English | 简体中文
Sponge is a powerful development framework that integrates automatic code generation, Gin and GRPC. Sponge has a rich set of code generation commands, and the generated different functional codes can be combined into a complete service (similar to how artificially broken sponge cells can automatically reassemble into a new complete sponge). From code generation, development, testing, API documentation to deployment, one-stop project development greatly improves development efficiency and reduces development difficulty, implementation of "low-code way" development projects.
If you are develop web or gRPC service with CRUD APIs, you don't need to write any Go code can be compiled and deployed to the linux server, docker, k8s, just need to connect to the database (mysql、mongodb、postgresql、tidb、sqlite) to generate a complete backend service Go code.
If you develop generic web or gRPC service, just focus on the three core parts of define tables in the database, define api description information in the proto files, fill in business logic code in the generated template files, and the rest of the Go code is automatically generated by sponge.
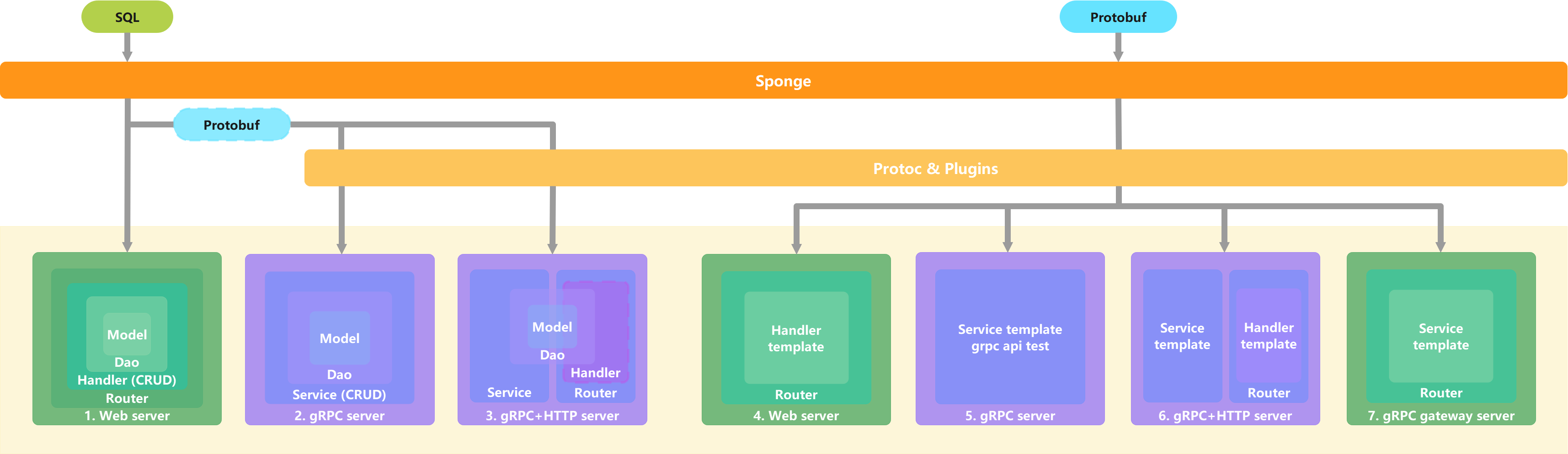
Sponge is mainly based on SQL and Protobuf two ways to generate code, each way has to generate code for different functions. SQL supports databases mysql, mongodb, postgresql, tidb, sqlite.
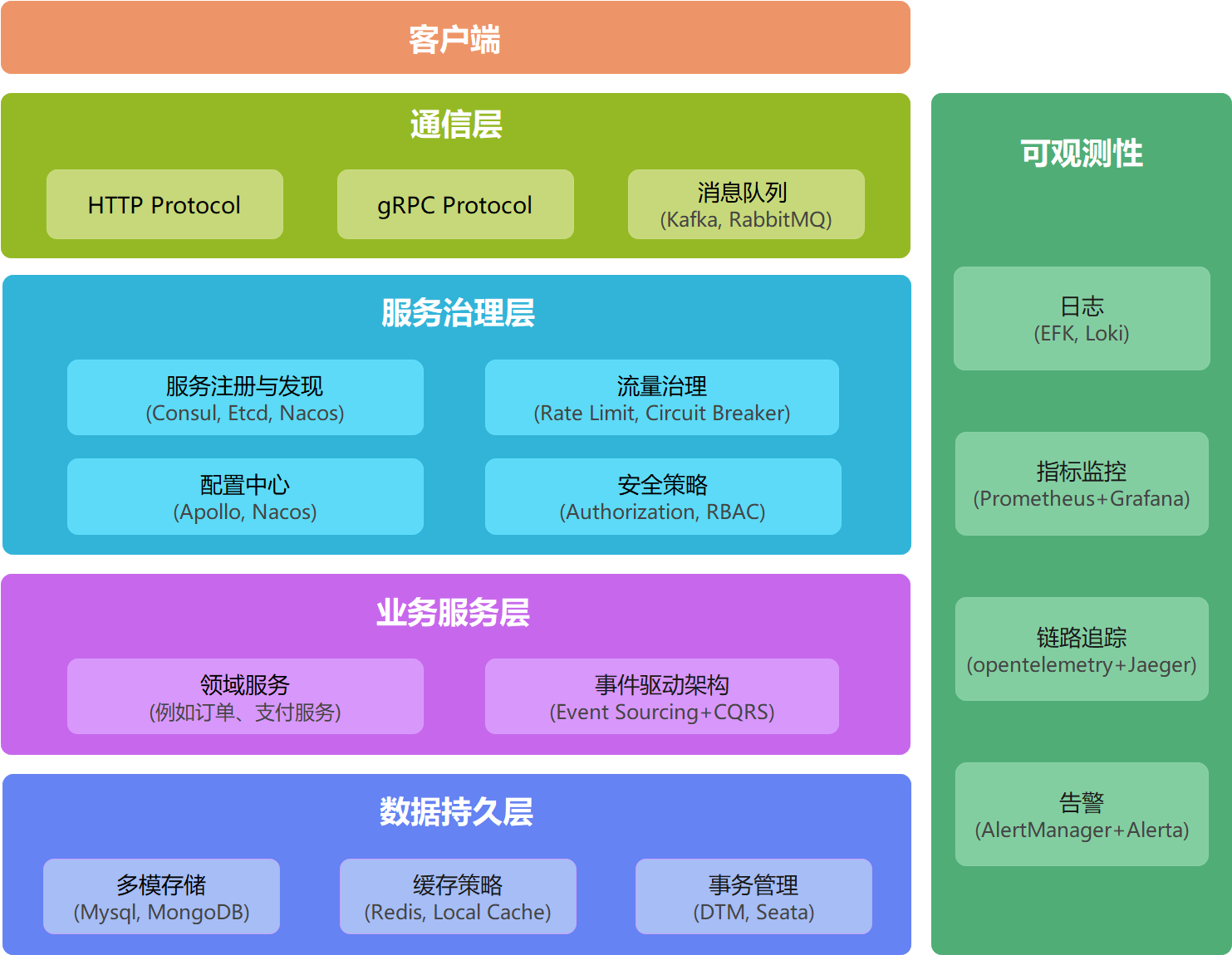
Sponge is also a microservices framework, the framework diagram is shown below, which is a typical microservice hierarchical structure, with high performance, high scalability, contains commonly used service governance features, you can easily replace or add their own service governance features.
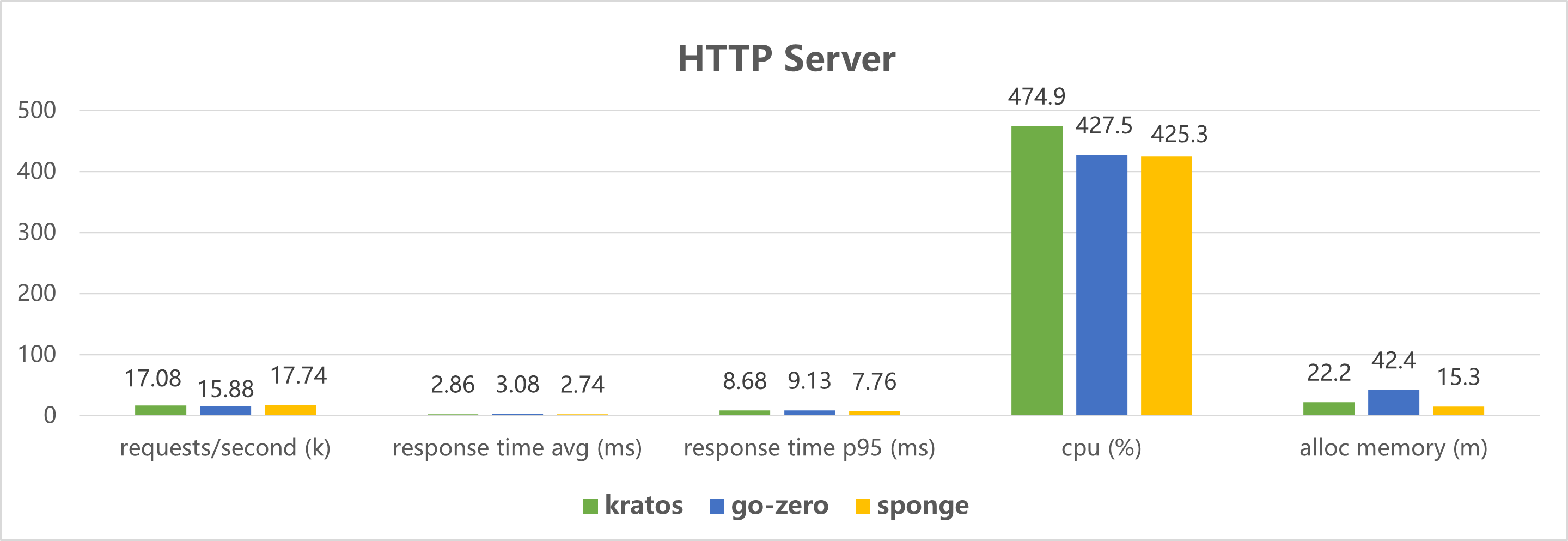
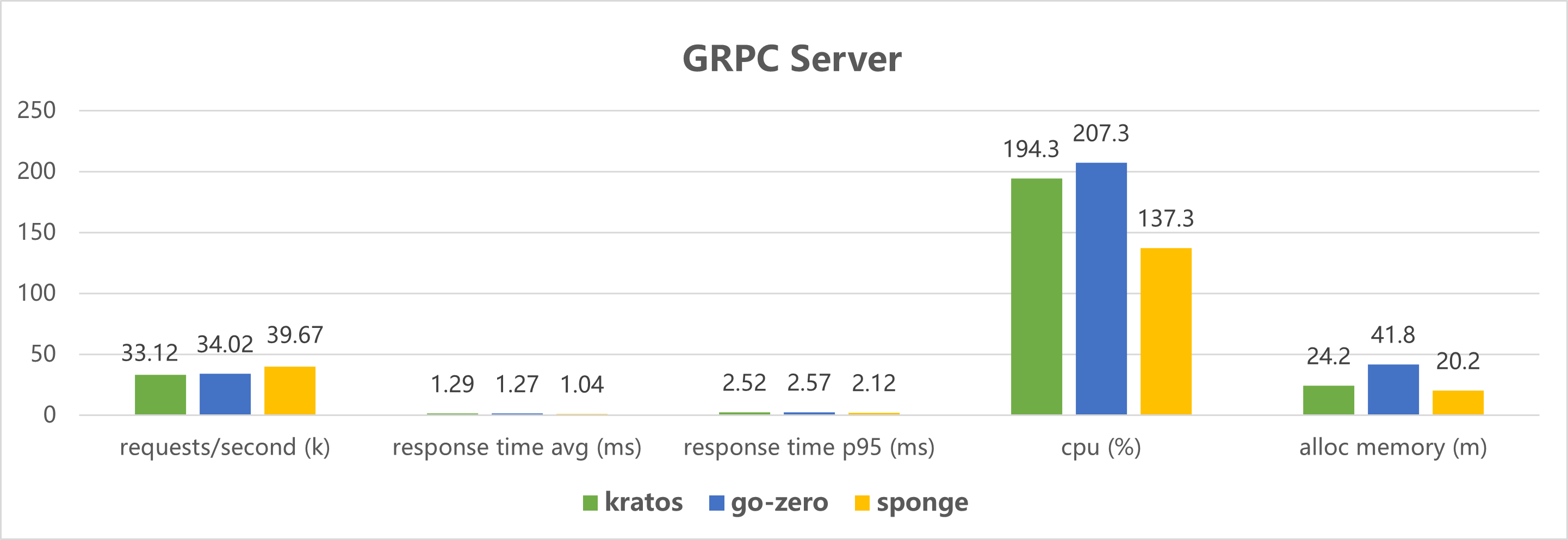
Performance testing of http and grpc service code created by the microservices framework: 50 concurrent, 1 million total requests.
Click to view the test code.
- Web framework gin
- RPC framework grpc
- Configuration parsing viper
- Configuration center nacos
- Logging component zap
- Database ORM component gorm, mongo-go-driver
- Cache component go-redis, ristretto
- Automated API documentation swagger, protoc-gen-openapiv2
- Authentication jwt
- Websocket gorilla/websocket
- Message Queue rabbitmq
- Distributed Transaction Manager dtm
- Parameter validation validator
- Adaptive rate limiting ratelimit
- Adaptive circuit breaking circuitbreaker
- Distributed Tracing opentelemetry
- Metrics monitoring prometheus, grafana
- Service registration and discovery etcd, consul, nacos
- Adaptive collecting profile
- Resource statistics gopsutil
- Code quality checking golangci-lint
- Continuous integration and deployment jenkins, docker, kubernetes
The project code directory structure created by sponge follows the project-layout and is structured as follows. Supported repository types are monolithic application single repository (monolith), microservice multi-repository (multi-repo), microservice single repository (mono-repo).
.
├── api # Directory for exposing external API interfaces, typically containing proto files and generated *.pb.go files. The directory structure is typically in the form `api/xxx/v1`, where v1 indicates the version.
├── assets # Store various static resources, such as images, markdown files, etc.
├── cmd # Program entry directory
│ └── serviceName
│ ├── initial # Program initialization, consisting of three files: initApp initializes configurations, registerServers registers services (HTTP or grpc), and registerClose registers resource cleanup.
│ └── main.go # Program entry file
├── configs # Directory for configuration files
├── deployments # Directory for deployment scripts, supporting Bare Metal, Docker and Kubernetes deployments.
├─ docs # Directory for API interface Swagger documentation.
├── i(I)nternal # Directory for business logic code, if the first letter is lowercase (internal), it means private code, if the first letter is capitalised (Internal), it means it can be reused by other code.
│ ├── cache # Cache directory wrapped around business logic.
│ ├── config # Directory for Go structure configuration files.
│ ├── dao # Data access directory.
│ ├── ecode # Directory for system error codes and custom business error codes.
│ ├── handler # Directory for implementing HTTP business functionality (specific to web services).
│ ├── model # Database model directory.
│ ├── routers # HTTP routing directory.
│ ├── rpcclient # Directory for client-side code that connects to grpc services.
│ ├── server # Directory for creating services, including HTTP and grpc.
│ ├── service # Directory for implementing grpc business functionality (specific to grpc services).
│ └── types # Directory for defining request and response parameter structures for HTTP.
├── pkg # Directory for shared libraries.
├── scripts # Directory for scripts, including compilation, execution, code generation, and deployment scripts.
├── test # Directory for scripts required for testing services and test SQL.
└── third_party # Directory for external helper programs, forked code, and other third-party tools.Sponge can be installed on Windows, macOS, Linux and Docker environments. Click here for instructions on installing sponge.
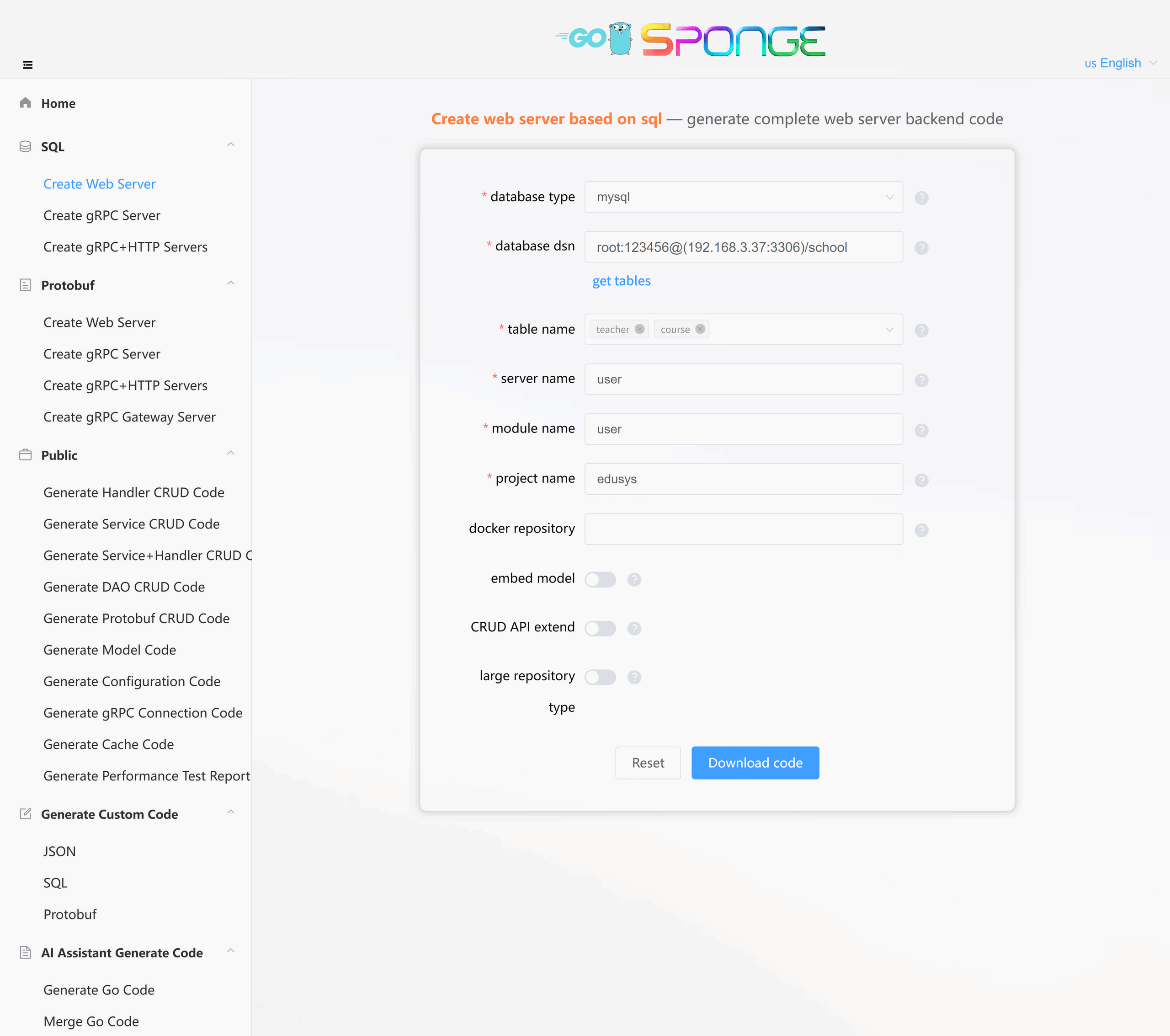
After installing the sponge, start the UI service:
sponge runAccess http://localhost:24631 in a local browser and manipulate the generated code on the UI page.
If you want to access it on a cross-host browser, you need to specify the host ip or domain name when starting the UI, example
sponge run -a http://your_host_ip:24631. It is also possible to start the UI service on docker to support cross-host access, Click for instructions on starting the sponge UI service in docker.
Detailed instructions for operating, configuring, and deploying a project using sponge development, Click here to view the sponge development documentation
- Create web service based on sql (including CRUD)
- Create grpc service based on sql (including CRUD)
- Create web service based on protobuf
- Create grpc service based on protobuf
- Create grpc gateway service based on protobuf
- Create grpc+http service based on protobuf
If it's help to you, give it a star ⭐.