In this guide, based on the Pareto principle, I will be showcasing 20% of HTML that you will end up using the most.
Let's start with what HTML is. HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. I like to think of HTML as the skeleton of my web apps. Hence, things related to structure of a web app, you can accomplish using html.
There are a few terminologies you should understand when working with HTML.
- tags: keywords in HTML that defines what element you want to create. Tags has a start tag and end tag.
example below:
<tagname> ...content </tagname>
-
elements: Everything from the beginning of a tag to the end of the tag is considered an element. For example if you have no content inside your tags, that is called an empty element.
-
attributes: provides additional information about an element. They are specified in the start tag. Example below. Attributes usually are defined with a name="value". tags have varying attributes so look out for that.
example below:
<tagname attributes="value"> ...content </tagname>
- DOM (Document Object Model): The DOM is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents. It represents your HTML markup as nodes and objects inside a web app. The DOM is what allows us to alter the behavior of our web app with Javascript and other scripting languages. We will have another lesson on the DOM itself. For now just understand that your HTML markup will get parsed to create the DOM.
In this section we will go over the most common tags
<html>: this tag is considered to be the root element. It is always at the very top and bottom of the document. It denotes to the website that this document is a html document.<head>: reserved for meta information about the website such as title, scripts, and style sheet tags<title>: defines the title of the page, helps for seo search, and also puts the title into the title bar. When you bookmark a page this is what gets stored as the title of the website<meta>: additional information that is very important for seo and other reason that are not visible to the users. website description, keywords, and other information like these will live here.<body>: All of the content that needs to be shown to the users will live here.<style>: css code for styling lives here. You can also link a path to your styles.<link>: allows you to link external style sheets to your website<script>: this is where your javascript or other scripts live. You can link a path your your script as well.
NOTE: understanding this section will be really helpful for seo (Search Engine Optimization).
NOTE: understanding this section will be really helpful for seo (Search Engine Optimization).
<div>: this is a generic container. We will be using this a lot.<h1>: h1 goes up to h6 but it denotes a heading textblock<p>: this is a paragraph tag that denotes where generic text should live<span>: this is an inline block container<br>: this break tag creates a line break.
NOTE: you will use the
NOTE: you will use the
<b>: this tag bolds the text<strong>: this is another way to bold your text<i>: this tag italics your text<em>: the emphasis tag is used to emphasis your text. In most browsers it will just italics your text<strike>: This take strikes through your tag
NOTE: you can do all of this with styling too.
NOTE: you can do all of this with styling too.
<a>: The anchor tag is the base for creating a hyperlink. You will need to pass it a href attribute with a link address to make this work<img>: The image tag displays images from a source.
NOTE: you need to provide the attribute href for tags and src for tags. More of this later.
NOTE: you need to provide the attribute href for tags and src for tags. More of this later.
<ol>: This is an order list. We use this tag when the order of the list is important.<ul>: This tag is an unordered list. This tag is used when the order of the list is not important<li>: the list item tag denotes each item of in the list.
<form>: The form tag creates a form that can be submitted to some service<label>: labels tags are form legends that act as captions to your fieldsets.<input>: the input tag allows us to capture user input.<textarea>: similar to the input tag, but it can collect a multiline input<select>: creates a dropdown with options for user input<option>: denotes each option that users can select from<button>: the button when embedded in a form will submit the form.
NOTE: Once I start the my lesson on REST i'll revisit forms as it is a important topic that I'm just briefly going over here.
NOTE: Once I start the my lesson on REST i'll revisit forms as it is a important topic that I'm just briefly going over here.
<table>: This tag creates that table element and houses all of its contents<thead>: denotes that table headers which is used to describe each columns contents<tbody>: the table body tag contains the main table's data<tfoot>: the table footer is used to describe the footer content<tr>: the table row contains information that should be included in a single row of a table<th>: the table header item contains information about a single header item<td>: the table data tag contains information about a single table cell<col>: the table column defines the information for a single column of a table
NOTE: Tables are not really used that much any more, however, it's used a lot for email templates.
NOTE: Tables are not really used that much any more, however, it's used a lot for email templates.
<header>: defines a area for where the header content should go<footer>: defines a area for where the footer content should go<main>: defines a area for where the main content should go<section>: used to logically break up the website into sections
NOTE: HTML5 is the latest addition to the html family, they are mostly used to break up / organize your mark up in a more descriptive way. For example i can use a
NOTE: HTML5 is the latest addition to the html family, they are mostly used to break up / organize your mark up in a more descriptive way. For example i can use a
alt: provides an alternative text for imagessrc: provides the source address for imageshref: provides the link url for anchor tagsid: defines a unique id for the elementclass: defines a class name for your element.style: provides an area for inline styling.title: specifies extra information about the element. Appears as tool tips.
NOTE: not all attributes are available for every tag.
NOTE: not all attributes are available for every tag.
You can comment your HTML by add left and right arrows. Don't forget the ! in the first arrow. You can do this multiple line as well.
<!-- HTML MARK UP -->
The above list is not an exhaustive list of html tags and attributes, they are just a collection of tags that I think you will need to hit the ground running. When you have time take a look at the additional resources. There are some good guides out there.
- follow the below designs and create a skeleton
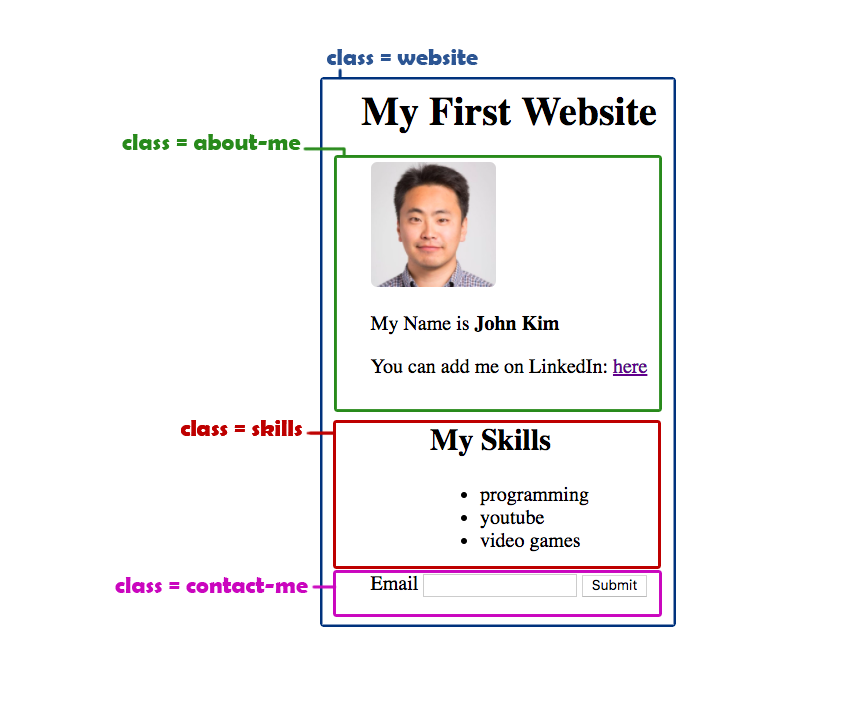
- add classes to your elements per the design
- use the provided style sheet in the playgrounds folder and link it to your html file.