COVID-19 Social Media Dashboard
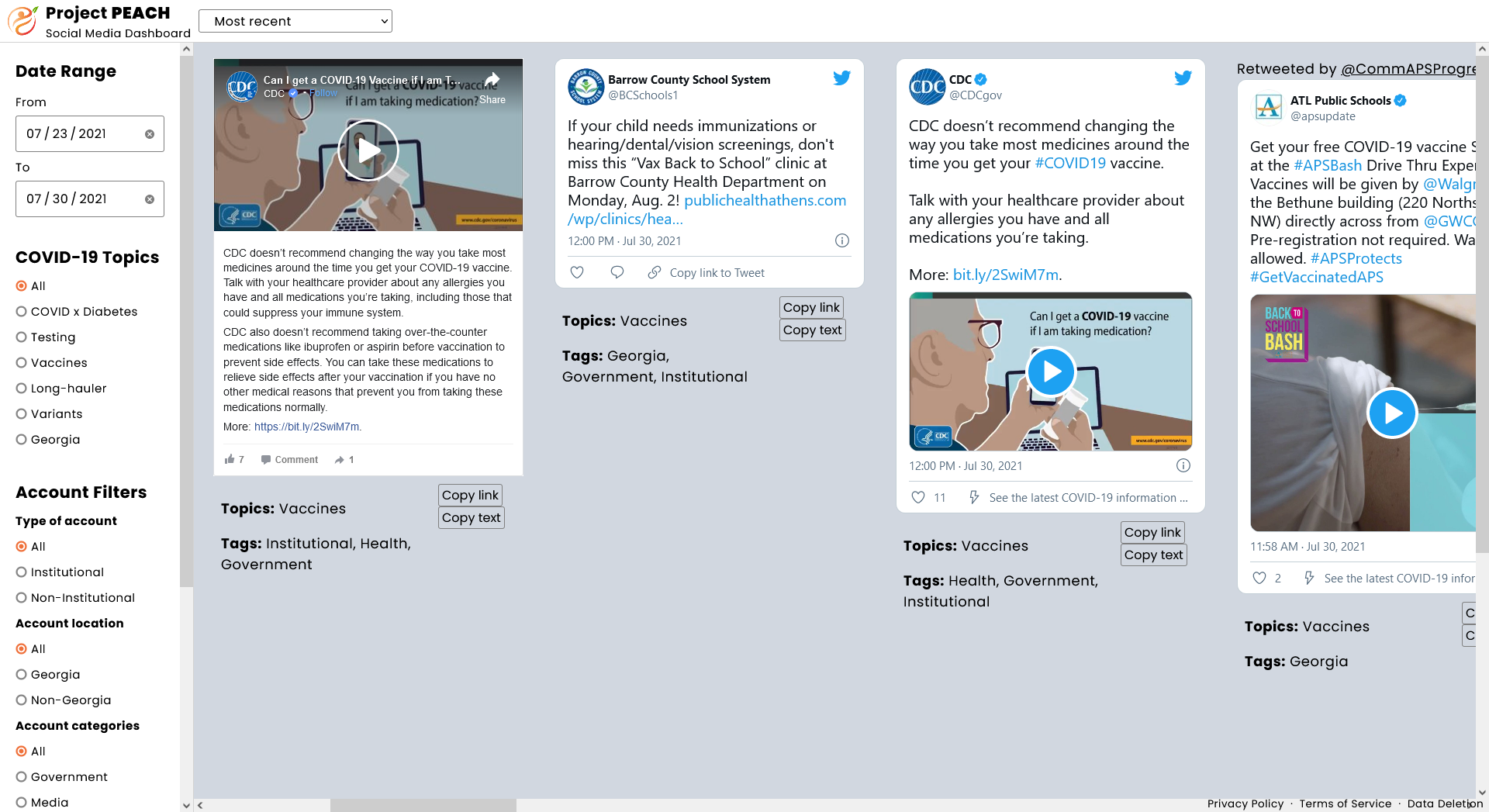
This repo contains the source code for the Project PEACH COVID-19 Social Media Dashboard: a dashboard intended to support the real-time monitoring of publicly available online COVID-19 posts across Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram by health-focused social sector organizations in the state of Georgia.
The dashboard is actively developed by the Technology & International Development Lab at Georgia Tech in collaboration with Emory University & the Morehouse School of Medicine.
Architecture Overview
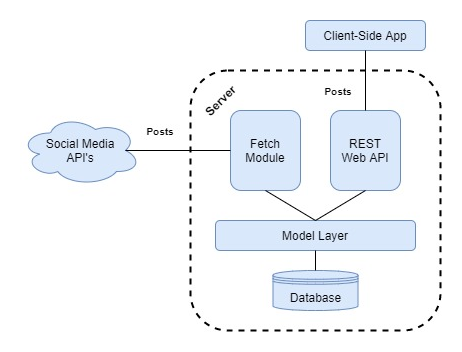
This dashboard is composed of two Node.js applications that commmunicate via a shared MongoDB database.
fetch is a Downstream app that aggregates and annotate social media posts across Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram in real-time and stores them in the database. For example, posts are annotated with various COVID-19 related tags (testing, vaccines, variants, etc.) based on their textual content.
server is an Express app that hosts both a client-side React application in production and a server-side RESTful web API that queries the database based on user input.
Both applications...
- interface with the database through the Mongoose model layer.
- are managed in production using PM2.
- pull their secrets & API keys from a shared .env file located at the project root folder.
Folder Structure
fetch/- Contains the source code for thefetchapplication.server/- Contains the source code for theserverapplication.client/- In development, this folder contains the source code for a self-hosted version of the client-side React application that comes with a bunch of goodies that you'll want to use (like hot module reloading). All client-side requests are proxied to the RESTful web API hosted by the server.
- In production, this folder contains a
build/folder that stores a bundled & optimized version of the React app which is served up as static files by theserver.
assets/- Contains image files for this README :-)
Development Environment
Installation
-
Clone this repository on your local machine.
-
Download the MongoDB Community server to your computer.
-
Install nvm. We'll use this to install Node.js properly in the next step.
3a. (Optional) Install ngrok IF you want to get Twitter login and posting working locally. First you will have to create an account and then do the basic setup on their page. We'll use ngrok to open our localhost to the internet on an HTTPS-based web address. Both HTTPS and a public web address are neccessary for Twitter Oauth to work.
-
Open a terminal and
cdto your clone of this repository. From there, runnvm installto install the right version of Node.js onto your machine. -
Run
npm installin thefetch/,server/, andclient/folders to install their respective dependencies. -
You're done! I'm proud of you. 😁👍
Setup
Create an empty .env file in the root folder for this repo and add the following environment variables using the dotenv format:
TWITTER_ACCESS_TOKEN- A Twitter access token; required for Twitter API access.TWITTER_ACCESS_TOKEN_SECRET- A Twitter access token secret; required for Twitter API access.TWITTER_CONSUMER_KEY- A Twitter consumer key; required for Twitter API access.TWITTER_CONSUMER_SECRET- A Twitter consumer secret; required for Twitter API access.CROWDTANGLE_INSTAGRAM_TOKEN- A CrowdTangle Instagram dashboard token.CROWDTANGLE_FACEBOOK_TOKEN- A CrowdTangle Facebook dashboard token.FACEBOOK_ACCESS_TOKEN- A Facebook access token for their oEmbed API.INSTAGRAM_ACCESS_TOKEN- An Instagram access token for their oEmbed API.SESSION_SECRET- An alphanumeric secret string used to secure user sessions; should be random.STORE_SECRET- An alphanumeric secret string used to encrypt user session information in the database; should be random.CALLBACK_URL- The callback URL used for Oauth. This is only needed for local testing. If not specified, our live website's URL is given.
Running
Running the dashboard in development requires starting up three separate Node.js applications and opening our local-host to the internet with ngrok for Twitter to recognize.
Open up four terminal windows or tabs, and then execute the commands below in the order they are listed, one to each terminal. In each case, make sure to cd into the corresponding folder first.
- (Optional, for local Twitter Posting) Run the
ngrokproxy to reroute localhost onto a secure web address- On Mac/Linux, run
./ngrok http http://localhost:3000 --host-header="localhost:3000" - On Windows, run
ngrok.exe http http://localhost:3000 --host-header="localhost:3000" - Everytime you must update
CALLBACK_URLin .env and inside your Twitter developer account "callbacks" section with the newly generated ngrok URL in HTTPS. The URL will look something likehttps://fcd6-128-61-35-51.ngrok.io.
- On Mac/Linux, run
- Run the
fetchapp withnpm run dev - Run the
serverapp withnpm run dev* - Run the
clientapp withnpm start
* A default admin user with the name Georgia Tech and password letmein1 will be created when you run the server app for the first time.
Maintenance
To do any maintenance on the production deployment of the dashboard, SSH into the virtual machine where the production dashboard is being hosted first.
PM2 Command Glossary
This project uses PM2 to manage its Node.js applications in production. Below is a handy glossary of important PM2 commands that you'll want in your maintenance tool belt.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
pm2 start <process> |
Starts a process. |
pm2 stop <process> |
Stops a process. |
pm2 restart <process> |
Stops and starts a process. |
pm2 status |
Reports the status (e.g. active, stopped, erroring) of all processes. |
pm2 logs <process> |
Prints out the recent logs from a process. |
For all commands above, your options for <process> are:
fetchserver
These processes are the two Node.js applications described above at the top of the Architecture Overview section.
Upgrading the dashboard
You've made changes to the source code, and now you want to apply those changes to the deployed dashboard. Depending on where you made your changes, you'll need to run different commands.
First, make sure that you've pushed those changes to this GitHub repo, and then pulled them down on the production VM with git pull.
If you made changes...
-
in the
client/folder, do nothing. There should be a git hook on the production VM that automatically builds the client-side React application for you with the new code. If you're paranoid, just runnpm run buildfrom theclient/folder to manually build the React app. -
in the
fetch/folder, runpm2 restart fetch. -
in the
server/folder, runpm2 restart server.
And that's it. You've upgraded the dashboard! Woo woo 🎉
Testing out the fetch application
If you're going to test out new changes that you've made to the fetch application locally and you intend on pulling in live data to play with, beware that you'll need to temporarily stop the production fetch app in order to stay under the API rate limits for each social media platform. Otherwise, both your local fetch app and the production instance will probably trigger those rate limits, and then neither will be able to pull in data.
In some cases, one way to avoid this problem is to just play with existing data. You'll have to get creative with simulating the production environment, but your development cycle will be much faster as a result!
License
This project is licensed under the GNU GPLv3 license.