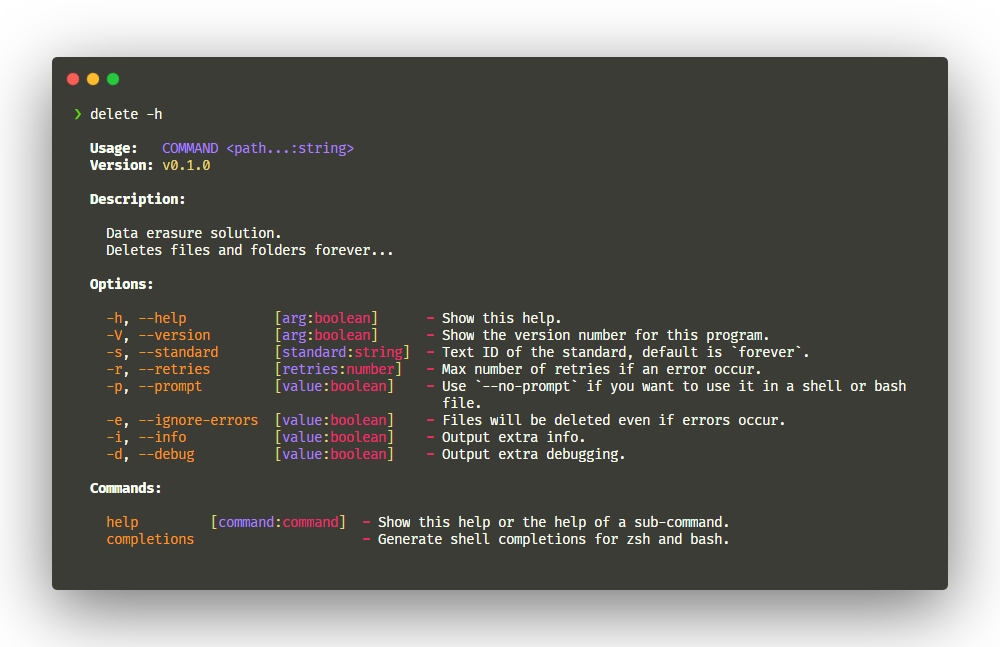
Data erasure solution for files on deno 🦕
When you delete a file using the rm UNIX command or with any software, it only removes direct pointers to the data disk sectors and make the data recovery possible with common software tools.
Permanent data erasure goes beyond basic file deletion commands, which:
- Allow for selection of a specific standard, based on unique needs,
- Verify the overwriting method has been successful and removed data across the entire device.
The basic principle is to write files before deletion in order to make recovery harder. With remove-forever, you get to choose the standard that follow your needs. Each one is composed of instructions about how many passes it should perform.
It goes from a simple pass of zeros to a 35 passes algorithm. Remove-forever comes with its own algorithm to ensure your data is safe:
- A pass of cryptographically strong pseudo-random data,
- The file is then renamed,
- Truncated to hide the file size.
- And finally files timestamps are randomized.
Remove-forever is composed of two parts: a deno module with a straightforward API and a command line interface optimized to delete files on the fly.
Deno required.
deno install --allow-write --allow-read --unstable -n remove https://deno.land/x/remove_forever/cli.tsNote: Due to the use of
Deno.utimeand the confirmation request in the CLI, you will need to use the--unstableflag.
If you want your application to delete specific files with a pass of cryptographically strong pseudo-random data, use one of these code snippets:
import remove from "https://deno.land/x/remove_forever/mod.ts";
await remove("./trash")
await remove("./vault/secret.txt")import { remove, fileStandards, directoryStandards } from "./mod.ts";
const count = await remove("./trash/secret.txt", {
fileStandard: fileStandards.gutmann.remove,
directoryStandard: directoryStandards.unsafe.remove,
ignoreErrors: true,
});
console.log(`Removed ${count} files and folders!`)See the changelog or releases.
See the open issues and project boards for a list of proposed features (and known issues).
Contributions are what make the open source community such an amazing place to be learn, inspire, and create. Any contributions you make are greatly appreciated.
- Fork the Project
- Create your Feature Branch (
git checkout -b feature/AmazingFeature) - Commit your Changes (
git commit -m 'Add some AmazingFeature') - Make sure that
deno testanddeno fmtdo not generate errors - Push to the Branch (
git push origin feature/AmazingFeature) - Open a Pull Request
Icon library by Icons8.
This project is under MIT License.