What is Unified Id? If GUID is too heavy for your application but you need a random global Id that can be used as a string or long basic type, you are in right place.
What are the main advantages?
| Feature | Unified | GUID |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 8 byte (13 as string) | 16 byte (36 as string) |
| Partitioning | Build-in | No, external can be added |
| Collisions | 0.00000001% in 10B IDs | 50% in 2.7e18 IDs |
| Cast | implicit(string, ulong, long) | explicit(byte[], Parse/ToString) |
| Generate | Build-in(byte[], string, GUID) | No, only random NewGuid |
| Null/Empty-handling | Friendly as Empty | Exception |
Install the NuGet package and write the following code:
using Unified;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var id = UnifiedId.NewId(); // AFHUTVDSGUGVQ
}
}You have created your first Unified Id!
Want to use it as a string? string id = UnifiedId.NewId(); or long? long id = UnifiedId.NewId();
UnifiedId could be used as DDD ValueObject in your entities.
using Unified;
class User
{
public UnifiedId UserId { set; get; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var user = new User
{
UserId = UnifiedId.NewId();
};
var settings = new JsonSerializerSettings // Could be added to global settings.
{
Converters = new List<JsonConverter>
{
new UnifiedIdConverter()
}
};
var json = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(user, settings); // { "UserId": "AFHUTVDSGUGVQ" }
}
}using Unified;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var guid = Guid.NewGuid();
var id = UnifiedId.FromGuid(guid);
var fnv = id.ToUInt64();
Console.WriteLine($"{guid} => {fnv} => {id}");
// 8dd02ad1-62cc-4015-9502-49658ba240ae => 15834445116674749764 => DNFPVU1LD2DA4
}
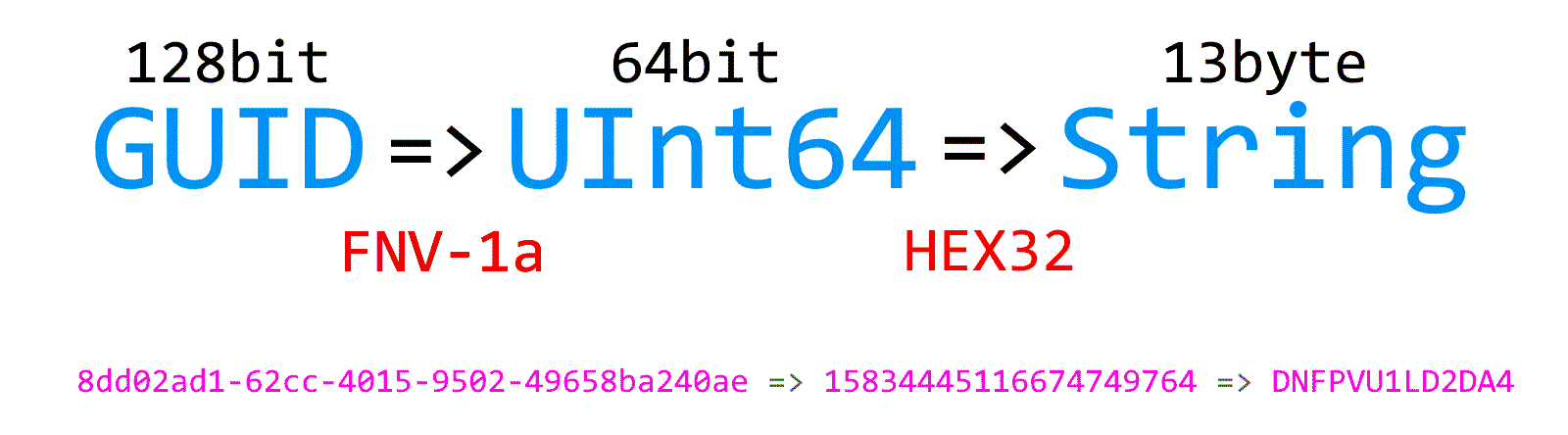
}Unified Id generates 64bit FNV-1a Id's based on GUID and converts it to HEX32 to use as string.
HEX32 is reversible, so you can convert it back from string to UInt64.
ulong number = UnifiedId.Parse("DNFPVU1LD2DA4");
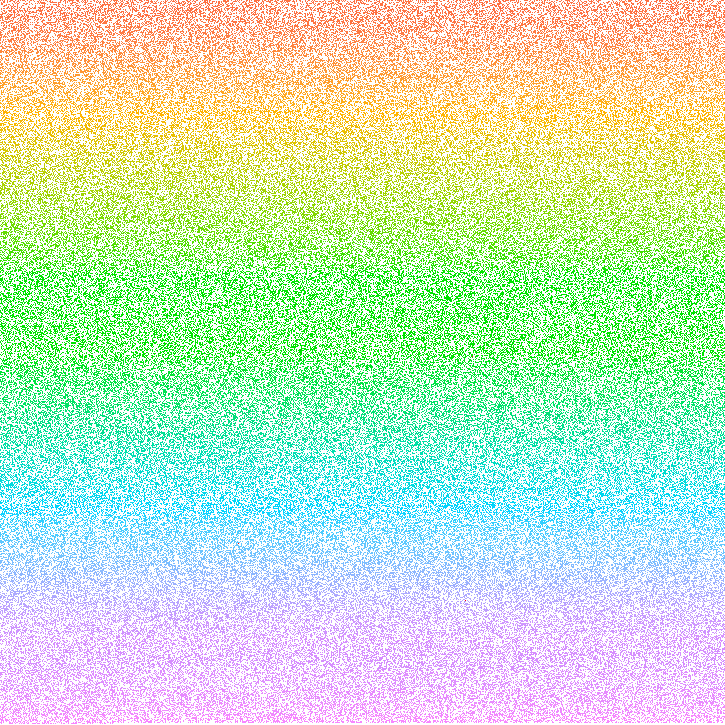
Why FNV-1a 64bit? because it has the best space randomization in the case of GUID conversion, below is space representation.
Default method of generation is GUID based using method var id = UnifiedId.NewId();.
This value could be used as string converted in HEX32 consisting of two parts.
[KEY][UNIFIED_ID] KEY - Partition/Shard Key and UNIFIED_ID as Row Unified Key together used as the global identity.
You can also generate this Id as a one-way hash using the following sources:
UnifiedId FromGuid(Guid id)UnifiedId FromBytes(byte[] bytes)UnifiedId FromString(string text)UnifiedId FromInt64(long number)UnifiedId FromUInt64(ulong number)
Do you need sequential Id? var id = new UnifiedId(DateTime.UtcNow.Ticks)
Want to save partitioned data? It's easy...
using Unified;
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Let's emulate the partitioned database.
var db = new Dictionary<string, List<UnifiedId>>();
// We will use 10M records, just to execute it fast.
var all = 10000000;
for (var i = 0; i <= all; i++)
{
// Generate random Id.
var id = UnifiedId.NewId();
// Get it's partition key. Number of partitions could be customized, default 16K.
var partition = id.PartitionKey();
// Initialize partitions in your DB.
if (!db.ContainsKey(partition))
{
db.Add(partition, new List<UnifiedId>());
}
// Add values to partitions.
db[partition].Add(id);
}
}
}Result:
DB Count : 16384
Each item contain : 610 elements +/-5%
We recommend using Unified Id for data sets size up to 10 billion Ids. More will increase the chance of collision.
© 2021 Serhii Seletskyi. All rights reserved.