This repository contains the code for the NPSN method applied to the trajectory forecasting models.
Non-Probability Sampling Network for Stochastic Human Trajectory Prediction
Inhwan Bae,
Jin-Hwi Park, and
Hae-Gon Jeon
Accepted to
CVPR 2022
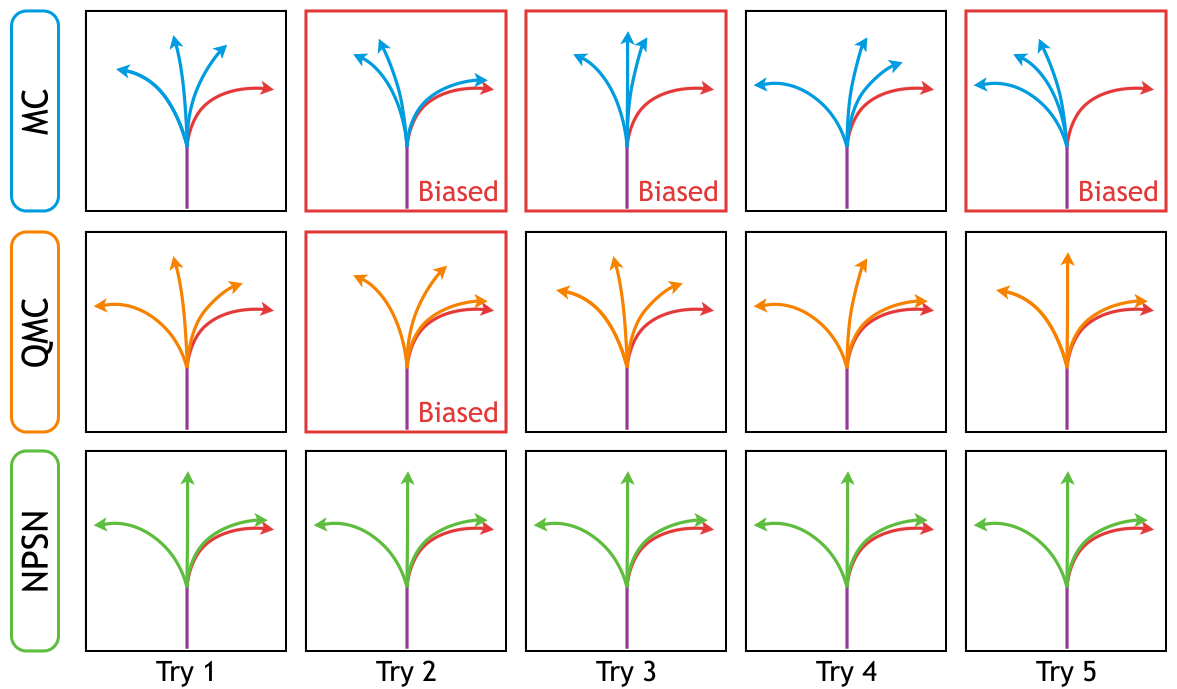
- Inferences of all stochastic models are biased toward the random sampling,
fail to generate a set of realistic paths from finite samples. - Quasi-Monte Carlo method, ensuring uniform coverage on the sampling space,
improves all the multimodal prediction results. - Non-Probability Sampling Network (NPSN), a very small network that generates purposive sample sequences,
can significantly improve both the prediction accuracy (up to 60%) and reliability. - Simply replacing one line of code on random sampling(
click) with our NPSN(here)!
Environment
All models were trained and tested on Ubuntu 18.04 with Python 3.7 and PyTorch 1.7.1 with CUDA 10.1.
Dataset
Preprocessed ETH and UCY datasets are included in this repository, under ./dataset/.
The train/validation/test splits are the same as those fond in Social-GAN.
Baseline models
This repository supports three baseline models: Social-STGCNN, SGCN and PECNet.
We have included model source codes from their official GitHub in the ./baselines/ folder.
To train our NPSN on the ETH and UCY datasets at once, we provide a bash script train.sh for a simplified execution.
./train.sh -b <baseline_model>For example, you can run the following command to train our NPSN with SGCN baseline with the best configuration.
./train.sh -b sgcnWe provide additional arguments for experiments:
./train.sh -t <experiment_tag> -b <baseline_model> -d <space_seperated_dataset_string> -i <space_seperated_gpu_id_string>
# Examples
./train.sh -b sgcn -d "hotel" -i "1"
./train.sh -t exp1 -b stgcnn -d "hotel" -i "1"
./train.sh -t npsn -b pecnet -d "eth hotel univ zara1 zara2" -i "0 0 0 0 0"If you want to train the model with custom hyper-parameters, use train_npsn.py instead of the script file.
python train_npsn.py --baseline <baseline_model> --tag <experiment_tag> --dataset <dataset_name> \
--num_samples <number_of_samples> --obs_len <observation sequence length> --pred_len <prediction sequence length> \
--batch_size <minibatch_size> --num_epochs <number_of_epochs> --lr <learning_rate> --lr_sh_rate <number_of_steps_to_drop_lr> \
--clip_grad <gradient_clipping> --gpu_num <gpu_id> --use_lrschd All the experiments in this work are performed with seed=0, strictly following PyTorch Reproducibility.
We checked that the same results were reproduced on RTX 2080Ti (Ubuntu 18.04, PyTorch 1.7.1, CUDA 10.1) and RTX 3090 (Ubuntu 20.04, PyTorch 1.9.0, CUDA 11.1) environments.
Baseline models
We use model source codes and pretrained weights from their official GitHub.
Pretrained baseline models are included in the ./pretrained/ folder.
Important note for PECNet (Click to expand)
-
Data Split
For an apple-to-apple comparison, we used the train-validation-test split of Social-GAN. We used the same data split strategy for all other baseline models. -
Dataloader
We used Social-GAN's dataloader instead of their pre-processed pickle file. To work similarly to PECNet's original dataloader, we wrote codes for custombatch-samplerandcollate-function. -
Data Types
We used torch.FloatTensor instead of torch.DoubleTensor as the data type of the model. We checked that the performance difference between them was negligible.
NPSN method
We have included pretrained NPSN models for each baseline model in the ./checkpoints/ folder.
You can use test_npsn.py to easily run any of the sampling methods on any of the baseline models.
python test_npsn.py --baseline <baseline_model> --tag <experiment_tag> --method <sampling_method> --gpu_num <gpu_id_for_evaluation>For example, you can replicate the Table 1 results for all datasets for SGCN baseline like this:
python test_npsn.py --baseline sgcn --tag npsn-sgcn --method mc --gpu_num 0
python test_npsn.py --baseline sgcn --tag npsn-sgcn --method qmc --gpu_num 1
python test_npsn.py --baseline sgcn --tag npsn-sgcn --method npsn --gpu_num 2If you find this code useful for your research, please cite our paper :)
@inproceedings{bae2022npsn,
title={Non-Probability Sampling Network for Stochastic Human Trajectory Prediction},
author={Bae, Inhwan and Park, Jin-Hwi and Jeon, Hae-Gon},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
year={2022}
}Part of our code is borrowed from Social-STGCNN, SGCN and PECNet. We thank the authors for releasing their code and models.