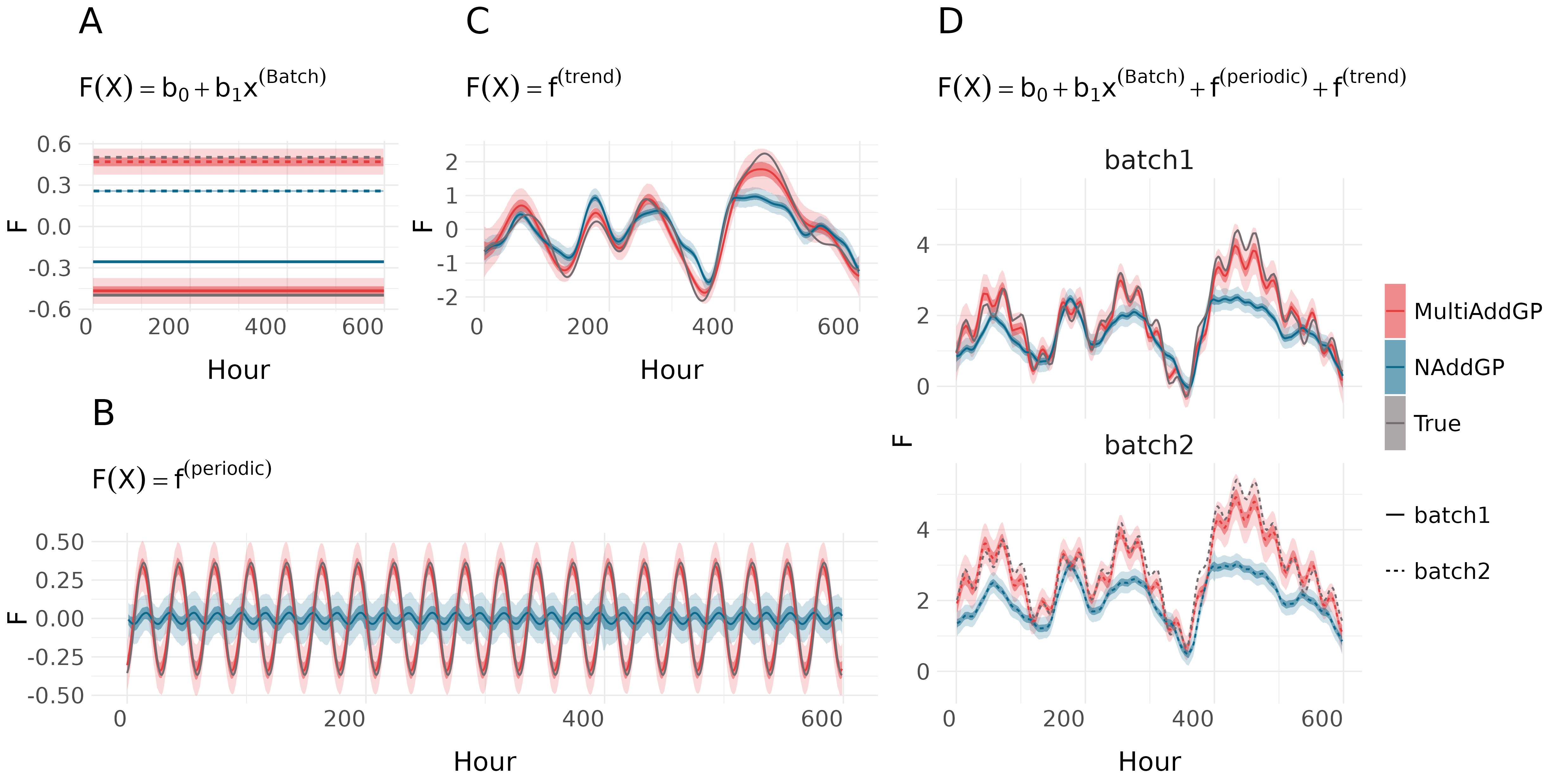
This repository contains code accompanying https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.03911
MultiAddGPs is a powerful statistical model designed to analyze additive linear and nonlinear effects on compositional count data, particularly suited for relative abundance analysis in microbiome studies or similar high-dimensional compositional datasets. The model leverages the Multinomial Logistic-Normal distribution, combined with Additive Gaussian Processes, to capture complex mixed linear and non-linear dynamics.
To reproduce the figures presented in the main text, follow the instructions below:
- Clone the repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/tinghua-chen/MultiAddGPs.git- Install the necessary R packages:
packages <- c("fido","dplyr","LaplaceDemon","mvtnorm","MASS","ggplot2","rBayesianOptimization","lubridate","gridExtra")
install.packages(packages)- Run
00_package_loading.Rto loading all necessary dataset
To generate Figure 1, simply run the figure1.R script. This will reproduce the figure based on the default dataset and model configuration.
To reproduce Figures 3 and 4, follow these steps:
- Run
01_data_preprocessing.Rto load and preprocess the artificial gut dataset - Run
02_analysis.Rto perform the required analysis on the dataset - Run
figure3&4.Rto generate Figures 3 and 4.
I have created a vignette demonstrating how to apply MultiAddGPs in practice using artificial gut data. You can view it here.
Note: MultiAddGPs extends the functionality of our previous fido package to accommodate both linear and nonlinear modeling in count data. If you haven't done so yet, I highly recommend reviewing the basset vignette in the fido package before working through the above example.
If you have any questions, don't hesitate to create an issue or reach out to tuc579@psu.edu