Implementation of MAML and Reptile algorithms with a JS demo on the sine regression toy experiment
Both MAML and Reptile attempts to solve the metalearning problem by learning an initialization for network parameters, such that the network is able to adapt to new tasks quickly.
If we consider the space of network parameters, then MAML and Reptile both seek to find an optimal starting point in this space, from which the network can rapidly move to (read: learn) a set of good parameters given a new task / training set.
$ python maml-reptile.py
Just run the above command to train 10000 iterations of MAML, Reptile and FOMAML on the sine regression task.
The script ends by visualizing 2 plots:
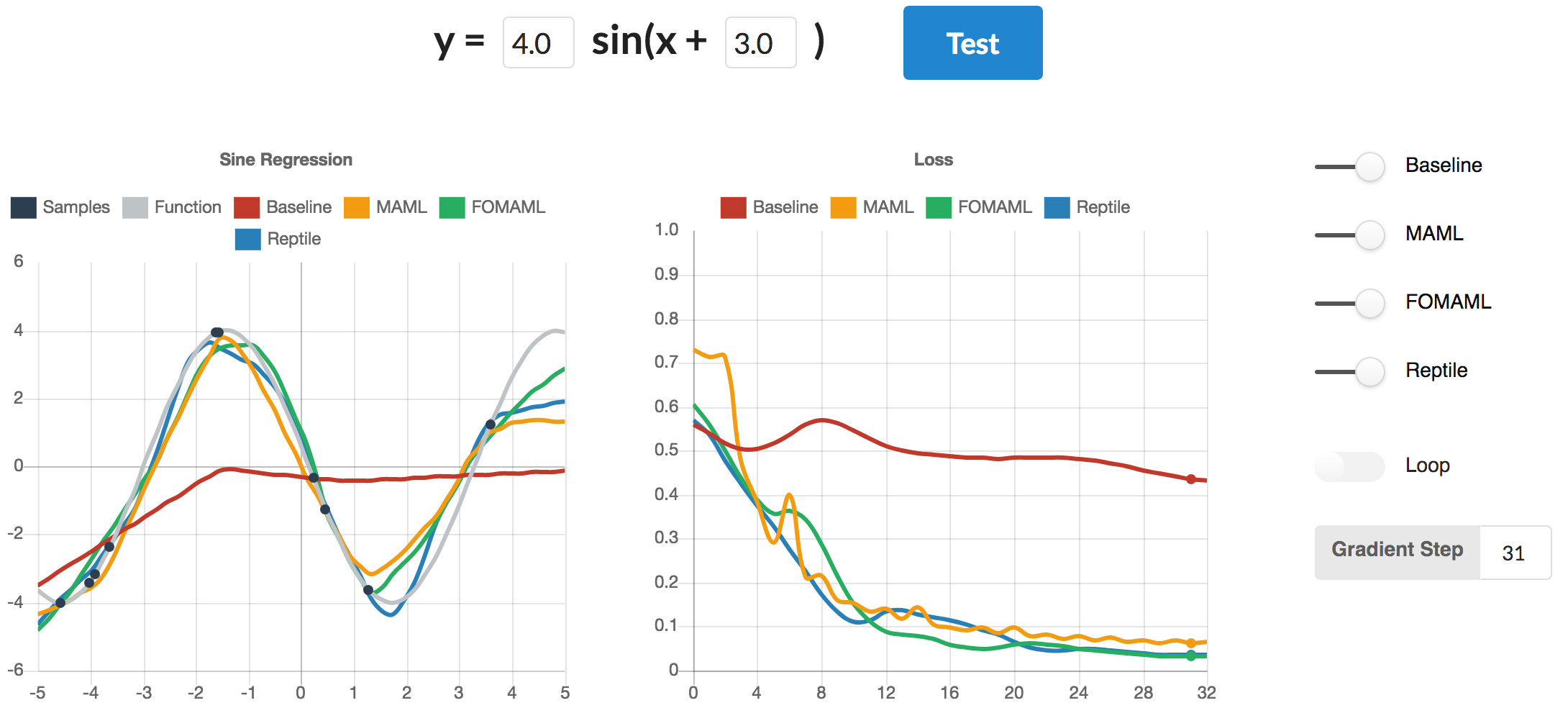
- The learned functions from each algorithm on a test task
- The loss against gradient step for each algorithm, averaged across 100 test runs.
There is also a GUI demo (uses Python3) that shows the performance of the algorithms on the sine regression task. We follow the task description in the Reptile paper.
To run the demo, run the following commands:
$ cd demo
$ open index.html
$ python3 -m server
Wait for the following message to appear:
* Running on http://0.0.0.0:8080/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Then click on Test. Wait for the data to load then toggle the options on the right side to show/hide the algorithms. Enable Loop to see how the learned functions change with each iteration. Disable Loop and enter a Gradient Step to see a specific iteration [0 - 32]. You can also change the amplitude and phase of the test task and hit Test again.