LLMRank aims to investigate the capacity of LLMs that act as the ranking model for recommender systems.
See our paper: Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Rankers for Recommender Systems
The code here is aligned with the new version in submission, please refer to [arxiv-branch] for the code that is aligned with our arXiv paper.
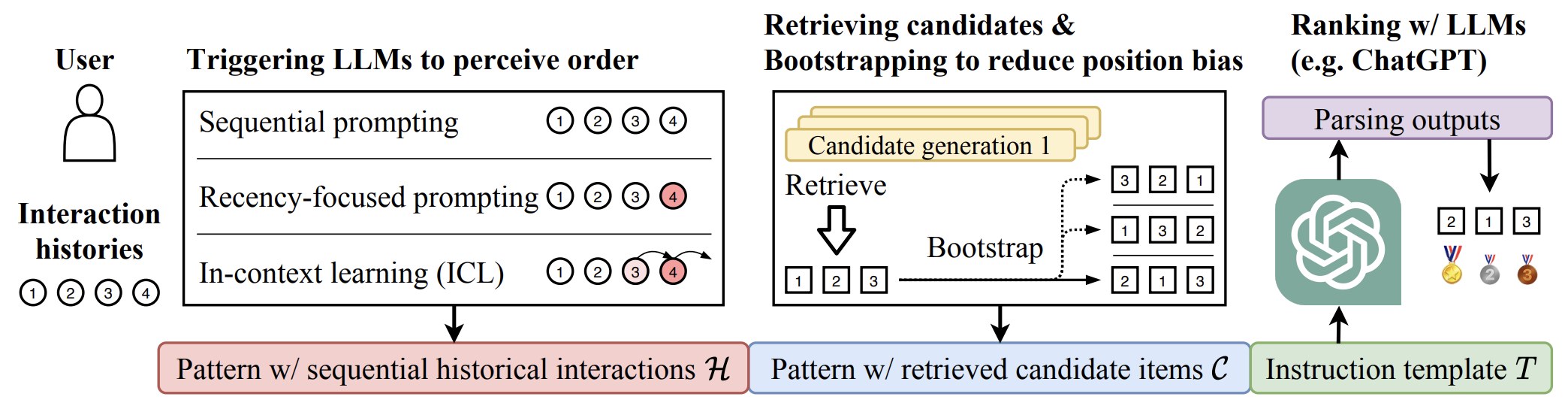
We use LLMs as ranking models in an instruction-following paradigm. For each user, we first construct two natural language patterns that contain sequential interaction histories and retrieved candidate items, respectively. Then these patterns are filled into a natural language template as the final instruction. In this way, LLMs are expected to understand the instructions and output the ranking results as the instruction suggests.
- Write your own OpenAI API keys into
llmrank/openai_api.yaml. - Unzip dataset files.
For data preparation details, please refer to [data-preparation].
cd llmrank/dataset/ml-1m/; unzip ml-1m.inter.zip cd llmrank/dataset/Games/; unzip Games.inter.zip
- Install dependencies.
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Evaluate ChatGPT's zero-shot ranking abilities on ML-1M dataset.
cd llmrank/ python evaluate.py -m Rank
Please click the links below each "Observation" to find the code and scripts to reproduce the results.
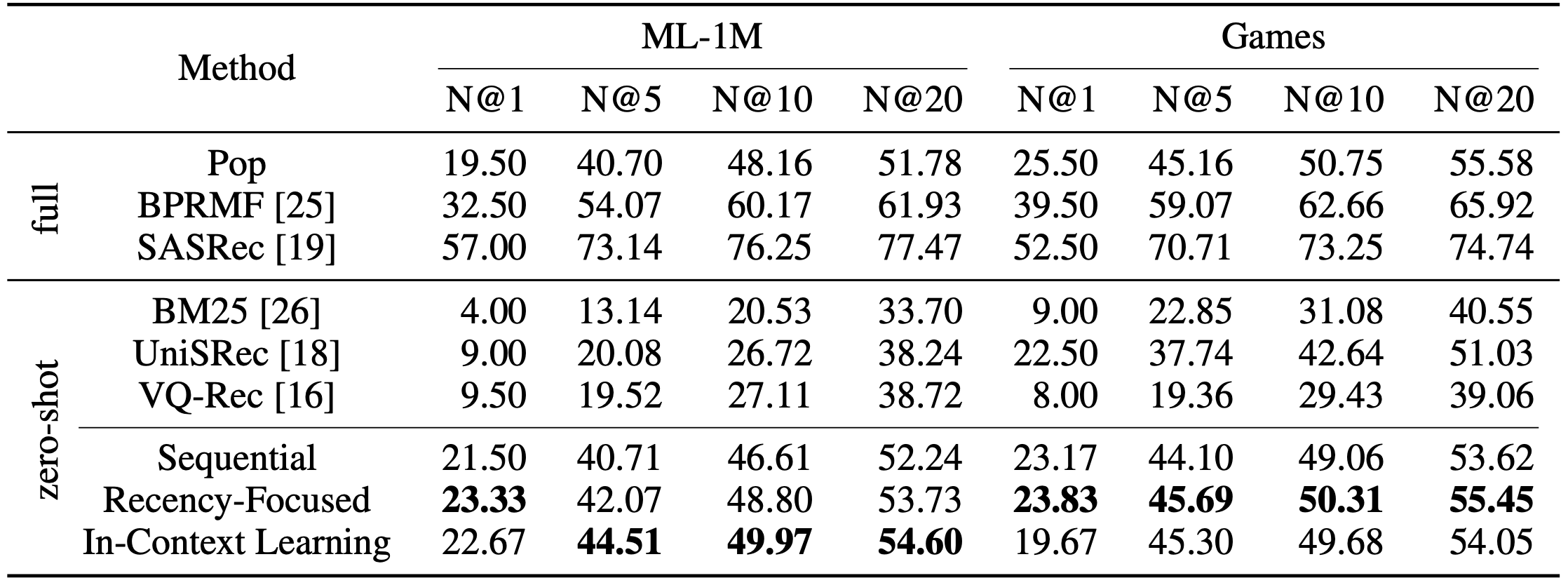
Observation 1. LLMs struggle to perceive order of user historie, but can be triggered to perceive the orders
LLMs can utilize historical behaviors for personalized ranking, but struggle to perceive the order of the given sequential interaction histories.
By employing specifically designed promptings, such as recency-focused prompting and in-context learning, LLMs can be triggered to perceive the order of historical user behaviors, leading to improved ranking performance.
Code is here -> [reproduction scripts]
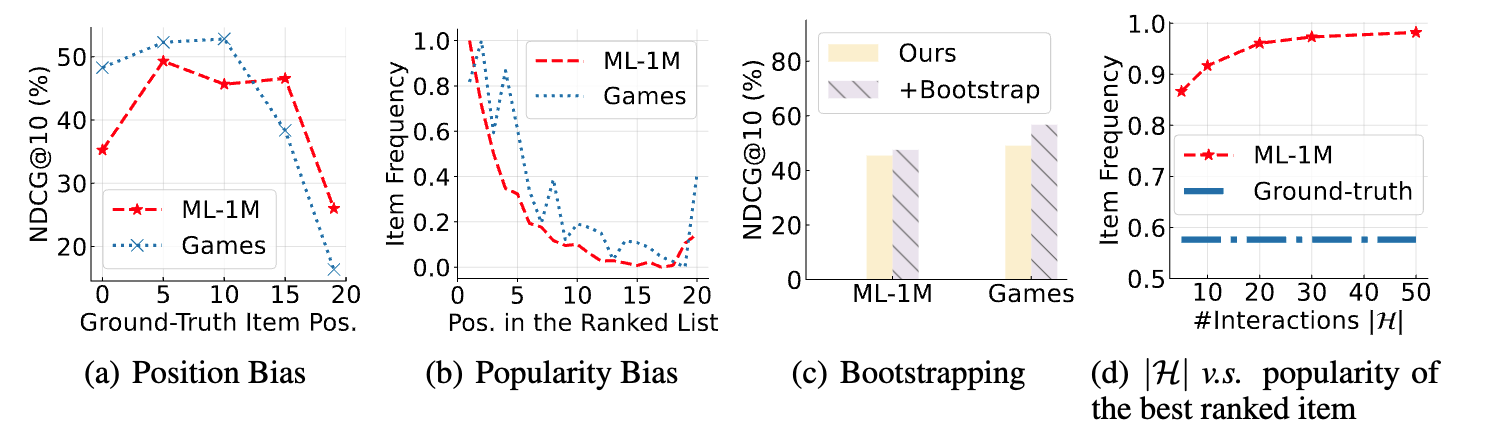
LLMs suffer from position bias and popularity bias while ranking, which can be alleviated by specially designed prompting or bootstrapping strategies.
Code is here -> [reproduction scripts]
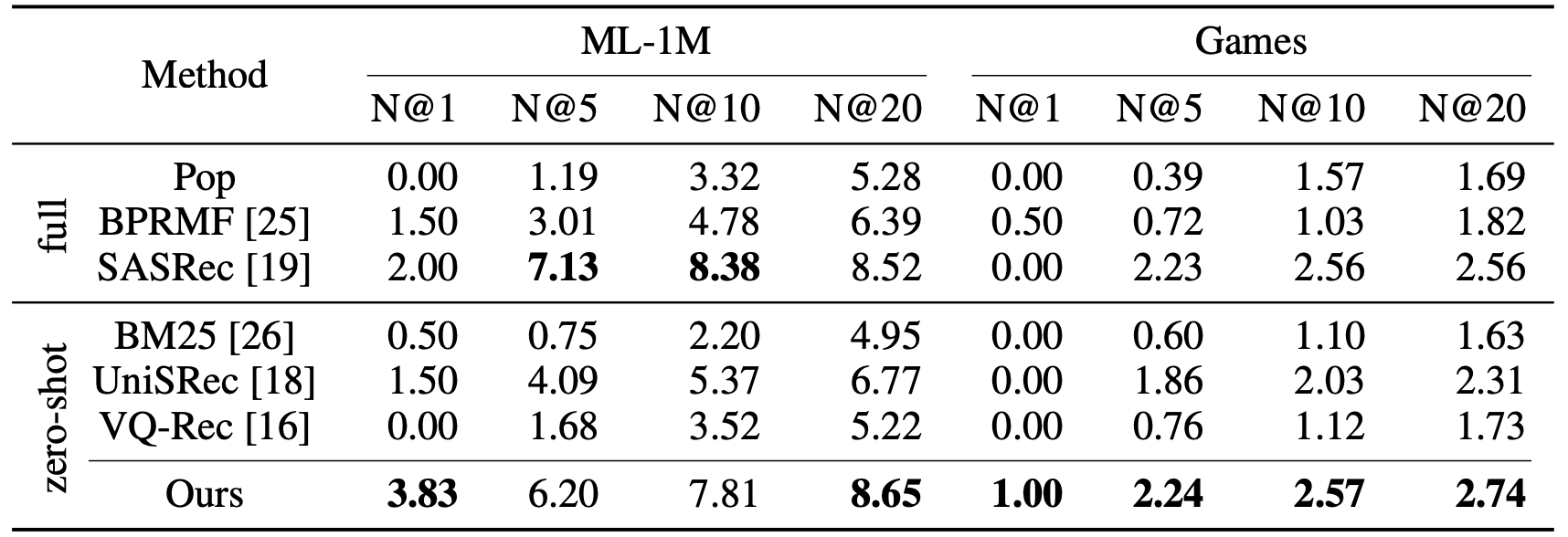
LLMs have promising zero-shot ranking abilities, especially on candidates retrieved by multiple candidate generation models with different practical strategies.
Code is here -> [reproduction scripts]
Please cite the following paper if you find our code helpful.
@article{hou2023llmrank,
title={Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Rankers for Recommender Systems},
author={Yupeng Hou and Junjie Zhang and Zihan Lin and Hongyu Lu and Ruobing Xie and Julian McAuley and Wayne Xin Zhao},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.08845},
year={2023}
}The experiments are conducted using the open-source recommendation library RecBole.
We use the released pre-trained models of UniSRec and VQ-Rec in our zero-shot recommendation benchmarks.
Thanks @neubig for the amazing implementation of asynchronous dispatching OpenAI APIs. [code]