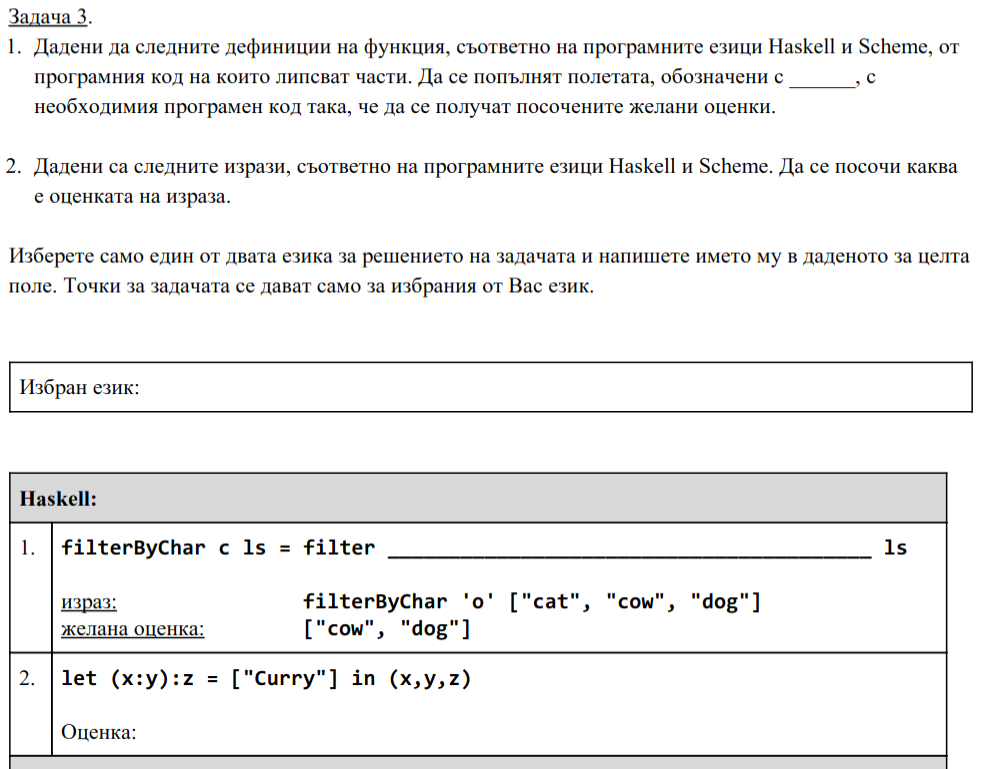
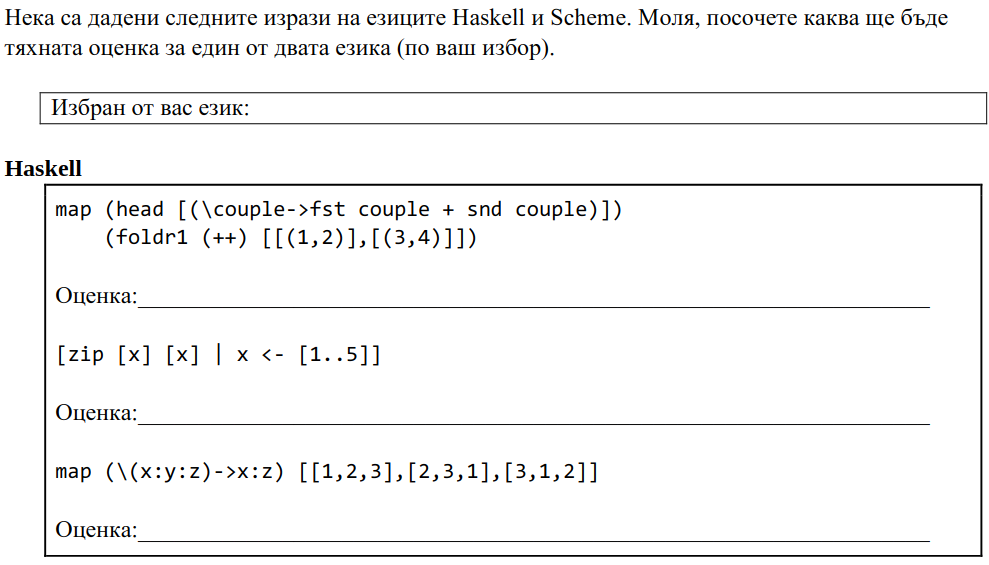
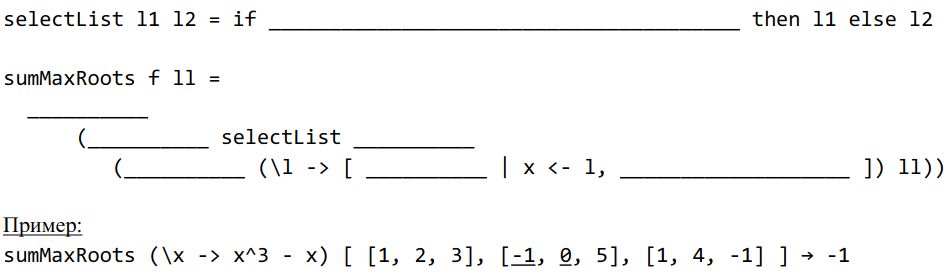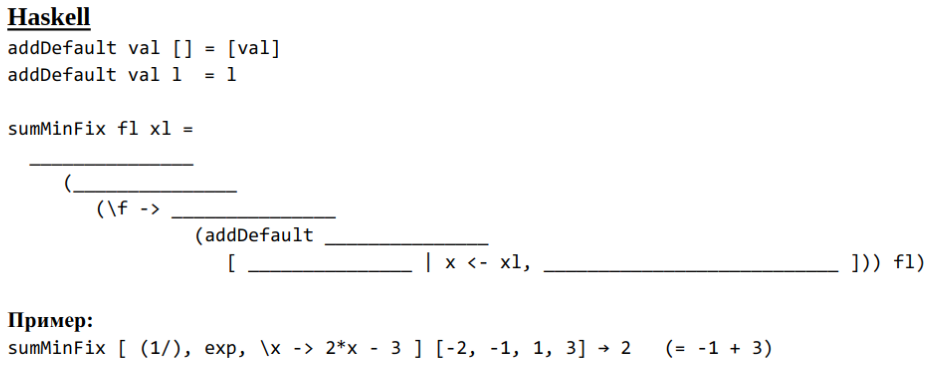notes_racket.txt, solve warmup tasks in Racket, 15 minute break.notes_haskell.txt, solve warmup tasks in Haskell, 15 minute break.- (iterate till 5 hours) solve 5 tasks from finals, 15 minute break.
https://www.fmi.uni-sofia.bg/bg/node/7349
- HASKELL IN 100 SECONDS
- Youtube channel (beginner to advanced)
- Book (read chapters [1 .. 8])
- Library for working with lists (Data.List)
- Library for working with characters/digits (Data.Char)
- Youtube channel (advanced)
- Learn Haskell in 1 hour
- CHEAT SHEET
- Introduction to Racket and Dr. Racket
- Racket API
- Working with numbers
- Working with lists and pairs
- Some built-in procedures
- Install DrRacket
- Go through
notes_racket.txt. - Go through
notes_haskell.txt.
Define functions that return:
- the smaller of two whole numbers:
- add a test with (a) negative number(s);
- using
if-else; - using guards;
- using a built-in function.
- the last digit of a number
- the quotient of the division of two whole numbers
- the quotient and remainder of the division of two whole numbers
- a whole number without its last digit
- the quotient and remainder of the division of two real numbers
- (for Haskell) the quotient of the division of two real numbers
- the average of two whole numbers
- the number rounded to the second digit after the
, - whether a whole number x is between two whole numbers - start and finish in one line without using if-else.
Test cases for Racket:
(= (my-min-if 15 60) 15)
(= (my-min-if 60 15) 15)
(= (my-min-guard 15 60) 15)
(= (my-min-guard 60 15) 15)
(= (my-min-built-in-p 5 6) 5)
(= (last-digit 154) 4)
(= (quotient-whole 64 2) 32)
(div-whole 154 17) ; 9 1/17
(= (remove-last-digit 154) 15)
(= (average-whole 5 1542) 773.5)
(= (round-two-dig pi) 3.14)Test cases for Haskell:
print $ min 5 6 == 5
print $ minIf 15 60 == 15
print $ minIf 60 15 == 15
print $ minGuard 15 60 == 15
print $ minGuard 60 15 == 15
print $ minBuiltIn 60 15 == 15
print $ lastDigit 154 == 4
print $ quotientWhole 64 2 == 32
print $ divWhole 154 17 == 9.058823529411764
print $ removeLastDigit 154 == 15
print $ divReal 154.451 10.01 == 15.42967032967033
print $ quotientReal 154.21 17.17 == 8
print $ avgWhole 5 1542 == 773.5
print $ roundTwoDig 3.1413465345321 == 3.14
print $ roundTwoDigButWithMagic 3.1413465345321 == 3.14
print $ inside 1 5 4 == True -- start = 1, finish = 5, x = 4
print $ inside 5 1 4 == True
print $ inside 10 50 20 == True
print $ inside 10 50 1 == FalseDefine a recursive polymorphic algebraic representing a binary tree. Create the following instances and print them:
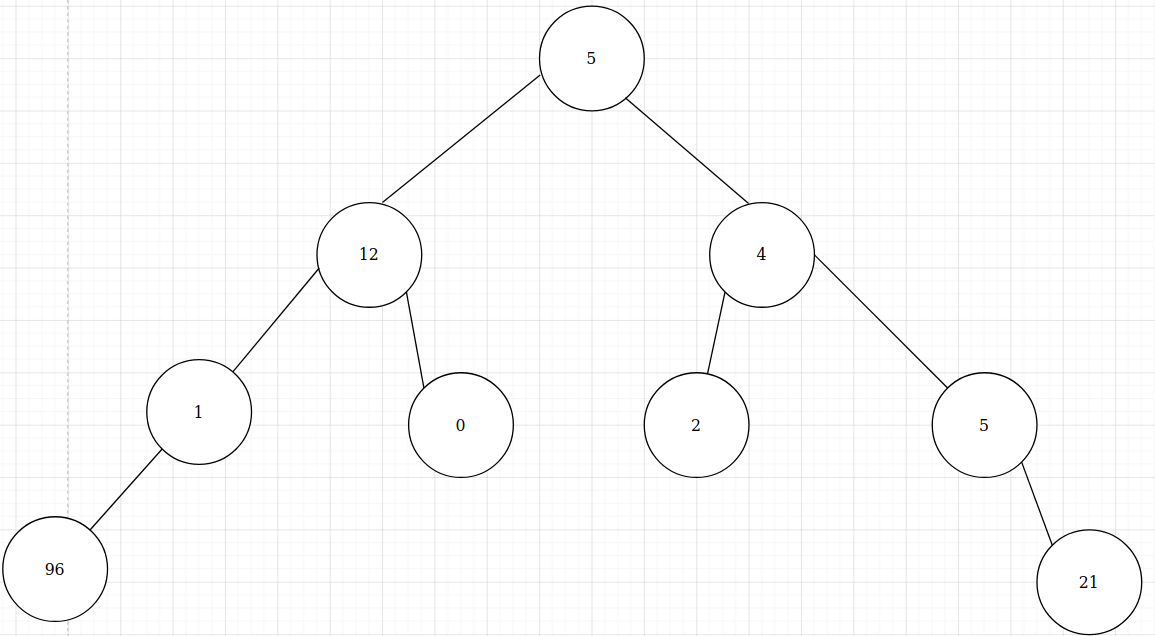
numberBTree:
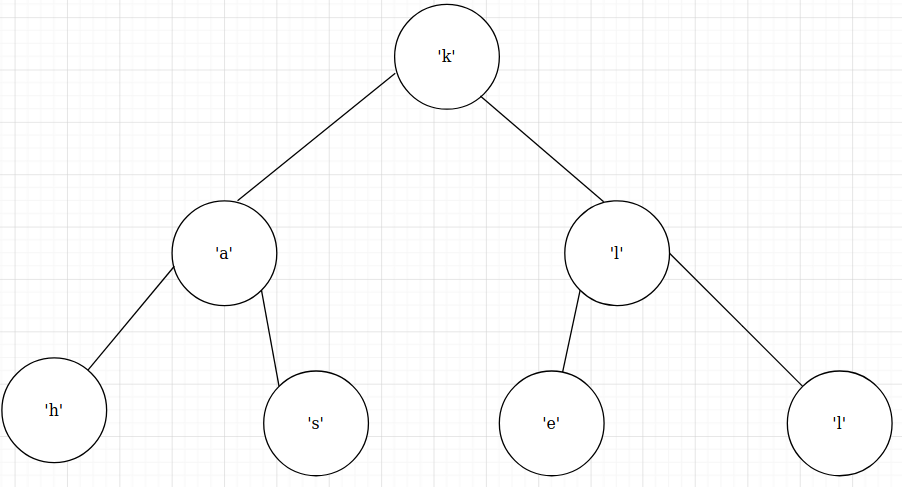
charBTree:
Define the following functions:
- size - returns the number of nodes;
- sumTree - returns the sum of the nodes (should work only for trees that store numbers in their nodes);
- traverseDFS - prints the nodes using DFS;
- getLevel - accepts a whole number k and returns the nodes at level k (root is at level 0);
- traverseBFS - prints the nodes using BFS;
- mapTree - maps an unary function to the tree.
- height (number of nodes along the longest branch);
- average - returns the average of the nodes (should work only for trees that store numbers in their nodes);
- sumLeaves - returns the sum of the leaves (should work only for trees that store numbers in their nodes);
- areEqual - checks whether two trees are identical;
- setLevels - replaces the values in all nodes with the vector ("level", "value");
- mirrorTree - returns the symmetric tree.
Test cases:
print $ numberBTree
print $ charBTree
print $ size numberBTree == 9
print $ size charBTree == 7
print $ sumTree numberBTree == 146
-- print $ sumTree charBTree -- should not work
print $ traverseDFS numberBTree == [96, 1, 12, 0, 5, 2, 4, 5, 21]
print $ traverseDFS charBTree == "haskell"
print $ getLevel numberBTree 2 == [1, 0, 2, 5]
print $ getLevel charBTree 1 == "al"
print $ getLevel charBTree 3 == []
print $ traverseBFS numberBTree == [5,12,4,1,0,2,5,96,21]
print $ traverseBFS charBTree == "kalhsel"
print $ mapTree numberBTree (*2) == Node 10 (Node 24 (Node 2 (Node 192 Nil Nil) Nil) (Node 0 Nil Nil)) (Node 8 (Node 4 Nil Nil) (Node 10 Nil (Node 42 Nil Nil)))
print $ mapTree numberBTree (show) == Node "5" (Node "12" (Node "1" (Node "96" Nil Nil) Nil) (Node "0" Nil Nil)) (Node "4" (Node "2" Nil Nil) (Node "5" Nil (Node "21" Nil Nil)))
print $ mapTree charBTree (toUpper) == Node 'K' (Node 'A' (Node 'H' Nil Nil) (Node 'S' Nil Nil)) (Node 'L' (Node 'E' Nil Nil) (Node 'L' Nil Nil))
print $ height numberBTree == 4
print $ height charBTree == 3
print $ average numberBTree == 16.22
--print $ average charBTree -- should not work
print $ sumLeaves numberBTree == 119
--print $ sumLeaves charBTree -- shouldn't work
print $ areEqual numberBTree (Node 5 (Node 12 (Node 1 (Node 96 Nil Nil) Nil) (Node 0 Nil Nil)) (Node 4 (Node 2 Nil Nil) (Node 5 Nil Nil))) == False
print $ areEqual charBTree charBTree == True
print $ areEqual numberBTree (Node 5 (Node 12 (Node 1 (Node 96 Nil Nil) Nil) (Node 0 Nil Nil)) (Node 8 (Node 2 Nil Nil) (Node 5 Nil (Node 21 Nil Nil)))) == False
print $ setLevels numberBTree == Node (0,5) (Node (1,12) (Node (2,1) (Node (3,96) Nil Nil) Nil) (Node (2,0) Nil Nil)) (Node (1,4) (Node (2,2) Nil Nil) (Node (2,5) Nil (Node (3,21) Nil Nil)))
print $ setLevels charBTree == Node (0,'k') (Node (1,'a') (Node (2,'h') Nil Nil) (Node (2,'s') Nil Nil)) (Node (1,'l') (Node (2,'e') Nil Nil) (Node (2,'l') Nil Nil))
print $ mirrorTree numberBTree == Node 5 (Node 4 (Node 5 (Node 21 Nil Nil) Nil) (Node 2 Nil Nil)) (Node 12 (Node 0 Nil Nil) (Node 1 Nil (Node 96 Nil Nil)))
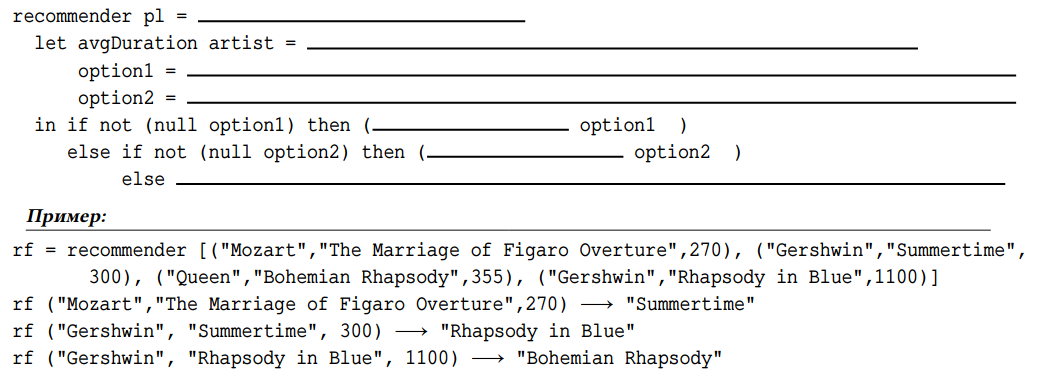
print $ mirrorTree charBTree == Node 'k' (Node 'l' (Node 'l' Nil Nil) (Node 'e' Nil Nil)) (Node 'a' (Node 's' Nil Nil) (Node 'h' Nil Nil))By using the following types define a function that accepts a list of records and returns the hardest subject. The difficulty of a subject is inversely proportional to the average grade of all students who are taking it.
Type definitions:
type Student = String
type Subject = String
type Note = Double
type Record = (Student, Subject, Note)Test cases for Racket:
(equal? (hardest-subject (list '("Maths" . 5) '("English" . 2) '("Programming" . 4) '("Programming" . 6) '("Maths" . 4) '("English" . 2))) "English")
(equal? (hardest-subject (list '("Maths" . 5) '("English" . 5) '("Programming" . 4) '("Programming" . 6) '("Maths" . 4) '("English" . 5))) "Maths")Test cases for Haskell:
print $ hardestSubject [("John", "Maths", 5), ("Kennedy", "English", 2), ("Joe", "Programming", 4), ("Claudia", "Programming", 6), ("Sam", "Maths", 4), ("Jenn", "English", 2)] == "English"
print $ hardestSubject [("John", "Maths", 5), ("Kennedy", "English", 5), ("Joe", "Programming", 4), ("Claudia", "Programming", 6), ("Sam", "Maths", 4), ("Jenn", "English", 5)] == "Maths"Define a function rf that takes two unary, whole-number functions as parameters - f and g and returns a binary function that takes a list - xs as its first argument, and an unary function - h as its second argument. The result from the call to rf should be a list containing elements in the form h(x) where x spans xs and f(x) > g(x).
Test cases for Racket:
(equal?
((rf (λ (x) (- -4 x)) (λ (x) (* x -2))) (range 1 11) (λ (x) (* x 3)))
(list 15 18 21 24 27 30)
) ; only 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 satisfy the conditionTest cases for Haskell:
print $ (rf ((-) (-4)) (* (-2))) [1..10] (* 3) == [15,18,21,24,27,30] -- only 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 satisfy the condition Define a function on a functional level that takes a word and returns a list of tuples in the form (x, xCount) where for each letter x, xCount is the number of times it is present in the word. Ignore capitalization.
Test cases for Racket:
(equal? (count-occurrences "Test") (list '("e" . 1) '("s" . 1) '("t" . 2)))
(equal? (count-occurrences "ThisIsAReallyLongWordContaingAlmostEveryCharacter") (list '("a" . 6) '("c" . 3) '("d" . 1) '("e" . 4) '("g" . 2) '("h" . 2) '("i" . 3) '("l" . 4) '("m" . 1) '("n" . 3) '("o" . 4) '("r" . 5) '("s" . 3) '("t" . 4) '("v" . 1) '("w" . 1) '("y" . 2)))Test cases for Haskell:
print $ countOccurrences "Test" == [('e',1),('s',1),('t',2)]
print $ countOccurrences "ThisIsAReallyLongWordContaingAlmostEveryCharacter" == [('a',6),('c',3),('d',1),('e',4),('g',2),('h',2),('i',3),('l',4),('m',1),('n',3),('o',4),('r',5),('s',3),('t',4),('v',1),('w',1),('y',2)]