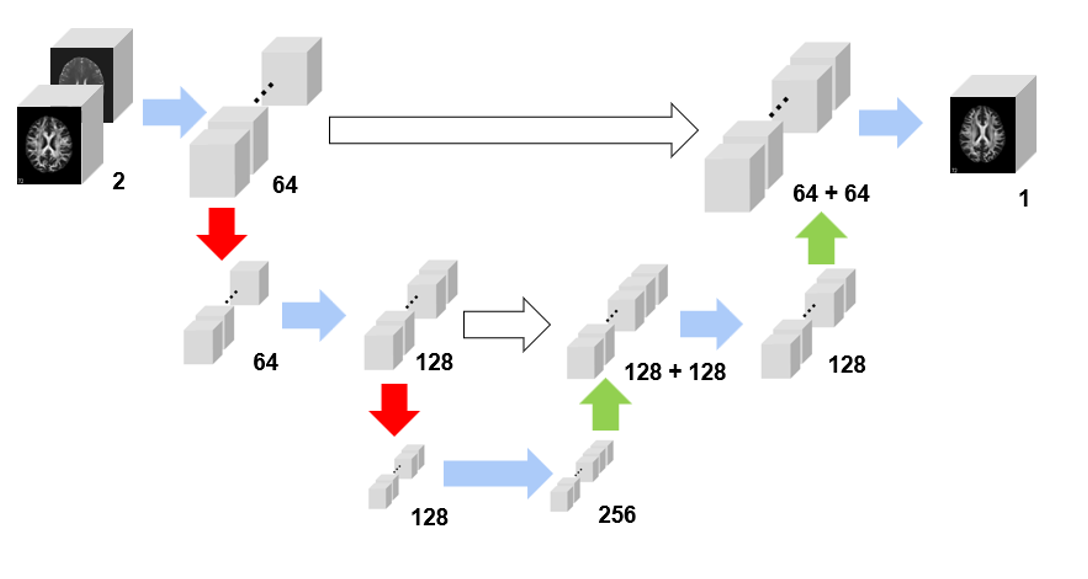
This is a 3D convolution U-Net to synthesize MRI FA and ADC phases. It can also work as a generator of condition GAN. This project wins the highest rank in Prof. Prince's EN.520.623 Midical Image Analysis in spring 2023. The final report can be found here.
This project aims to synthesize Fractional Anisotropy (FA) and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) maps from T1-weighted (T1w) and T2-weighted (T2w) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images. These maps provide crucial information about various tissue properties, some of which are not readily available during the MRI scanning process. To achieve this objective, we will utilize learning-based methods to extract the brain region, align the multi-slice images, and perform pixel-wise synthesis. Additionally, we will explore various optimization strategies, develop state-of-the-art neural networks, and establish balanced evaluation criteria. The effectiveness of the proposed approach will be evaluated comprehensively.
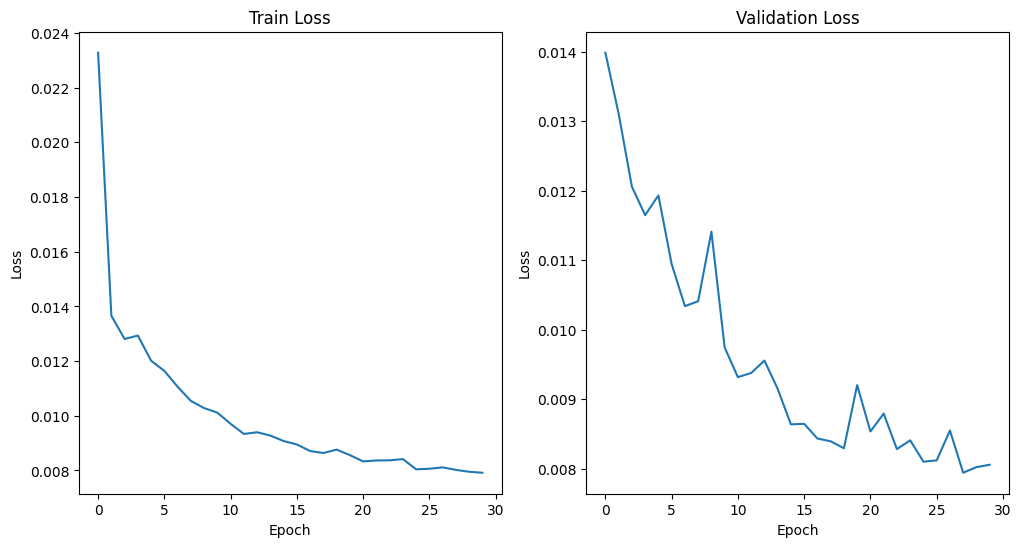
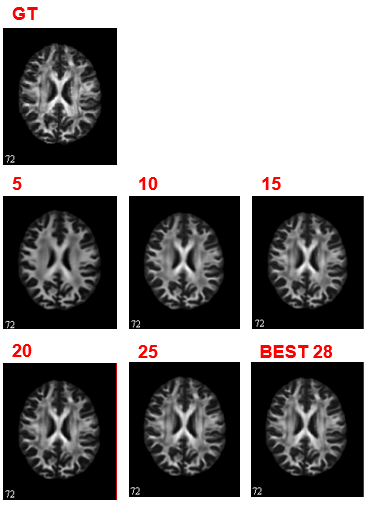
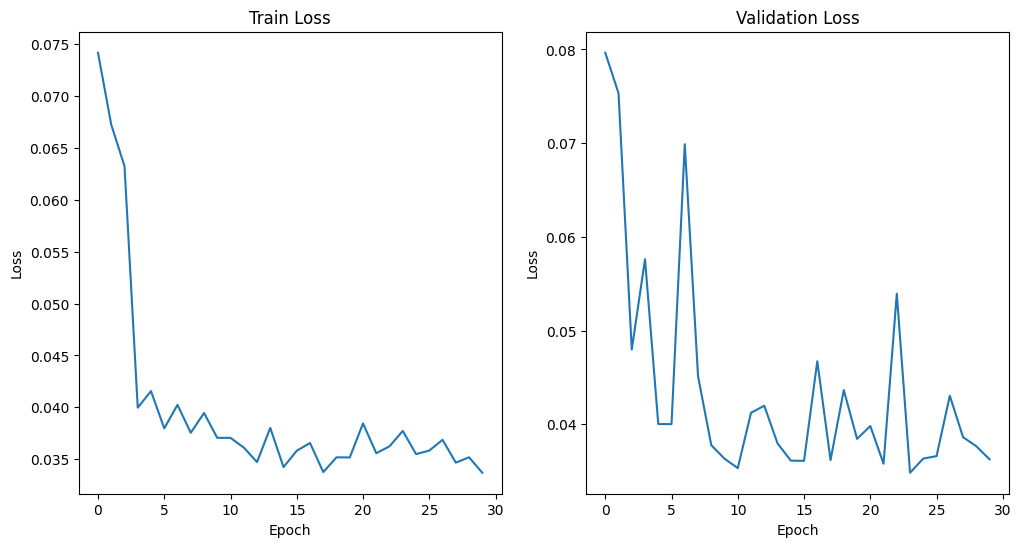
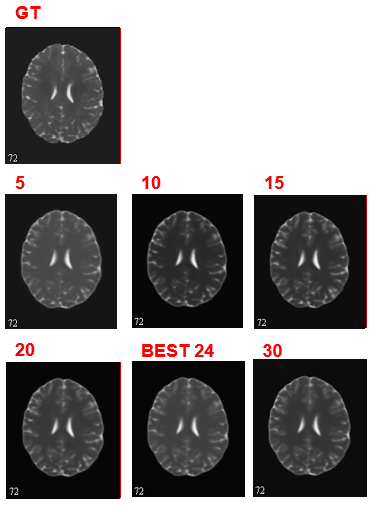
The FA network converges and get the minimal MAE loss 0.0079 at epoch 28. For ADC learning, there is still spike and plummet after 30 epochs. But they are of very small scale and hence be regarded as convergence. We find the minimal MAE loss 0.0348 at epoch 24.
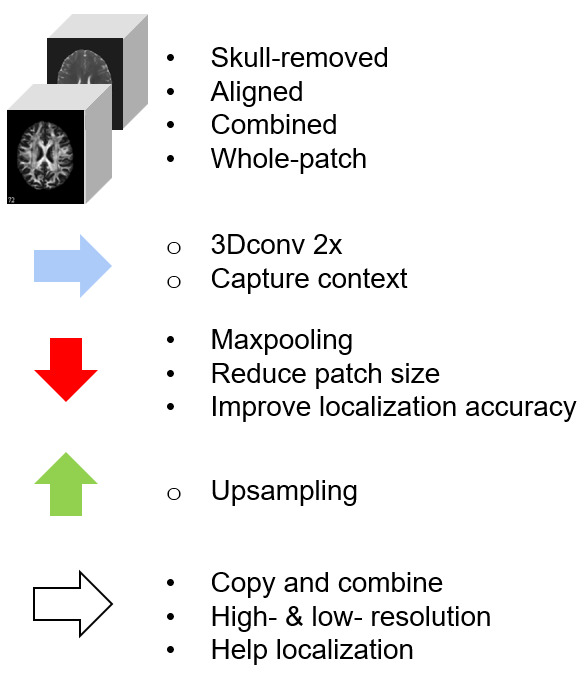
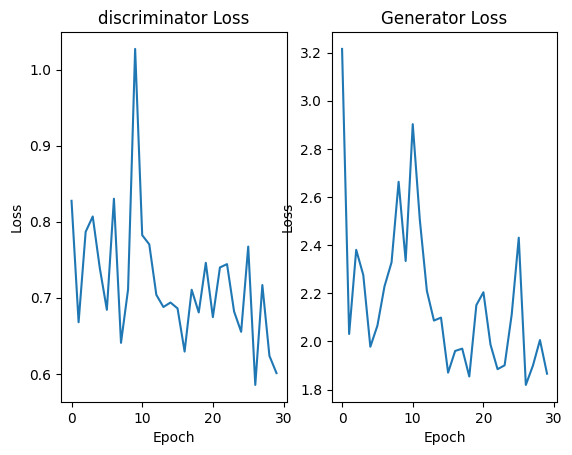
We copy the design of the U-Net architecture to set up the generator and develop five layers of 3D convolution to distinguish the images. We use MAE loss to evaluate the image quality of the generator and BCE loss to quantify the real and fake judgement. A smoothing label strategy is applied to prevent the model from being too confident about the binary calss labels.
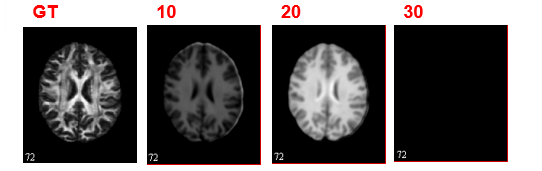
We set a ratio of 1:20 to train generator for one batch and discriminator for the next twenty batches. The ration will increase with iteration and finally reach 1:2. This setting would allow the CGAN reach a minimal generator loss of 1.8190 at epoch 25. The collapse happens at epoch 30 with a relatively high loss. We still need to fine-define a more balanced loss and try different architectures.
The raw dataset of 200 subjects are available, each containing four different types (T1w, T2w, FA, ADC) of MRI images.
We employ a pre-trained HD-BET model to extract the brain region by removing the skull. Subsequently, we utilize the registration function of the ANTsPy library to align the images to the T1w reference.
Python 3.9.16
PyTorch 2.0.0
NiBabel 5.1.0
NumPy 1.24.3
Matplotlib 3.7.1
tqdm 4.65.0