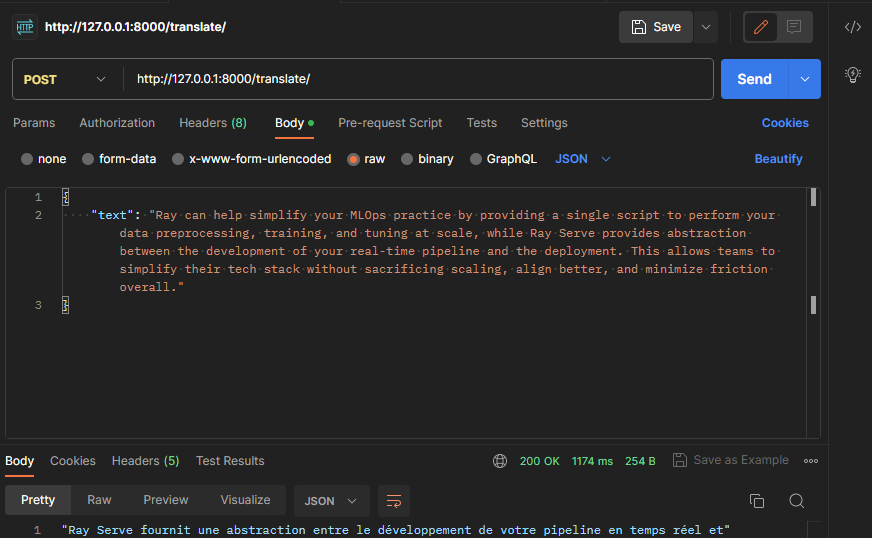
A basic example of a Ray Serve application. It demonstrates composing multiple-model machine learning models together into a single application; it combines multiple machine learning models (Summarize English text & Translate the summary into French) into a single API endpoint:
For the API, integrate with FastAPI to define more complex HTTP handling logic. This allows you to define a Serve deployment using the @serve.ingress decorator that wraps a FastAPI app with its full range of features (e.g. Automatic docs etc.)
To test locally, we run the script with the serve run CLI command. This command takes in an import path to our deployment formatted as module:application. Make sure to run the command from the directory containing the main.py file, so it can import the application:
serve run main:appThis command will run the FastApi application and then block, streaming logs to the console. It can be killed with Ctrl-C, which will tear down the application.
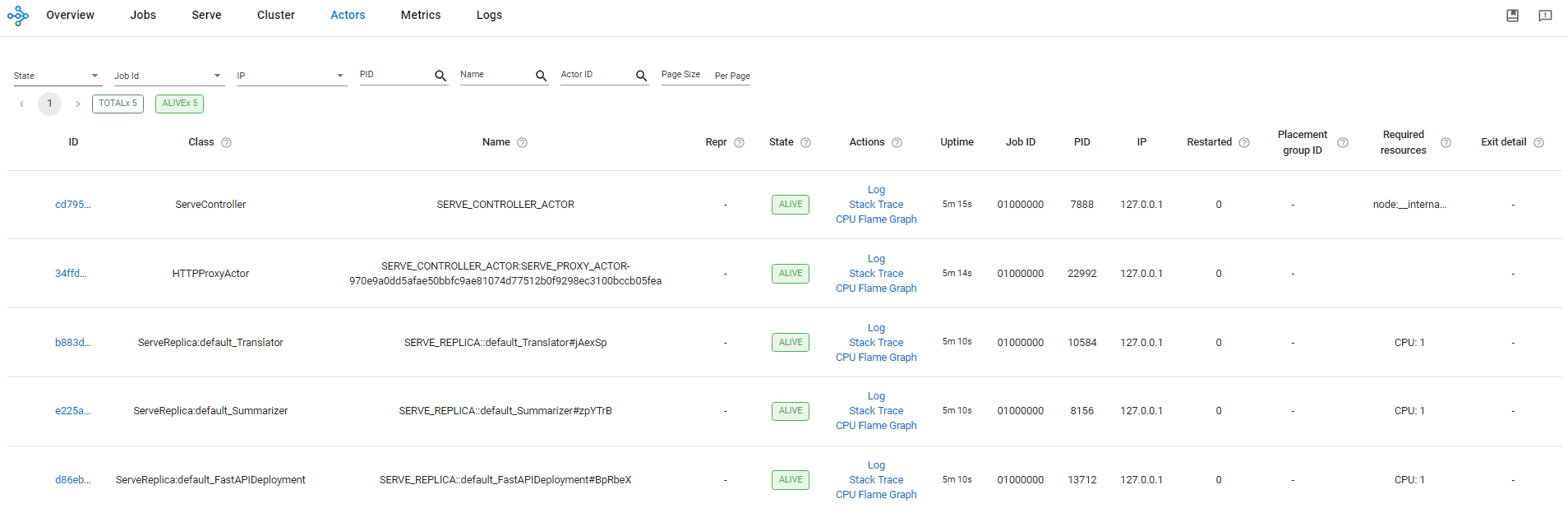
Ray provides a web-based dashboard for monitoring and debugging Ray applications. The visual representation of the system state, allows users to track the performance of applications and troubleshoot issues:
Here, we can:
- Analyze, monitor, or visualize status and resource utilization metrics for logical or physical components: Metrics view, Cluster view
- Monitor Job and Task progress and status: Jobs view
- Locate logs and error messages for failed Tasks and Actors: Jobs view, Logs view
- Analyze CPU and memory usage of Tasks and Actors: Metrics view, Cluster view
- Monitor a Serve application: Serve view
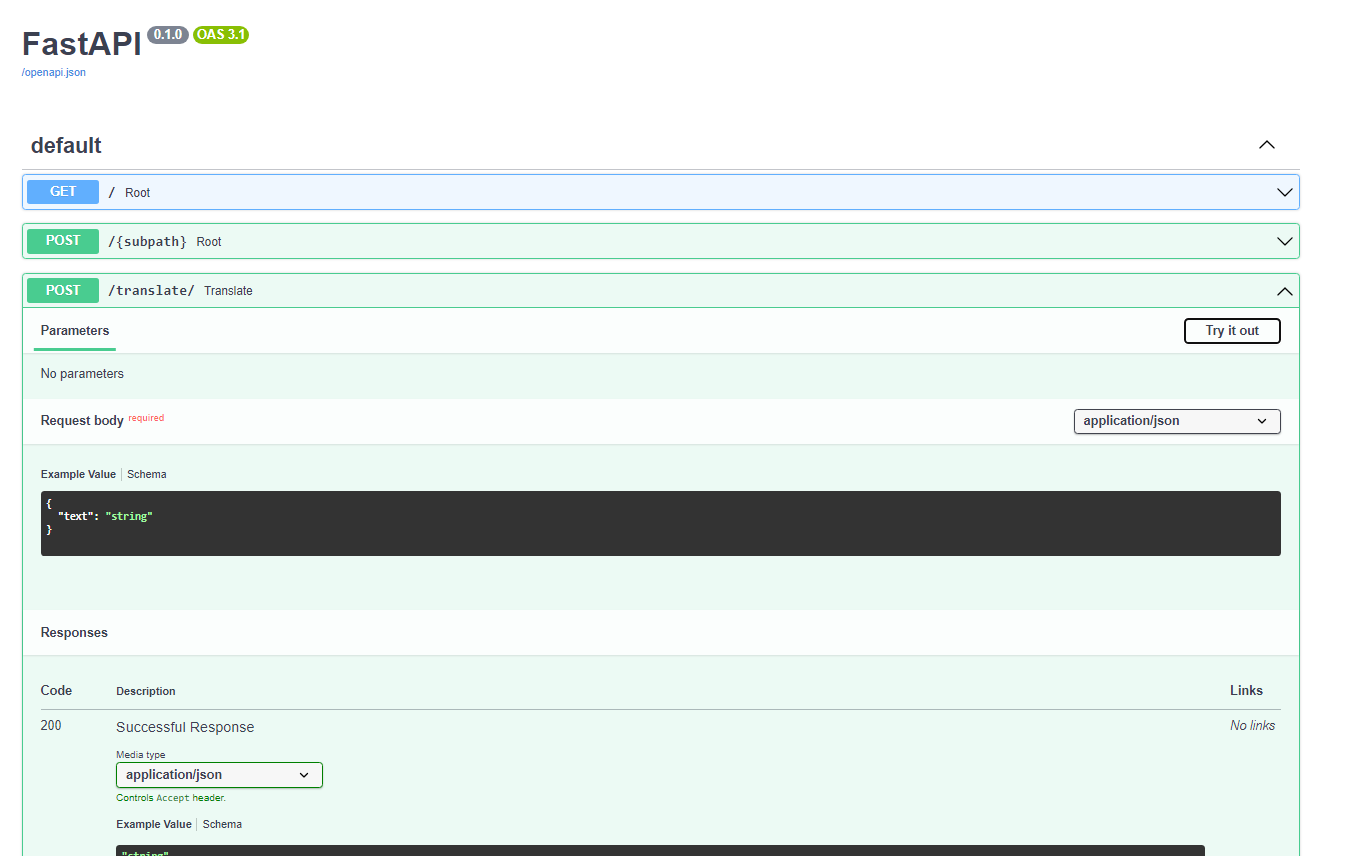
FastAPI provides Interactive API documentation and exploration web user interfaces. As the framework is based on OpenAPI, there are multiple options, 2 included by default. This one is Swagger UI, with interactive exploration, so you can call and test your API directly from the browser.
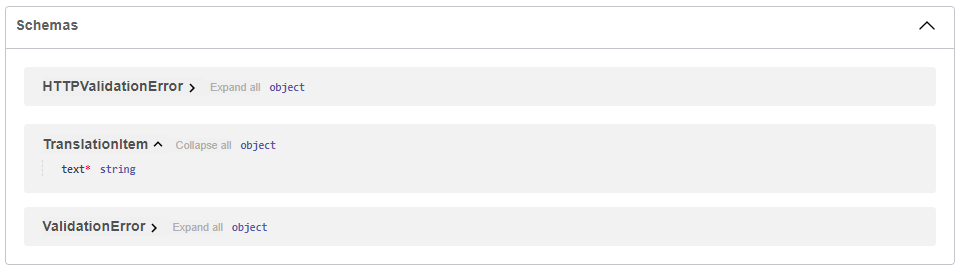
Since we declared our data model as a class that inherits from BaseModel from Pydantic like this:
from pydantic import BaseModel
class TranslationItem(BaseModel):
text: strThe JSON Schema of the model will be part of the OpenAPI generated schema, and will be shown in the interactive API docs:
Alternative API documentation with ReDoc is also available.