI
You should do these steps on a real Mac.
- Insert a USB-Stick with at least 16GB. A stick with an LED is recommended to see if it is doing something.
- Erase the stick with GUID partition scheme and macOS Journaled (Extended) format.
- Rename the volume to "MyVolume".
- Download macOS from the App Store. After downloading you should have an installer in the applications folder.
- Go to this page and copy the terminal command for your macOS version: Create a bootable USB installer for macOS
- Open terminal and paste the command, e.g. for Monterey
sudo /Applications/Install\ macOS\ Monterey.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia --volume /Volumes/MyVolume - Hit enter and commit the upcoming questions with Y for Yes. macOS should now create your macOS Installer stick.
- When the installer stick creation is finished, the installer volume should be mounted.
- Download and open Hackintool and go into the "Disks" menu. Click the double arrow beside your installer stick to mount its EFI-partition.
- Copy the EFI folder into the root of the EFI-partition. When you open the EFI-partition you should have EFI-folder with the OC and Boot folder inside.
- Adjust your BIOS-settings and boot from the stick in the UEFI-mode.
- Start the macOS installation.
To get Secure Boot running, you need to set a "Secure Boot Model" that is fitting your SMBIOS.
And you need to enroll all .efi files from you EFI-folder into your BIOS-Secure Boot options.
This whitelists the checksums of all .efi files allowed to be booted from.
So every time you exchange any of the .efi files, you need to enroll them again. E.g. when you update OC.
BIOS-Settings for Secure Boot:
- Set Secure Boot to Enabled
- Set Secure Boot Mode to Custom
- Go to Key Management and then unroll all .efi files in your EFI-folder. This is very different on every board. On Gigabyte the option you have to use is called Enroll EFI Image. In the upcoming prompt you have select your boot-stick and then enroll all *.efi Files one by one: BOOTX64.efi, all drivers(OpenRunTime.efi, OpenHFSPlus.efi, OpenCanopy.efi) and of course the OpenCore.EFI.
- Discrete Thunderbolt Support: Enabled
- Wake From Thunderbolt Devices: Disabled
- Native OS security for TBT: Disabled
-
Thunderbolt USB Support: Disabled
-
Thunderbolt Boot Support: Disabled
-
Titan Ridge Workaround for OSUP: Disabled
-
Tbt Dynamic AC/DC L1: Disabled
-
GPIO3 Force Pwr: Enabled
-
Wait time in ms after applying Force Pwr: 200
-
GPIO filter: Enabled
-
DTBT Controller x Configuration: all Settings in this Submenu BIOS-Default
Editor: MacIASL (https://github.com/acidanthera/MaciASL/releases)
In general: Don't just copy and paste .aml files from other EFIs. The .aml files are highly specifically for each system. Especially the paths for each device are different from one system to the other.
E.g. sometimes the paths start with SB.PCI0 and sometimes they start with SB.PC00. If this path is wrong, they won't do anything. Luckily the ones from Dortania are kind of universal and cover many platforms. They contain many variants of different paths for each platform.
For more information: Getting started with ACPI
| .aml-file | Description |
|---|---|
| SSDT-AWAC.aml | Fixes RTC clock issues. |
| SSDT-EC-USBX.aml | Fixes both the embedded controller and USB power. |
| .aml-file | Description |
|---|---|
| SSDT-PLUG-DRTNIA.aml | Enables native CPU Power Management. But as 11th Gen is not supported, this SSDT has no effect on my 11900k or at least I can't tell I feel a difference. X86Plugin is not getting enabled. |
| SSDT-USBW.aml | If you have the wake issue that it requires two keypresses to wake the display after sleep. |
| SSDT-RHUB.aml | If you experience issues with USB when booting macOS, try this AML to force a USB reset. But USB issues probably result from a faulty USB-port mapping. |
| SSDT-DTGP.aml | Thunderbolt 4 Support. |
| SSDT-MAPLE-RIDGE-RP05-V2.aml | Thunderbolt 4 Support. You have to check the PCI-path of your Thunderbolt device. On Gigabyte Z590i Vision D and propably most Z590 boards it is RP05. |
| Kext | Description |
|---|---|
| Lilu.kext | Acidanthera plug-in manager |
| VirtualSMC.kext | Emulates the SMC chip found on real macs, without this macOS will not boot. |
| Whatevergreen.kext | Lilu plugin for managing both internal GPU and AMD GPUs |
| RestrictEvents.kext | Suppress notifications e.g. on wrong RAM placement |
| USBPorts_Z590i_VisionD.kext | You need a USB-port mapping that stays within the 15 port limit. Total number of HSxx and SSxx ports count. Otherwise macOS will not boot. This is just a sample of the Gigabyte Z590i Vision D which stays within the 15 ports limit and is a good initial setup. Many ports will work with other boards, but you need to customize this for your board if you want all the ports working correctly. Hint: This Kext is for MacPro7,1 SMBIOS. If you want to use is with other SMBIOS like iMacPro1,1 you have to search and replace the SMBIOS in the info.plist of the Kext. |
| Kext | Description |
|---|---|
| AppleIntelI210Ethernet.kext | Intel 2.5Gbit Ethernet (I225V) Support for macOS Ventura |
| AppleALC.kext | Onboard Audio support. If your onboard audio is connected via USB (HS11 on my Z590i Vision D) then you don't need this. But if not and you want onboard audio, you need to find out your layout-id (alcid). Add it in the bootargs e.g. 'alcid=1'. To find out your alcid/layout-id, see here: Supported Codecs |
| SMCProcessor.kext | VirtualSMC-plugin for CPU Sensor Data e.g. CPU Core Temp |
| SMCSuperIO.kext | VirtualSMC-plugin for Mainboard Sensor Data e.g. case fan speed |
As the 11th Gen Intel is not supported officially, we have to emulate the 10th Gen Intel in the Kernel-Emulate section of the config.plist.
| Key | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cpuid1Data | DATA | <55060A00 00000000 00000000 00000000> |
| Cpuid1Mask | DATA | <FFFFFFFF 00000000 00000000 00000000> |
| Kext | Description |
|---|---|
| AppleALC.kext | Onboard Audio support. |
If your onboard audio is connected via USB (HS11 on my Z590i Vision D) then you don't need this. But if not and you want onboard audio, you need to find out your layout-id (alcid). Add it in the bootargs e.g. 'alcid=1'. To find out your alcid/layout-id, see here: Supported Codecs
The 10Gbit Acquantia and the 2.5Gbit Intel I225-V should work out of the box.
For the Acquantia I have the patches already in my config.plist included in the Kexts/patches section.
And for the 2.5Git Intel the bootargs 'e1000=0' (Monterey and Ventura), 'dk.e1000=0' (Big Sur) and the AppleIntelI210Ethernet.kext (Ventura).
Other Ethernet Kexts:
| Kext | Description |
|---|---|
| IntelMausi.kext | Intel's 82578, 82579, I217, I218 and I219 NICs are officially supported. |
| AtherosE2200Ethernet.kext | Required for Atheros and Killer NICs. Note: Atheros Killer E2500 models are actually Realtek based, for these systems please use RealtekRTL8111 instead. |
| RealtekRTL8111.kext | For Realtek's Gigabit Ethernet. Sometimes the latest version of the kext might not work properly with your Ethernet. If you see this issue, try older versions. |
Reference Guide: Wireless Buyers Guide
If you want to use your onboard Intel Wifi/BT card, you can do with this Kext: itlwm
But I recommend installing a macOS compatible Wifi/BT card from Broadcom.
If you have a PCI-slot, then I recommend the Fenvi FV T919 (Bluetooth 4.0). It should work out of the box when you have plugged in the USB-cable, your USB-port mapping has the Fenvi's USB-port enabled and the USB-port of the onboard Intel Wifi/BT is disabled.
If you want to replace the onboard Intel Wifi/BT card, you have to check if your board supports any other Wifi/BT card.
I have used and recommend the BCM94360NG as a replacement.
iGPUs in the 11th Gen Intel CPUs or newer are not supported anymore.
That is why I use dGPU SMBIOS like iMacPro1,1 or MacPro7,1.
But as you can install 10th Gen Intel CPUs on Rocket Lake boards, this is how you can enable the iGPU.
In the config.plist set your SMBIOS to either iMac20,1 (for anything less than 10900k) or iMac20,2 (for 10900k) with 'SystemProductName'='iMac20,2'.
Remember, when choosing a different SMBIOS, you need to adjust your USBMapxx.kext accordingly. Open the info.plist and replace iMacPro1,1 with your current SMBIOS e.g. iMac20,2.
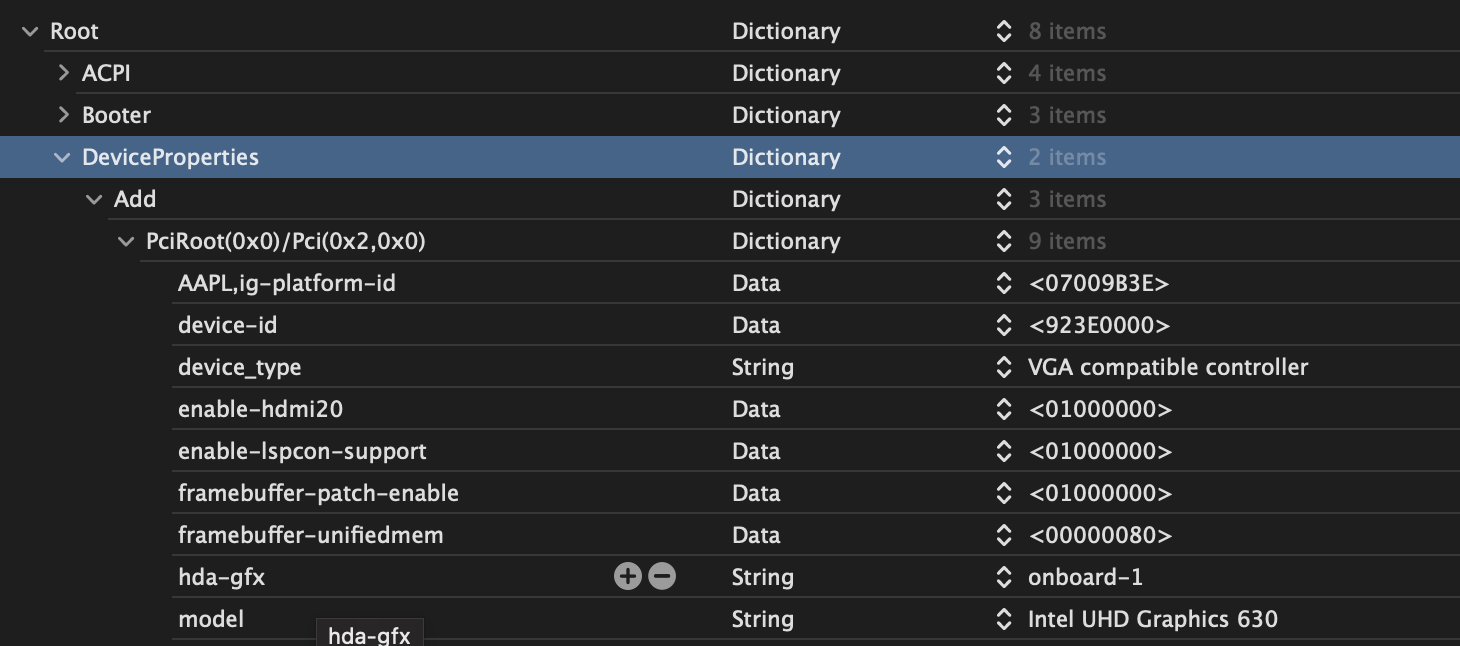
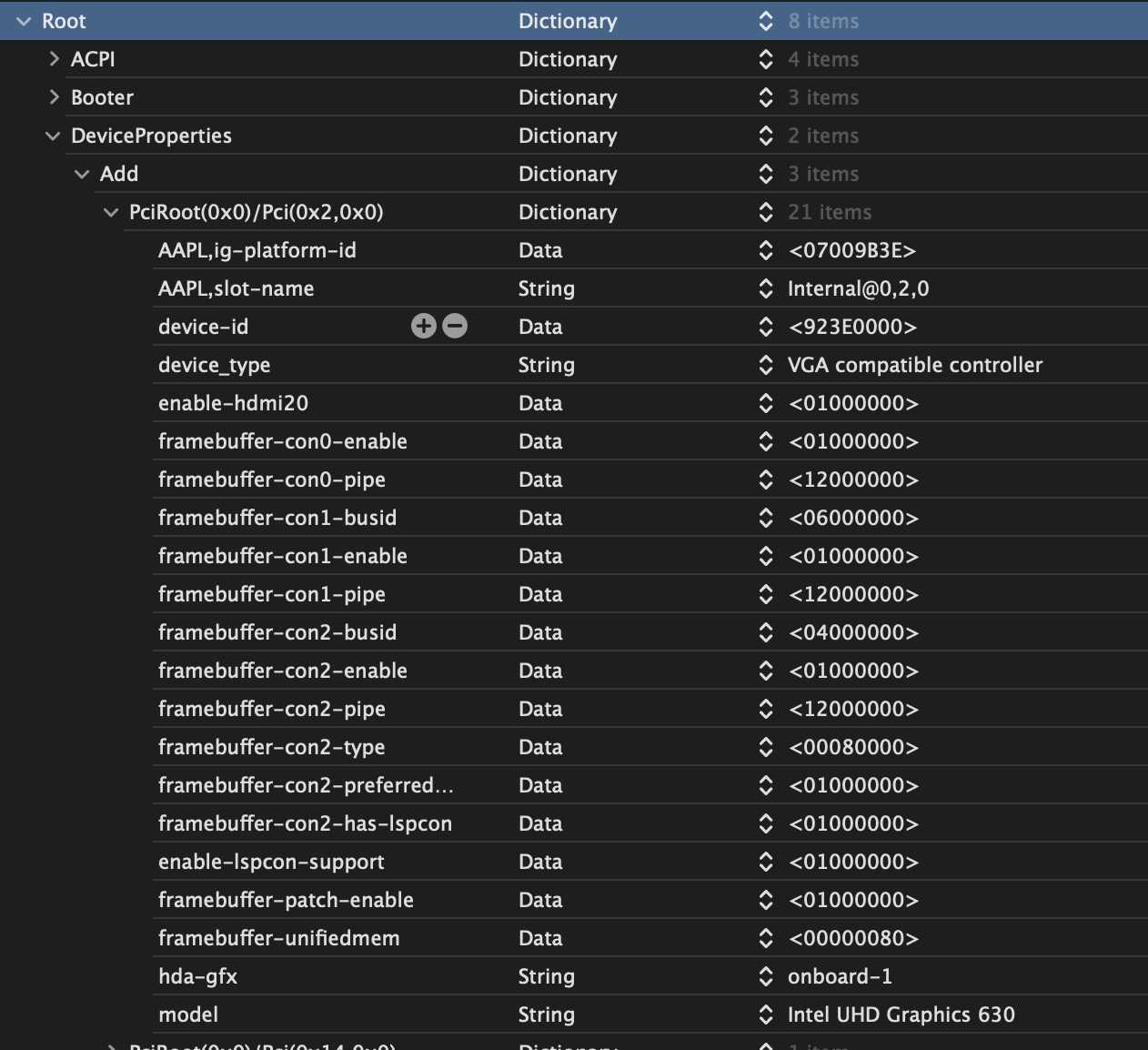
These device properties only activate the iGPU for display. But you might add much more properties to have video output from HDMI/DP.
See my iGPU Device Properties from my 10900k of my Gigybte Z490 Vision D for reference.
More information here: Framebuffer Patching Guide
In this Base-EFI is a Kext-based USB-Mapping.
Personally I don't use the Kext-based USB-configuration anymore. Instead, I use the USB-Port configuration via SSDT (e.g. SSDT-USB-Ports-Z590i-VisionD.aml).
In this repos folder "USB-Mapping via SSDT" you will find a sample SSDT for my Gigabyte Z590i Vision D that you can use for reference. The SSDT-USB-Ports-Z590i-VisionD.aml has the same USB-port mapping as the Kext-based USBPorts_Z590i-VisionD.kext.
Use them as a reference.
The benefit of the SSDT-based configuration is, that we don't need specific kexts for each SMBIOS (iMac20,2; iMacPro1,1 etc.) and it is the cleanest way of doing the USB-Port Mapping.
There are many guides available how to do a Kext-based USB-Mapping. E.g. see this Guide here: USB Mapping
In my SSDT you will see the comments for each port, some are enabled, some are disabled.
Per port you have two relevant methods:
- GUPC (Gigabyte variant of the standard method _UPC: USB port Capabilities)
- GPLD (Gigabyte variant of the standard method _PLD: Physical Location of Device)
GUPC describes the USB-port capabilities.
E.g. GUPC (One, 0x03) means this port is enabled (one) and is a USB3-Type A (0x03) The first variable means enabled/disabled (one or 0xFF/zero or 0x00), the second variable describes the port itself.
- zero is the same as 0x00
- one is the same as 0xFF
Port types:
- 0x00 or zero: standard USB2 port (usually black)
- 0x03: USB3 Type A (usually blue, red or yellow)
- 0x09: Type-C with switch, where it doesn't matter which direction you plug the device in, it is always the same port.
- 0x0A: Type-C without switch, where there are used two ports, each for one direction.
- 0xFF: internal devices used for RGB, Audio, Bluetooth etc.
GPLD-method describes the port location.
E.g. GPLD (One, 0x09) means this port is available on this board (one) and has the location HS09 (0x09).
HS11 would be (0x0B). SS ports start with 1. E.g. SS01 is 0x11, SS10 is 0x1A.
If you don't know the Hex-names of the ports, you can use Hackintool, e.g. Decimal 9 is also Hex 9 but 10 is A:

If you want to disable ports for macOS-only, you should wrap them like this:
If (_OSI ("Darwin"))
{
Return (GUPC (Zero, Zero))
}
Else
{
Return (GUPC (0xFF, 0x09))
}
_OSI ("Darwin") means "If the operating system is macOS (Darwin Kernel) do this..."
This way other OS like Windows or Linux would use the Else-case where this port is enabled (0xFF) and has is a type-C with switch (0x09).
You also need to Delete the original ACPI-table for the USB-Port Mapping: SSDT-7-xh_cmsd4.aml