- git?
- git is a version control software
- It keep track of code changes
- It helps to collaborate in a project
- It is installed and maintained locally
- It provides Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Released in April 7, 2005
- Developed by Linus Torvalds & Junio C Hamano
- github?
- GitHub is a hosting service where we can keep our git repositiory/folders
- It is maintained on cloud/web
- It provides Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Founded in 2008
- Download and install git on your pc: https://git-scm.com/
- check git version: open terminal or cmd then use the command
git --versionto find out whether git is installed or not. if git is installed it will return a version number of git.
git configuration
- check all configuartion options:
git config - set global user name and user email for all repository/git folders (if you want to set different username and email for different git repository then remove --global)
- set global user name:
git config --global user.name "anisul-islam" - set global user email:
git config --global user.email "anisul2010s@yahoo.co.uk"
- set global user name:
- list all git configuration:
- list all the configuration:
git config --list - list user name:
git config user.name - list user email:
git config user.email
- list all the configuration:
- change global username & email
- change global user name:
git config --global user.name "PUT_NEW_USER_NAME_HERE" - change global user email:
git config --global user.email "PUT_NEW_USER_EMAIL_HERE"
- change global user name:
- creating a git folder
-
ls -a : list all files inside of a directory
mkdir DIRECTORY_NAME_HERE cd DIRECTORY_NAME_HERE git init Example: mkdir notes cd notes git init ls -a
- adding new files in git folder
-
git status : displays the state of the working directory and staging area
ls -a touch fileName.extension open fileName.extension git status Example: touch day1.txt open day1.txt write something inside the file -
Git is aware of the file but not added to our git repo
-
Files in git repo can have 2 states – tracked (git knows and added to git repo), untracked (file in the working directory, but not added to the local repository)
-
To make the file trackable stagging or adding is required
- adding files to stagging area:
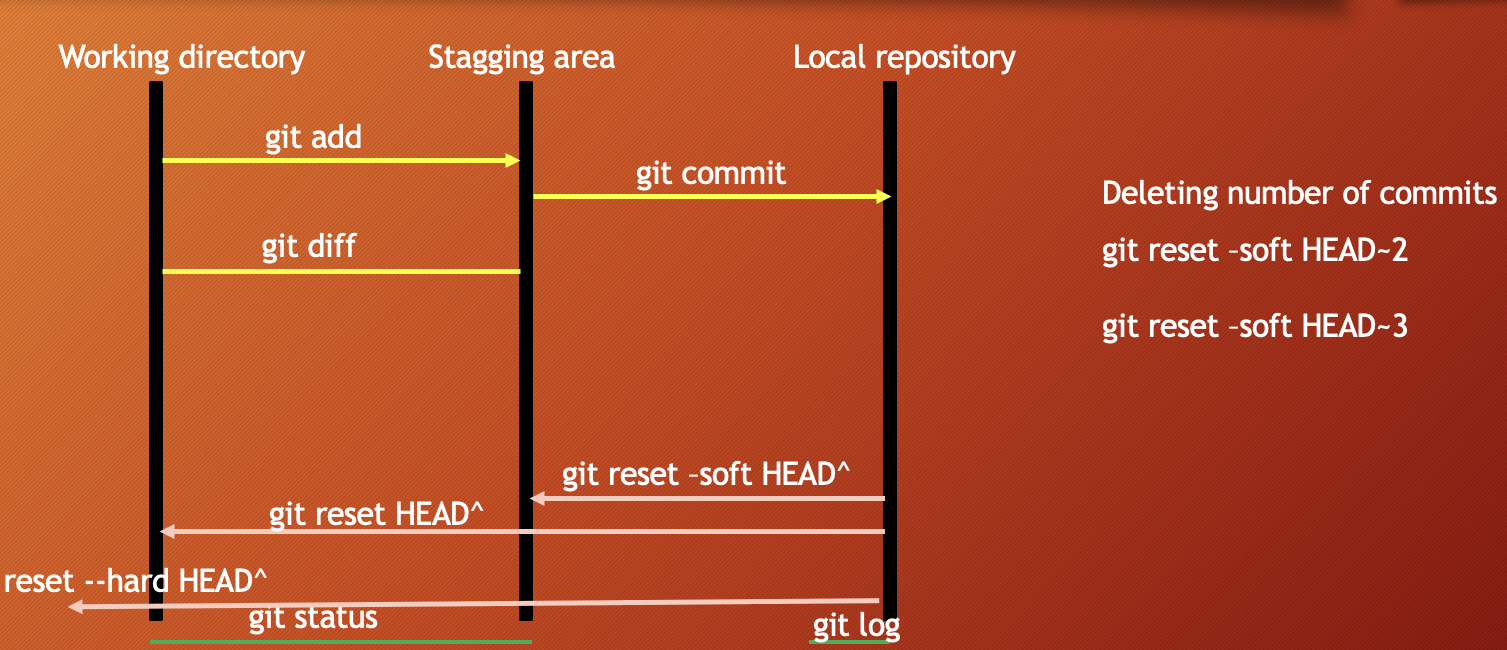
git add fileNameadd a file in staging area / indexgit add .add all files of directory to stagging area not subdirectorygit add -Aadd all files of directory and subdirectory to stagging areagit rm --cached fileNameunstage a file from staging areagit diff- checking the differences of a staged filegit restore fileName- restore the file
git commit -m "message"move the file to local repository from stagging areagit logcheck the commit historygit reset --soft HEAD^uncommit the commit in HEAD and move to staging areagit reset HEAD^uncommit the commit in HEAD and move to unstaging / working areagit reset --hard HEAD^uncommit the commit in HEAD and delete the commit completely with all the changes
git log --onelinegit showgit show HEAD^git show commit-idgit checkout commit-idgit checkout master
- create a .gitignore file and add the things you do not want to add in the stagging area
- Inside .gitignore we can keep secret files, hidden files, temporary files, log files
secret.txtsecret.txt will be ignored*.txtignore all files with .txt extension!main.txtignore all files with .txt extension without .main.txttest?.txtignore all files like test1.txt test2.txttemp/all the files in temp folders will be ignored
- sign in to your github account
- create a git repo
- Everything you need to know about README.md is discussed in the video.
- 6 heading levels: number of hashes define heading levels. check the following examples:
# heading 1 level text is here## heading 2 level text is here
- bold syntax:
__text goes here__ - italic syntax:
_text goes here_ - italic syntax:
_text goes here_ - strikethrouh syntax:
~this is~~ - single line code syntax: `` place code inside backticks
- multiple line code syntax: ``` place code inside three open and closing backticks
- multiple line code syntax: ```html for specific lanaguage use language name when starting; not closing
- for more please check the video by clicking the link given above
- check remote connection:
git remoteorgit remote -v git remote add name <REMOTE_URL>example: git remote add origin http://...
- push a branch
git push -u origin branch_name - push all branches
git push --all - pull from a repo:
git pullwhich is equivalent to git fetch + git merge
- Branch is a new and separate branch of master/main repository
- create a branch
git branch branch_name - List branches
git branch - List all remote branches
git branch -r - List all local & remote branches
git branch -a - move to a branch
git checkout branch_name - create and move to a branch
git checkout -b branch_name - delete a branch:
git branch -d branch_name - merge branches:
git checkout branchName git merge branchName git log --oneline --all --graph
- Reeference: