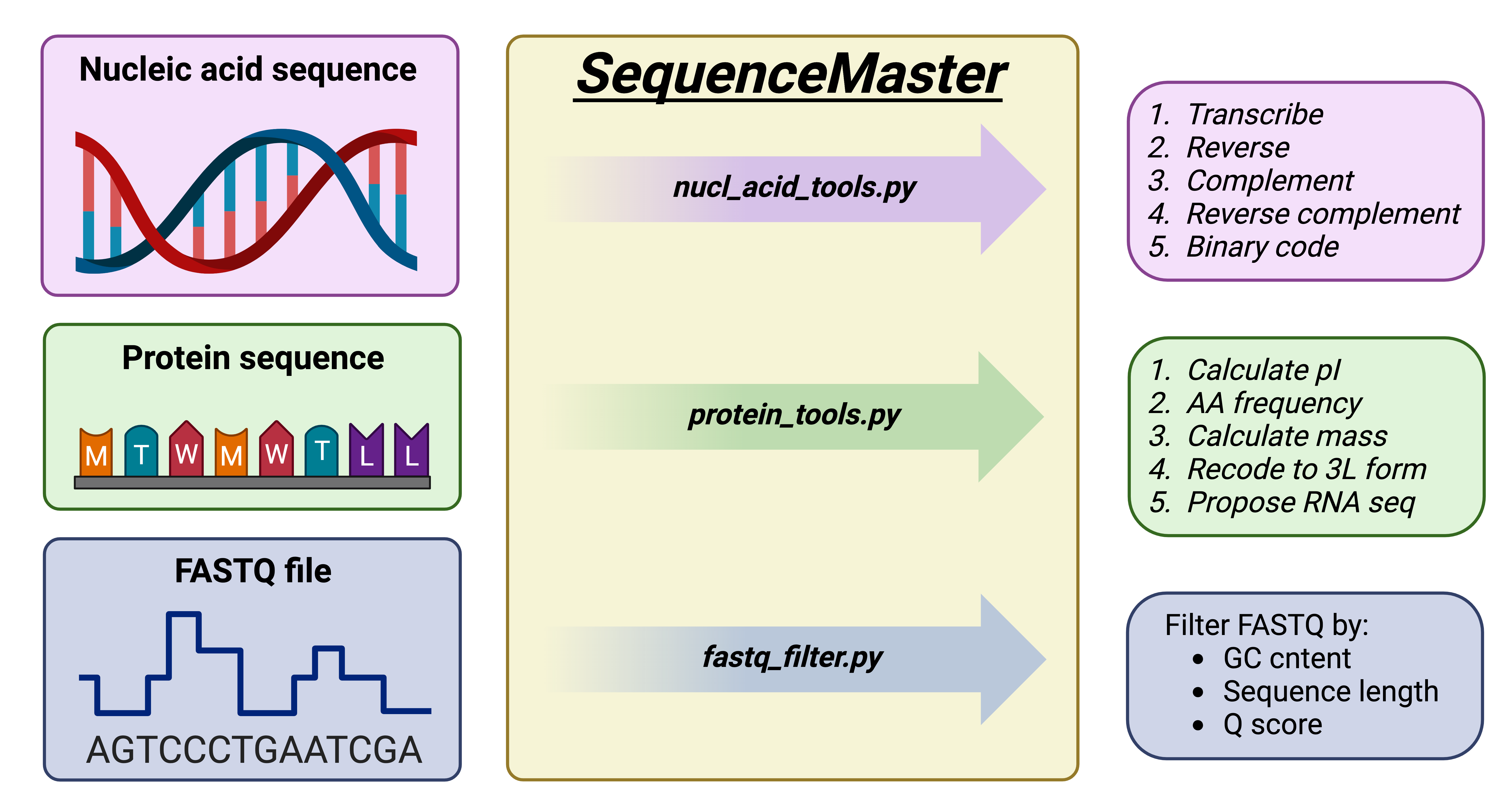
P.S. You may run test.py in terminal/command line to check the code! Hope you enjoy it!
A powerful and minimalistic bioinfomatical tool to work with sequences of nucleic acids and proteins. Moreover, you may manipulate with your data in FASTQ, FASTA and GBK formats
-
Nucleic Acid Analysis: SequenceMaster offers comprehensive tools for analyzing DNA and RNA sequences.
-
Protein Analysis: Explore protein sequences with advanced tools for pI calculation, protein mass calculation,
-
FASTQ File Filtering: Easily filter FASTQ files depending on quality, sequence length and GC content
-
FASTA File Manipulation: Convert multiline FASTA to oneline FASTA and shift starting point
-
GBK Data Extraction: Extract sequence of your gene of interest and his neighbouring genes
To get the tool clone the git repository::
git clone https://github.com/SuleimanovShakir/SequenceMaster.git && cd SequenceMasterSequenceMaster consits of 2 independent scripts: sequence_tools and bio_files_processor. sequence_tools mostly aimed to work with your sequence as well as filtering data from FASTQ. bio_files_processor helps you to manipulate with FASTQ and extract data from GBK.
As we live in the world of central dogma of molecular biology, this function checks is the sequence DNA or RNA. This is an important limit because some of the functions may use only DNA sequence in it's work.
To start working with nucleic acids, just run this command:
nucleic_acid_tools(*sequences: str, action: str)
- Firstly, you have to enter your DNA or RNA sequences just as 'str' type as positional arguments
- Last arguments is always an action that you prefer to perform to your sequences. Here is a list of possible actions
Supported Actions:
- "transcribe": Transcribes DNA sequence to RNA sequence.
- "reverse": Reverses DNA or RNA sequences.
- "complement": Makes the complement sequence. Takes only DNA sequences.
- "reverse_complement": Gives reversed and complement to inputed DNA sequence.
- "make_binary": Recodes DNA or RNA sequence in binary code.First number is always reffered to nucleic acid type: 0 - DNA, 1 - RNA.
To start working with proteins, just run this command:
protein_tools(*sequences: str, action: str)- Firstly, you have to enter your protein sequence just as 'str' type as positional arguments. You have to use one-letter coding.
- Last arguments is always an action that you prefer to perform to your sequences. Here is a list of possible actions
Supported Actions:
- "get_pI": Calculate isoelectric points for each amino acid in the sequence.
- "calculate_aa_freq": Calculate the frequency of each amino acid in a protein sequence.
- "translate_protein_rna": Translate amino acid sequence to RNA, using _*random codons*_ for each amino acid.
- "three_letter_code": Convert one-letter amino acid sequence to three-letter coding.
- "protein_mass": Calculate the molecular weight of the protein sequence.
To start filtering your FASTQ files, just run this command fastq_filter:
fastq_filter(input_path: str = None, output_filename: str = None,
gc_bound: Union[tuple, int, float] = (0, 100), length_bound: tuple = (0, 2**32),
quality_threshold: Union[int, float] = 0) -> NoneList of positional arguments:
- input_path (str): full path to the file that you want to work with is mandatory
- output_filename (str): enter just a name of the file, don't add extention!
List of keyword arguments:
- gc_bound: tuple of required range of GC percentage (inclusive), num or float if only higher border of the range is needed (exclusive). (0,100) is a defaul range of GC content.
- length_bound: tuple of required range of sequence length (inclusive). (0,2**32) is a defaul range of length.
- quality_threshold: int of lowest level of Q-score (inclusive). 0 is a default Q-score
There is only one action - filter input FASTA by this parameters and give back filtered FASTQ file. This would be saved to fastq_filtrator_resuls subfolder. Please, provide name for the output file, otherwise it will be saved with the name of the input file.
To convert multiline FASTA to oneline format, one may run convert_multiline_fasta_to_oneline:
convert_multiline_fasta_to_oneline(input_fasta: str, output_fasta: str = None) -> None:This function converts multiline FASTA to oneline FASTA
List of positional arguments:
- input_path (str): full path to the file that you want to work with is mandatory
- output_filename (str): enter just a name of the file, don't add extention
As an output, user gets converted file in FASTA format, which is saved to one_line_results subfolder. Please, provide name for the output file, otherwise it will be saved with the name of the input file.
To shift starting position of your FASTA sequence, user may try change_fasta_start_pos. This function work only with oneline FASTA:
change_fasta_start_pos(input_fasta: str, shift: int, output_fasta: str = None) -> None:This function shifts sequence to n positions from the start. But nothing is deleted! Part of sequence which is now goes before shift is located in the end of the new sequence
List of positional arguments:
- input_path (str): full path to the file that you want to work with is mandatory
- shift (int): the number of nucleotides by which the starting position in the file must be shifted
- output_filename (str): enter just a name of the file, don't add extention
As an output, user gets fixed file in FASTA format, which is saved to change_pos_results subfolder. Please, provide name for the output file, otherwise it will be saved with the name of the input file.
To exctract names and translation for your genes of interest and their neibourhing genes, one may definitely use select_genes_from_gbk_to_fasta:
select_genes_from_gbk_to_fasta(input_gbk: str, output_fasta: str = None,
*, genes_of_interest: list, n_before: int = 1, n_after: int = 1) -> None:This function uses gbk database files to extract FASTA sequence of proteins. User enters name of interested genes and how much genes before and after this gene of interest he want to extract with proteins sequences for these genes.
Arguments (positional):
- input_gbk (str): full path to the file that you want to work with is mandatory
- output_fasta (str): enter just a name of the file, don't add extention!
Arguments (keyword):
- genes_of_interest (list): list of gene names user is interested in
- n_before (int): how many of genes before particular genes you want to extract
- n_after (int): how many of genes after particular genes you want to extract
As an output, user gets fixed file in FASTA format, which is saved to gbk_fasta_resuls subfolder. Please, provide name for the output file, otherwise it will be saved with the name of the input file.
print(nucl_acid_tools('ATG', action='transcribe')) -> 'AUG'
print(nucl_acid_tools('ATG', 'GAT', action='reverse')) -> ['GTA', 'TAG']
print(nucl_acid_tools('ATG', 'tAg', 'AAA', action='complement')) -> ['TAC', 'aTc', 'TTT']
print(nucl_acid_tools('ATG', 'tAg', 'AAA', action='reverse_complement')) -> ['CAT', 'cTa', 'TTT']
print(nucl_acid_tools('ATG', action='make_binary')) -> '0,0,0,0,1,1,0'print(protein_tools('KKLMN', action='calculate_aa_freq')) -> {'K': 2, 'L': 1, 'M': 1, 'N': 1}
print(protein_tools('KLMN','PRST', action='translate_protein_rna')) -> ['AAGCUAAUGAAC', 'CCAAGGAGCACG']
print(protein_tools('KLMN', 'pRsT', action='three_letter_code')) -> ['Lys-Leu-Met-Asn', 'Pro-Arg-Ser-Thr']
print(protein_tools('KLMN', action='protein_mass')) -> 486.26244fastq_filter(INPUT_FASTQ, 'filtered_fastq', gc_bound=(40,60), length_bound=(0, 200), quality_threshold=25) -> "Filtered FASTA is written!"convert_multiline_fasta_to_oneline(INPUT_FASTA, 'oneline_fasta') -> "Multiline FASTA is converted to oneline!"change_fasta_start_pos(INPUT_ONELINE_FASTA, 3, 'shifte_fasta') -> "Starting position in FASTA is shifted!"select_genes_from_gbk_to_fasta(INPUT_GBK, 'genes_of_interest', genes_of_interest=['mngA', 'araE', 'trpA'], n_before=4, n_after=5) -> "Genes of interest with their sequences are extracted from GBK to FASTA!":| Type of the problem | Probable cause |
|---|---|
| ValueError: No such action: {action} | You have entered a wrong action. Please, check function docstring |
| ValueError: Your sequence is empty | You have entered empty sequence. Please notice, this error occurs only when you enter 1 sequence. |
| Working with protein | |
| ValueError: Sequence is not a protein, input should be protein | You have entered a wrong sequence |
| Working with nucleic acids | |
| ValueError: Sequence is not a DNA, input should be DNA | You have entered a wrong sequence |
| ValueError: Sequence is not a DNA/RNA, input should be DNA/RNA | You have entered a wrong sequence |
| Working with FASTQ | |
| ValueError: There are no fastq sequences | Your FASTQ input is empty |
| ValueError: Your arguments are not suitable! | You enter wrong type of arguments Please, check function docstring |
| TypeError: takes from 0 to 1 positional arguments but n were given | Sequences are not collected into the list type |
| ValueError: You didn't enter any PATH to file | Please, provide full path to your file |
| Working with FASTA | |
| ValueError: You didn't enter any PATH to file | You have entered a wrong sequence |
| ValueError: Shift arguments has to be numeric | Please, enter shift arguments in numeric type |
| Working with GBK | |
| ValueError: Your arguments are not in suitable type | You enter wrong type of arguments |
| ValueError: You have entered an empty list of genes | Please, check that your list of genes is not empty |
| ValueError: You didn't enter any PATH to file | Please, provide full path to your file |
Shakir Suleimanov,
Please, do not hesitate to contact me via Git-Hub or e-mail.